Sending and detection method of downlink control information, network side device and user equipment
A network-side device and user equipment technology, which is applied to the use of forward error control, the separation device of transmission paths, and the use of return channels for error prevention/detection, etc., can solve the problem of increasing scheduling delay, reducing multi-user diversity gain, limiting Terminal peak rate and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0146] In this embodiment, masking the CRC is used to implicitly indicate the extended 1-bit HPN, so that the HPN is extended from 3 bits to 4 bits, which will be described in detail below.
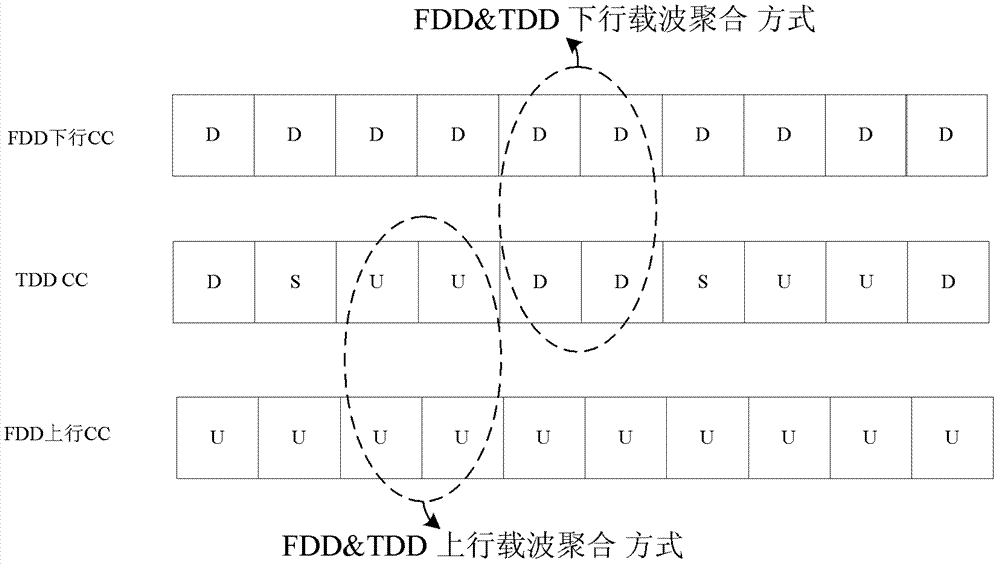
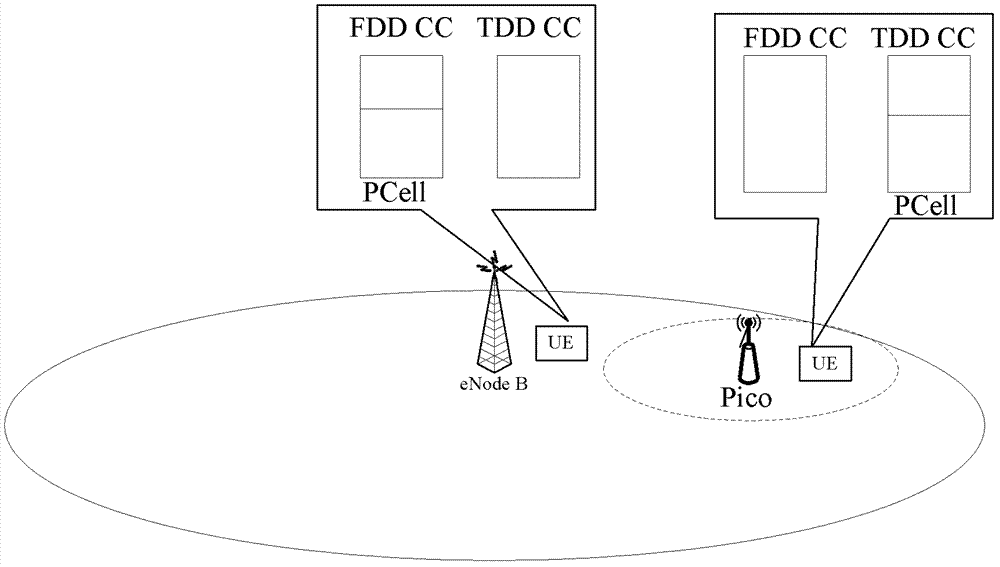
[0147] The DCI sending method described in this embodiment is applied in a carrier aggregation scenario between a TDD system and an FDD system, and the primary component carrier in the carrier aggregation scenario is configured as a TDD component carrier. Please refer to Figure 7 , which shows that when the sending method described in this embodiment is applied to a network side device, specifically an eNB, it may specifically include the following steps:
[0148] Step 11, the network side device determines the HPN value of the FDD component carrier corresponding to the user equipment (UE), and the value is represented by a 4-bit binary data.
[0149] Here, since the maximum number of HARQ processes on the FDD component carrier may exceed 8, 4-bit binary data is used to represent the ac...
Embodiment 2
[0217] In this embodiment, the scrambled result is punctured, so that the extended 1-bit HPN is carried in the scrambled CRC sequence, so that the HPN is extended from 3 bits to 4 bits, which will be described in detail below.
[0218] The DCI sending method described in this embodiment is applied in a carrier aggregation scenario between a TDD system and an FDD system, and the primary component carrier in the carrier aggregation scenario is configured as a TDD component carrier. Please refer to Figure 8 , which shows that when the sending method described in this embodiment is applied to a network side device (such as an eNB), it may specifically include the following steps:
[0219] Step 81 , the network side device determines the HPN value of the FDD component carrier corresponding to the user equipment (UE), and the value is represented by a 4-bit binary data.
[0220] Here, since the maximum number of HARQ processes on the FDD component carrier may exceed 8, 4-bit binar...
Embodiment 3
[0260] In this embodiment, the mapping position of the PDCCH is used to implicitly indicate the extended 1-bit HPN, so that the HPN is extended from 3 bits to 4 bits, which will be described in detail below.
[0261] The DCI sending method provided in this embodiment is also applicable to a carrier aggregation scenario between a TDD system and an FDD system, and the primary component carrier in the carrier aggregation scenario is configured as a TDD component carrier. The sending method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0262] Step 41 , the network side device determines the HPN value of the FDD component carrier corresponding to the user equipment, and the value is represented by a 4-bit binary data.
[0263] Step 42, splitting the binary data into 3-bit first data and 1-bit second data.
[0264] Step 43: Generate FDD DCI, and construct a PDCCH for carrying the FDD DCI, wherein the FDD DCI includes a 3-bit HPN field, and the HPN field is filled wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com