Method of manufacturing chemically strengthened glass plate
A manufacturing method and glass plate technology, applied in glass manufacturing equipment, glass tempering, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problem of glass breaking into pieces
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] As a glass plate before ion exchange (chemical strengthening), prepare soda lime glass (by mass %, SiO 2 : 71.3%, Na 2 O: 13.0%, K 2 O: 0.85%, CaO: 9.0%, MgO: 3.6%, Al 2 o 3 : 2.0%, Fe 2 o 3 : 0.15%, SO 3 : 0.1%), prepare a disk-shaped substrate (hereinafter referred to as a glass blank) with a diameter of about 80 mm.
[0126] As the first process, the prepared glass blank is dipped in a sodium nitrate (NaNO 3 ) 100mol% molten salt (first salt, ratio X: 100mol%) bath for 2 hours.
[0127] Then, the glass blank was taken out from the bath, and the surface of the glass blank was washed and dried.
[0128] The composition of the glass base plate before and after the first step was measured by fluorescent X-rays, and it was confirmed that the ratio of sodium in the surface layer after the first step was about 1 mass % higher than the ratio of sodium in the surface layer before the first step .
[0129] Next, as a second process, the dried glass blank is immersed ...
Embodiment 2
[0139] As the second salt used in the second step, a mixed molten salt (ratio Y: 1 mol %) composed of 99 mol % of potassium nitrate and 1 mol % of sodium nitrate was prepared.
[0140] A chemically strengthened glass plate was manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the second step was performed using the above-mentioned second salt.
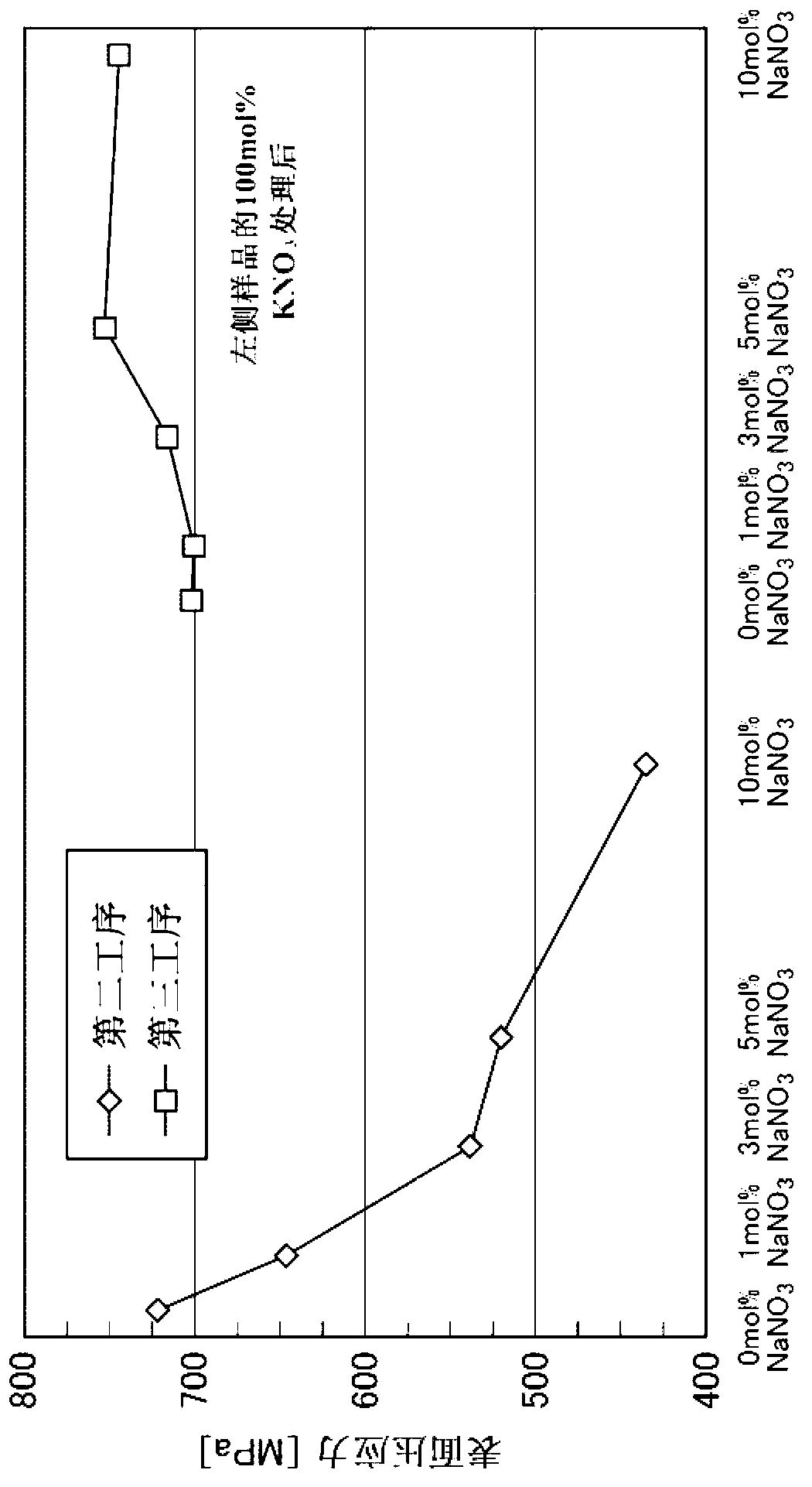
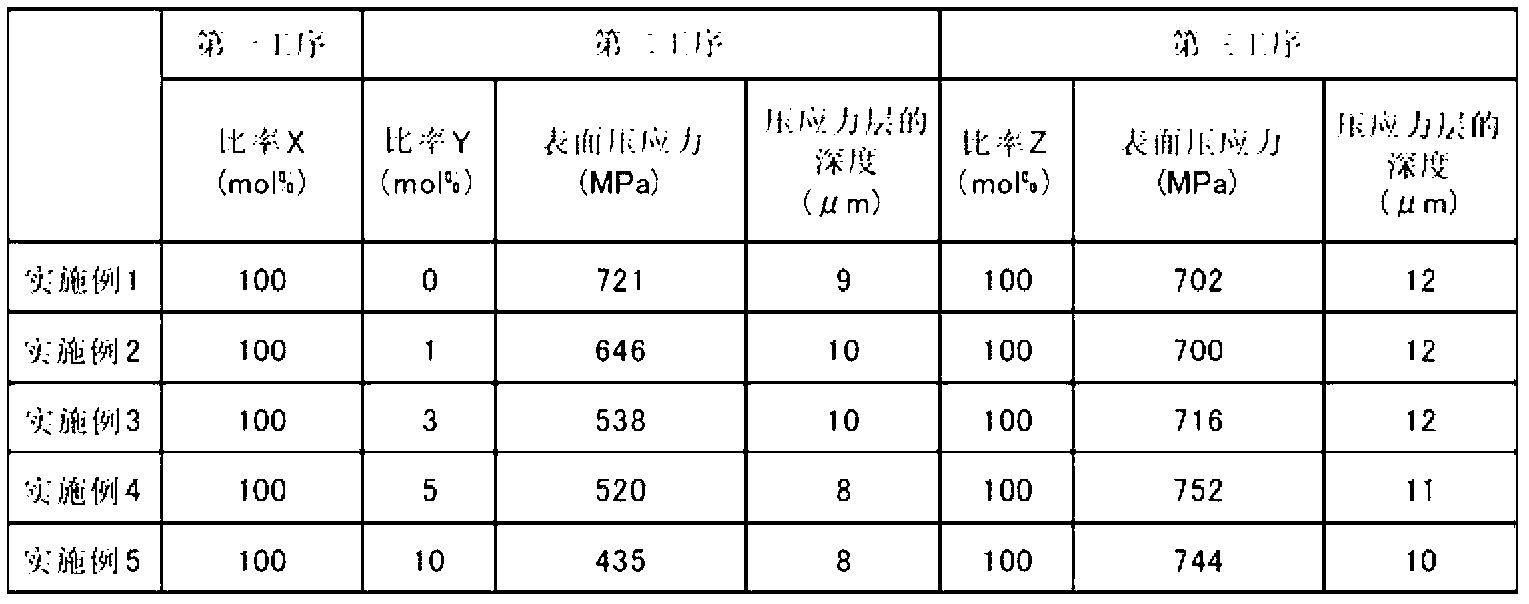
[0141] The surface compressive stress of the glass sample after the second process was 646 MPa, and the depth of the compressive stress layer was 10 μm. In addition, the surface compressive stress of the glass sample (chemically strengthened glass plate of Example 2) after the third step was 700 MPa, and the depth of the compressive stress layer was 12 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0143] As the second salt used in the second step, a mixed molten salt composed of 97 mol % of potassium nitrate and 3 mol % of sodium nitrate (ratio Y: 3 mol %) was prepared.
[0144] A chemically strengthened glass plate was manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the second step was performed using the above-mentioned second salt.
[0145] The surface compressive stress of the glass sample after the second process was 538 MPa, and the depth of the compressive stress layer was 10 μm. In addition, the surface compressive stress of the glass sample (chemically strengthened glass plate of Example 3) after the third step was 716 MPa, and the depth of the compressive stress layer was 12 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strain point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com