Laser Controller that Controls Pulse Width and Frequency Simultaneously
A technology of simultaneous control and controller, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of dense laser energy, difficult control of laser frequency and pulse, increase the thermal effect of cutting, etc. Cutting accuracy and cutting quality, the effect of a wide range of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
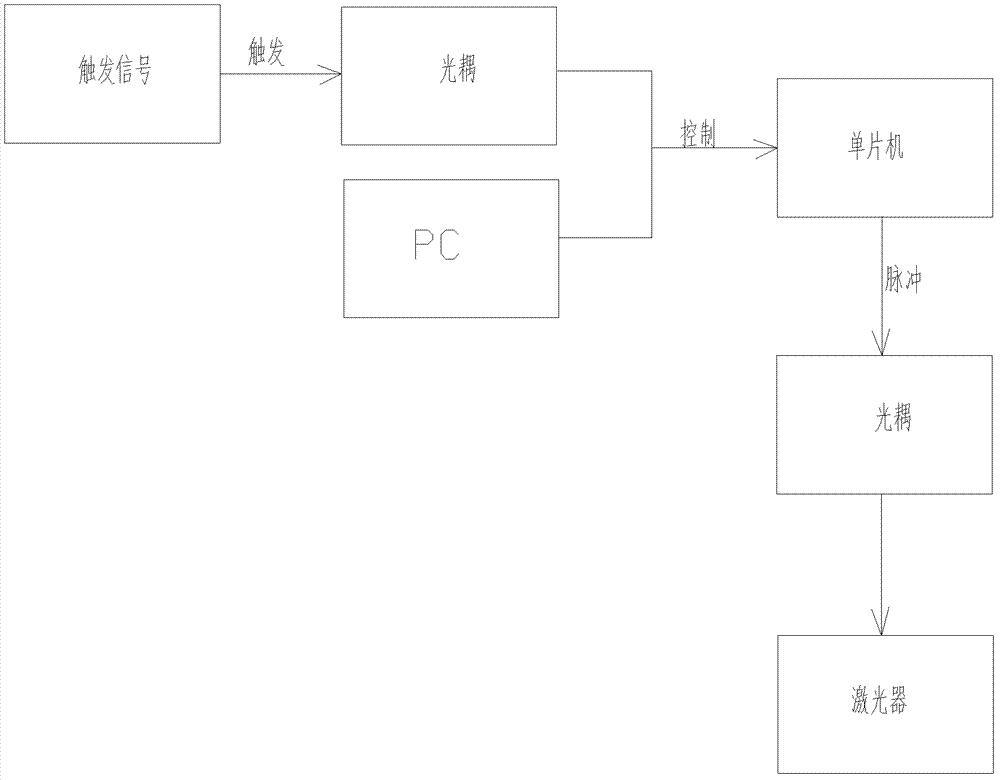
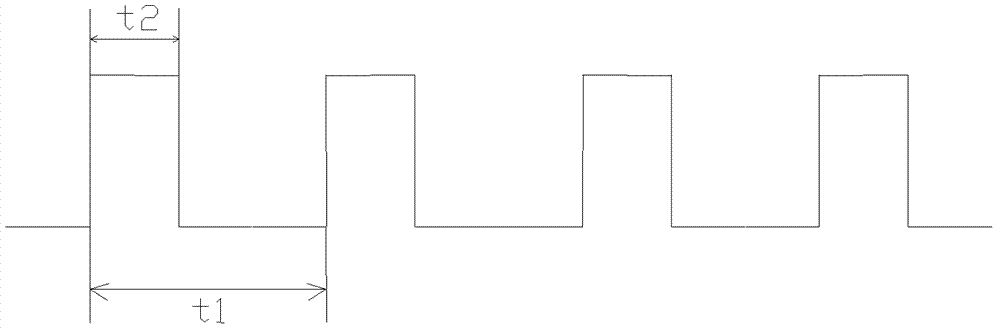
[0024] A laser controller that controls pulse width and frequency at the same time, including resistors, optocouplers I, optocouplers II, trigger terminals and single-chip microcomputers. For the principle of the controller, see figure 1 . The work of the laser controller is divided into the following steps: first, input a single high-pulse I / O signal from the signal source to the controller, and connect it to the trigger terminal of the optocoupler I through a resistor divider to trigger the optocoupler Ⅰ; the other end of the optocoupler I controls the trigger signal of the single-chip microcomputer, and at the same time sets the pulse width and frequency output by the single-chip microcomputer through the PC; the single-chip microcomputer controls the trigger end of the optocoupler II through its output signal; Coupling II controls the output signal of the controller to control the laser to emit laser with a specific pulse width and frequency. For the pulse signal output by...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A laser controller that simultaneously controls pulse width and frequency, including a resistor, optocoupler I, optocoupler II, a trigger terminal, and a single-chip microcomputer. The work of the laser controller is divided into the following steps: first, a single The high-pulse I / O signal is input to the controller, and connected to the trigger end of the optocoupler I through the resistor divider to trigger the optocoupler I; the other end of the optocoupler I controls the trigger signal of the single-chip microcomputer, and at the same time, it is set by the PC. Determine the pulse width and frequency output by the single-chip microcomputer; the single-chip microcomputer controls the trigger terminal of the optocoupler II through its output signal; controls the output signal of the controller through the optocoupler II to control the laser to emit laser with a specific pulse width and frequency . Different resistors are selected by means of jumpers for voltage divi...
Embodiment 3
[0028] A laser controller that simultaneously controls pulse width and frequency, including a resistor, optocoupler I, optocoupler II, a trigger terminal, and a single-chip microcomputer. The work of the laser controller is divided into the following steps: first, a single The high-pulse I / O signal is input to the controller, and connected to the trigger end of the optocoupler I through the resistor divider to trigger the optocoupler I; the other end of the optocoupler I controls the trigger signal of the single-chip microcomputer, and at the same time, it is set by the PC. Determine the pulse width and frequency output by the single-chip microcomputer; the single-chip microcomputer controls the trigger terminal of the optocoupler II through its output signal; the output signal of the optocoupler II can also enter the optocoupler III, and control the output signal of the controller through the optocoupler III , to control the laser to emit laser light with a specific pulse widt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com