Back collector structure of power semiconductor devices
A power semiconductor and collector technology, applied in semiconductor devices, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of complex reliability of back gold process, mismatch of heterogeneous materials lattice, and greater impact on device performance than the original process. Achieve the effect of improving turn-off characteristics, improving on-state voltage drop, and reducing carrier lifetime
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
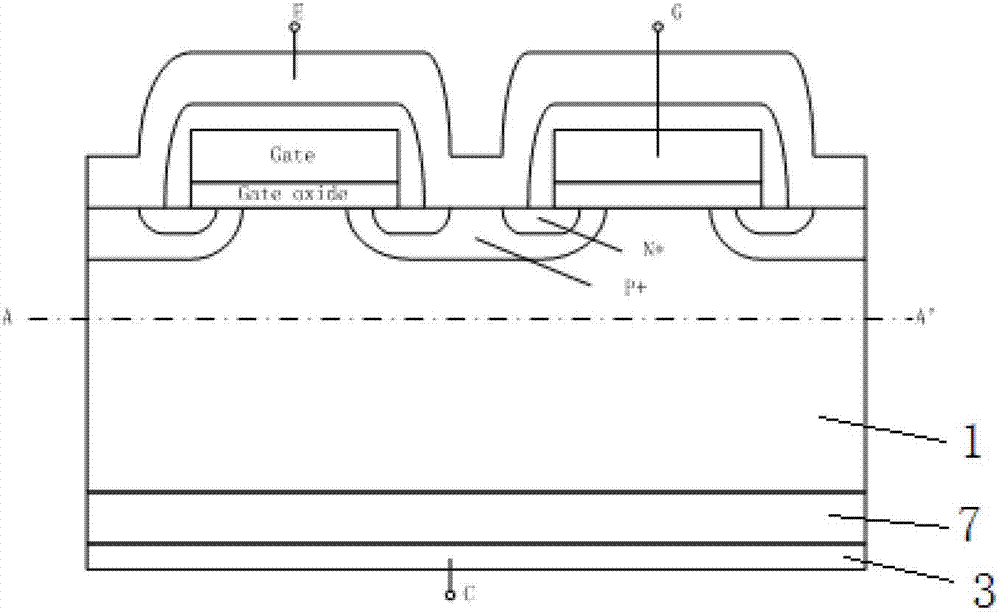
[0025] Such as figure 2 As shown in the back collector structure of the power semiconductor device, a P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2 is provided on the back surface of the N conductivity type silicon substrate 1 , and a collector electrode 3 is provided on the back surface of the P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2 .
[0026] figure 2 The area above the middle BB' line is the front structure of the power semiconductor device, which is related to figure 1 The front structures of the power semiconductor devices in the region above the middle AA' line are exactly the same. This embodiment is similar to Embodiment 1, and it replaces the P conductivity type silicon collector layer 7 in Embodiment 1 with the P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2 .
[0027] The P-conductivity-type gallium nitride layer 2 material on the back is prepared by epitaxy. Since the doping concentration of the P-conductivity-type gallium nitride layer 2 cannot be too high, the ...
Embodiment 2
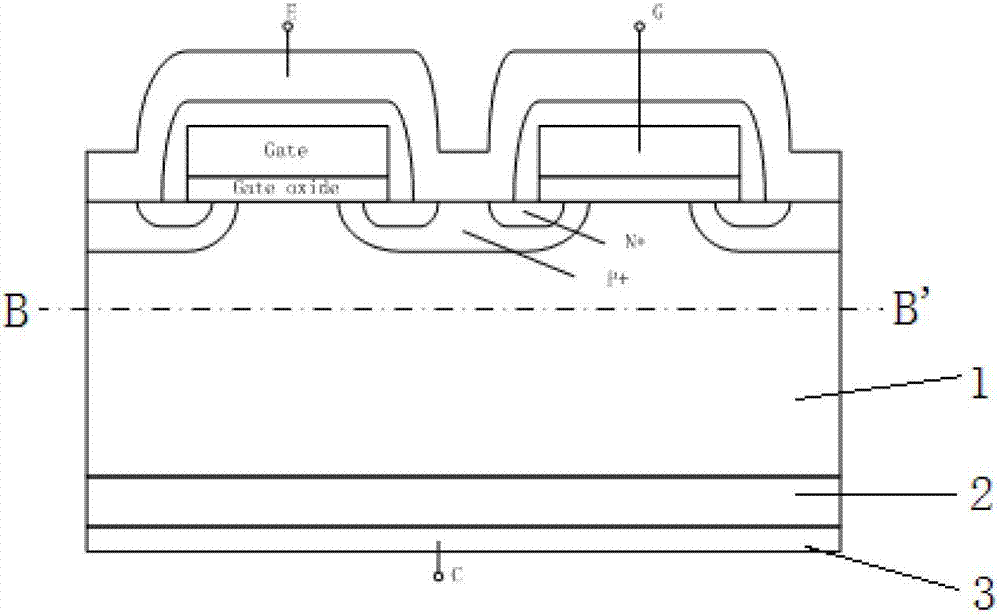
[0032] Such as image 3 As shown in the back collector structure of the power semiconductor device, a P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2 is provided on the back surface of the N conductivity type silicon substrate 1, and a collector electrode 3 is provided on the back surface of the P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2. A first buffer layer 4 is provided between the N conductive type silicon substrate 1 and the P conductive type gallium nitride layer 2 , and the first buffer layer 4 is an N conductive type silicon buffer layer.
[0033] image 3 The area above the middle CC' line is the front structure of the power semiconductor device, which is related to figure 1 The front structures of the power semiconductor devices in the region above the middle AA' line are exactly the same. This embodiment is similar to Embodiment 1, a first buffer layer 4 is added between the N conductivity type silicon substrate 1 and the P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2, ...
Embodiment 3
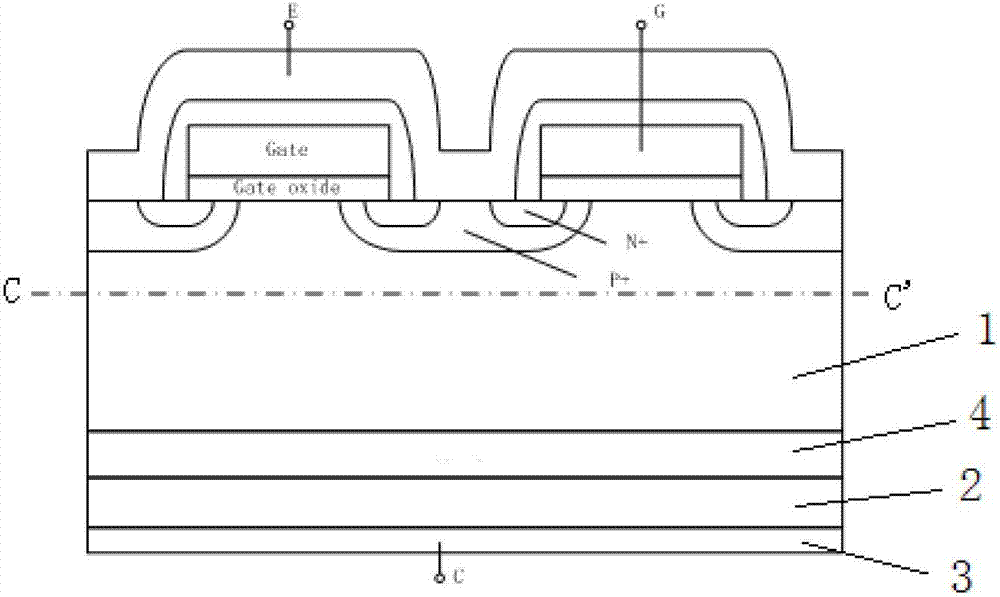
[0035] Such as Figure 4 As shown in the back collector structure of the power semiconductor device, a P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2 is provided on the back surface of the N conductivity type silicon substrate 1, and a collector electrode 3 is provided on the back surface of the P conductivity type gallium nitride layer 2. Between the N conductive type silicon substrate 1 and the P conductive type gallium nitride layer 2, a first buffer layer 4 is provided, and the first buffer layer 4 is an N conductive type silicon buffer layer, and between the first buffer layer 4 and the P A second buffer layer 5 is arranged between the conductive type gallium nitride layer 2, and the second buffer layer 5 is an amorphous gallium nitride layer or an aluminum nitride buffer layer; between the P conductive type gallium nitride layer 2 and the collector 3 is provided with an indium gallium nitride layer 6 .
[0036] Figure 4 The front structure of the medium-power semiconduct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com