Distributed beam forming system and carrier synchronization method of transmitting antennas at source end of distributed beam forming system
A technology of beam synthesis and carrier synchronization, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, synchronization devices, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve precise synchronization of carrier frequency, inability to achieve synchronization, increase system delay, etc., to increase effective Communication time, effect of reducing synchronization overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
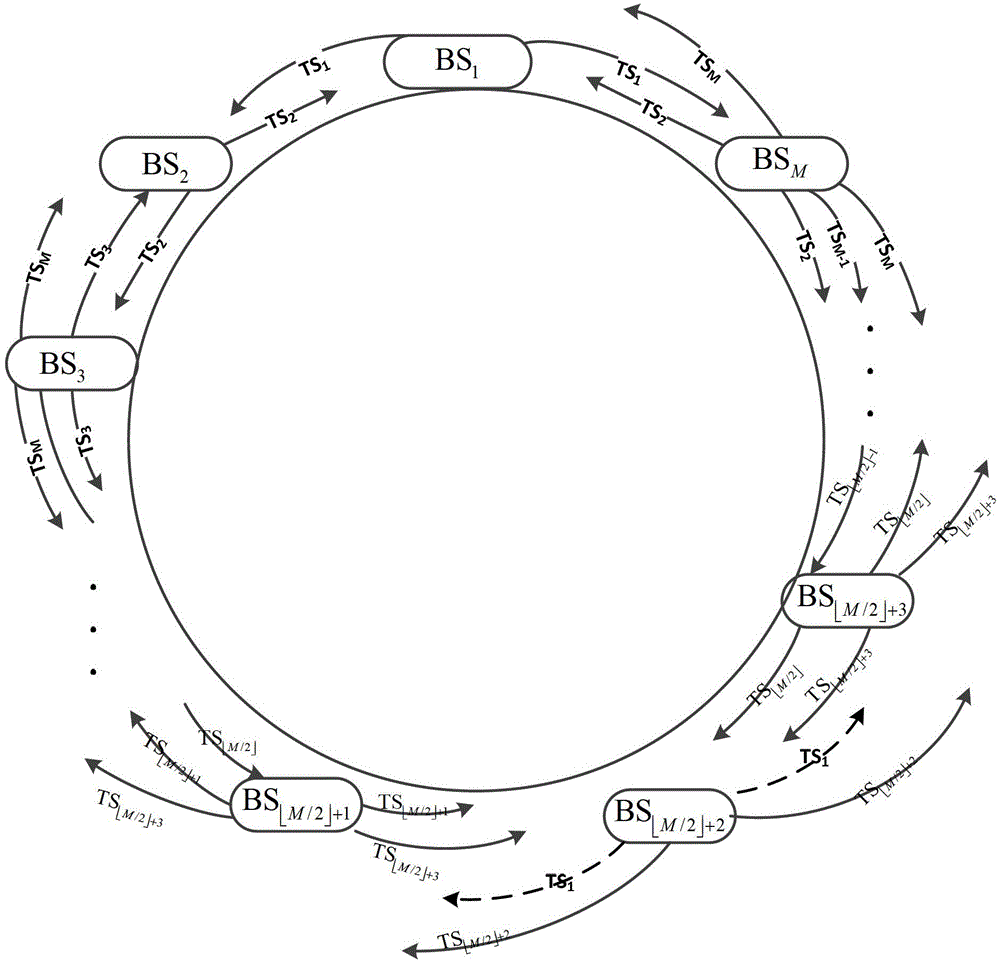
[0038] Embodiment 1: An odd number of base stations at the source end forms a closed-loop structure, and the synchronization signal generating base station is any base station in the closed-loop structure, such as figure 1 shown. Step A specifically includes the following steps: Step A1, in the first time slot, the adjacent base stations on both sides of the intermediate base station respectively estimate the phase offset of the channel with the intermediate base station. figure 1 In the figure, the solid line represents the transmission process of the synchronization signal among the base stations, and the signal transmitted each time is the periodic extension of the previous time slot signal, and the dotted line represents the channel estimation process. At this time, a time slot TS1 is needed for channel estimation ( base station estimate and The channel phase between, estimate and channel phase between), where TS i Indicates the ith time slot, BS i Indicates ...
Embodiment 2
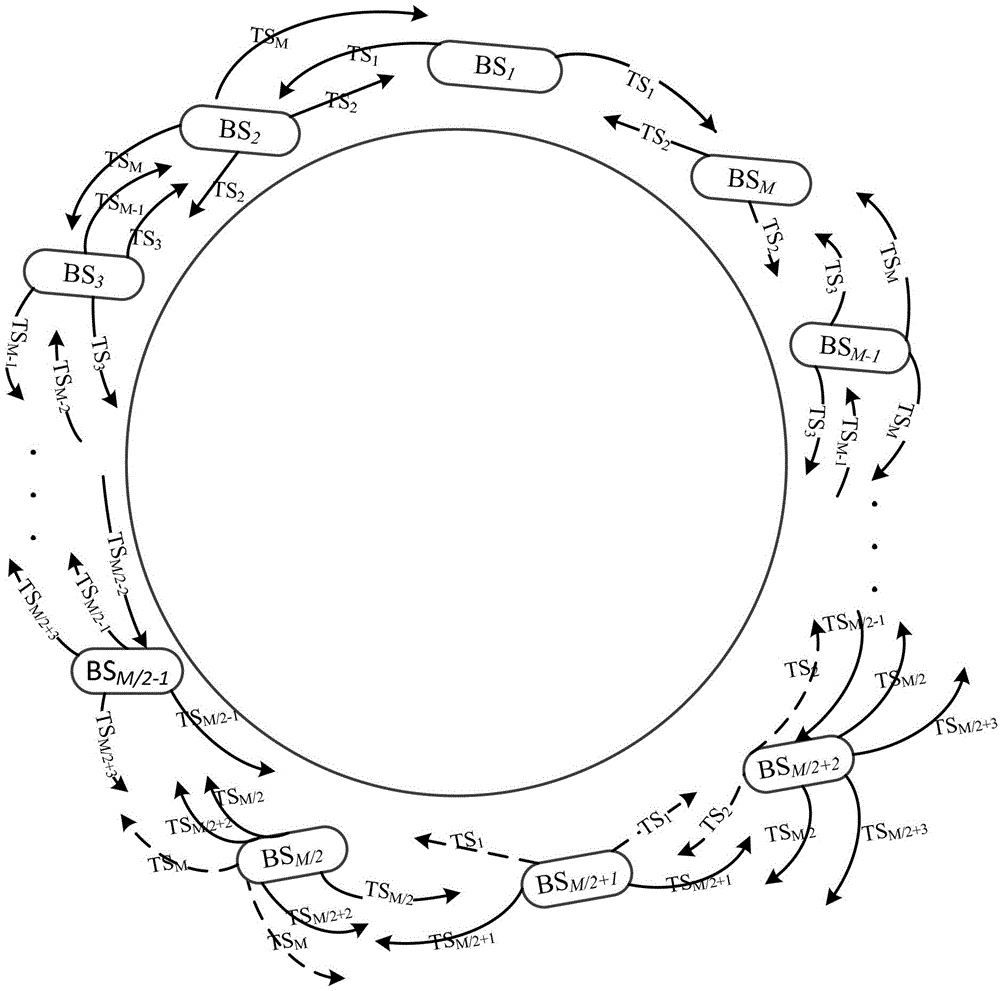
[0039] Embodiment 2: An even number of base stations at the source end forms a closed-loop structure, and the synchronization signal generating base station is any base station in the closed-loop structure, such as figure 2 shown. Step A specifically includes the following steps: Step A2, in the first time slot, the adjacent base stations on both sides of the intermediate base station respectively estimate the phase offset of the channel with the intermediate base station; in the second time slot, the intermediate base station estimates its The phase offset of the channel with the adjacent base station on one side; in the last time slot of the reverse broadcast transfer, the intermediate base station estimates the phase offset of the channel between it and the adjacent base station on the other side. figure 2 In , the solid line represents the transmission process of the synchronization signal between the base stations. The signal transmitted each time is a periodic extensio...
Embodiment 3
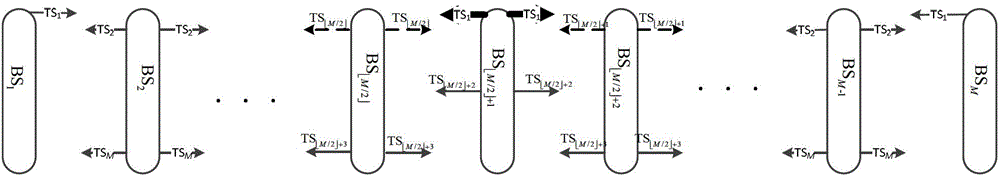
[0040] Embodiment 3: Multiple base stations at the source end can form a linear structure, and the synchronization signal generating base stations are base stations at both ends of the linear structure. At this time, it can be image 3 Odd number of base stations shown, can also be Figure 4 The even number of base stations shown is different from the ring structure in that the synchronization signals generated by the base stations at both ends can be the same or different. Step A specifically includes the following steps: Step A3, in the first time slot, the adjacent base stations on both sides of the intermediate base station respectively estimate the phase offset of the channel with the intermediate base station. for image 3 In the case of , the thin solid line represents the transmission process of the synchronization signal between the base stations. The signal transmitted each time is a periodic extension of the previous time slot signal. The thick solid line represent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com