Method for producing a selective doping structure in a semiconductor substrate in order to produce a photovoltaic solar cell
A technology of solar cells and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, photovoltaic power generation, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as complex needs, high cost, and recombination loss, and achieve high efficiency and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
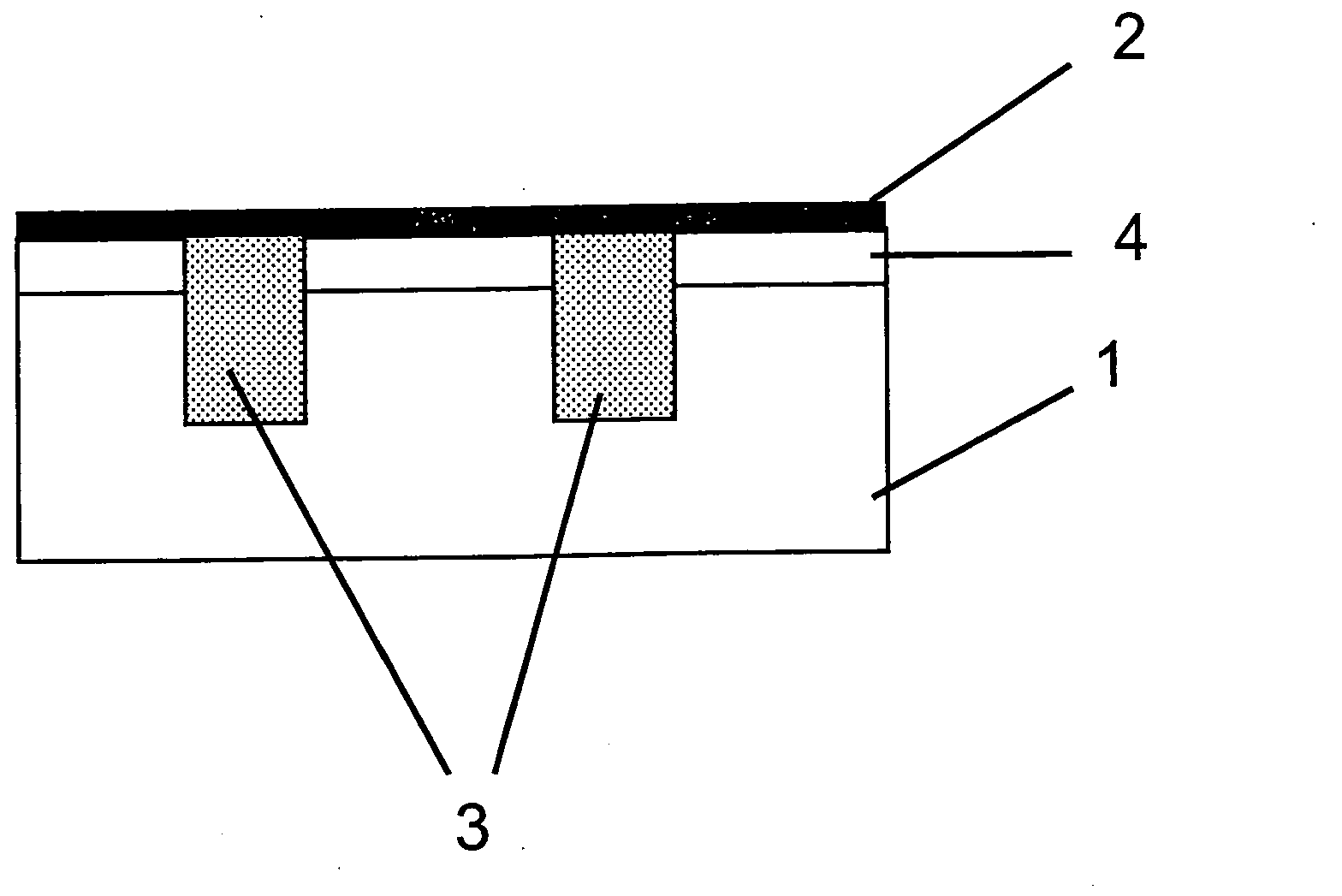
[0073] 1 and 2 each show a detail of a semiconductor substrate 1 in the form of a silicon wafer. semiconductor substrate with N A =1.5E16cm -3 The p-doped and extended to the left and right respectively. The semiconductor substrate 1 has a thickness of 200 μm and is approximately square with a side length of 15 cm.
[0074] The same reference numerals in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 denote the same parts.
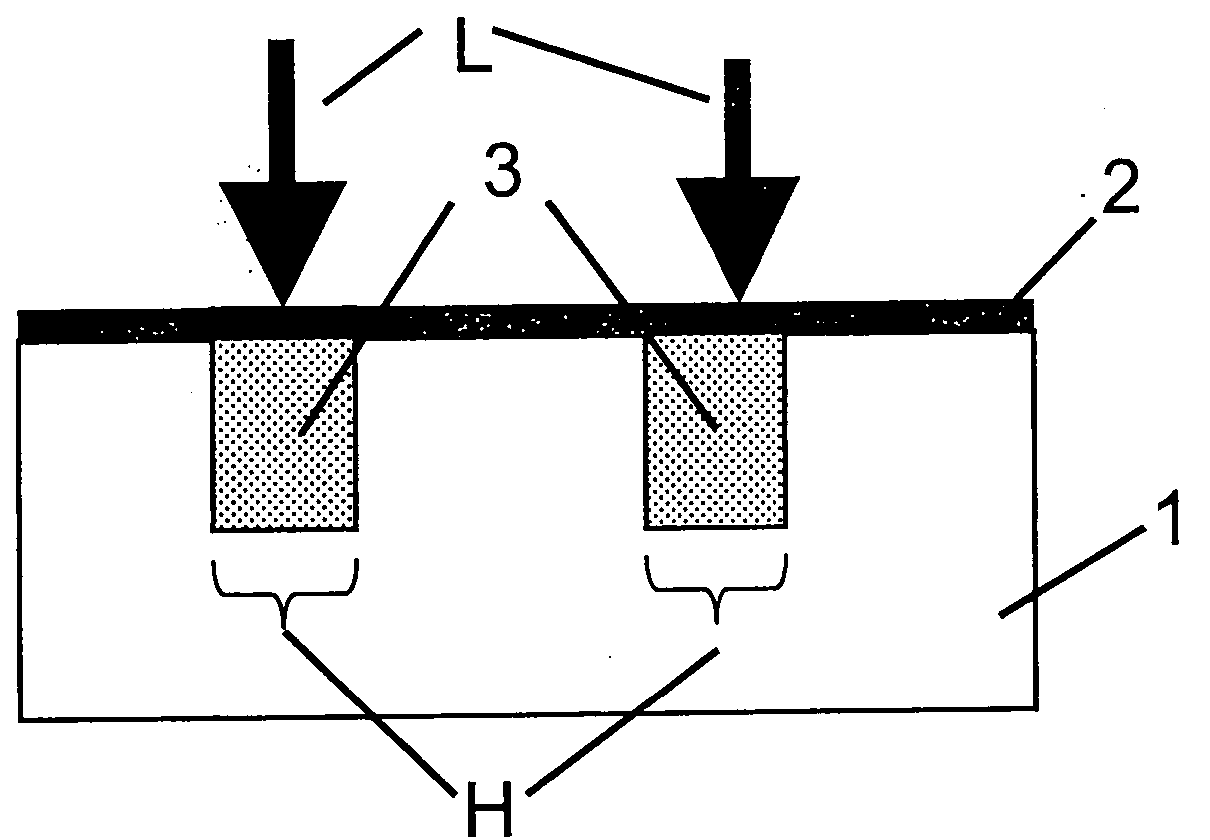
[0075] In a first embodiment of the method according to the invention shown in FIG. 1 , in method step A a doping layer 2 is applied to the upper front side of the semiconductor substrate 1 which is designed for the solar cell to be produced. light incident.
[0076] The doped layer 2 is deposited by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and made of SiO x : P (phosphosilicate glass PSG), that is, contains phosphorus as a dopant, and the concentration of phosphorus is 4 to 8% by weight.
[0077] In method step B, local heating by means of the laser beam L produces within a short time i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com