Nucleic acids, compositions and methods for the excision of target nucleic acids
A technology for target nucleic acid and endonuclease nucleic acid, which is applied in the fields of nucleic acids, compositions and methods for excising target nucleic acid, and can solve the problems of low frequency of excision events and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] 6.1 Example 1: Construction of x-marked construct
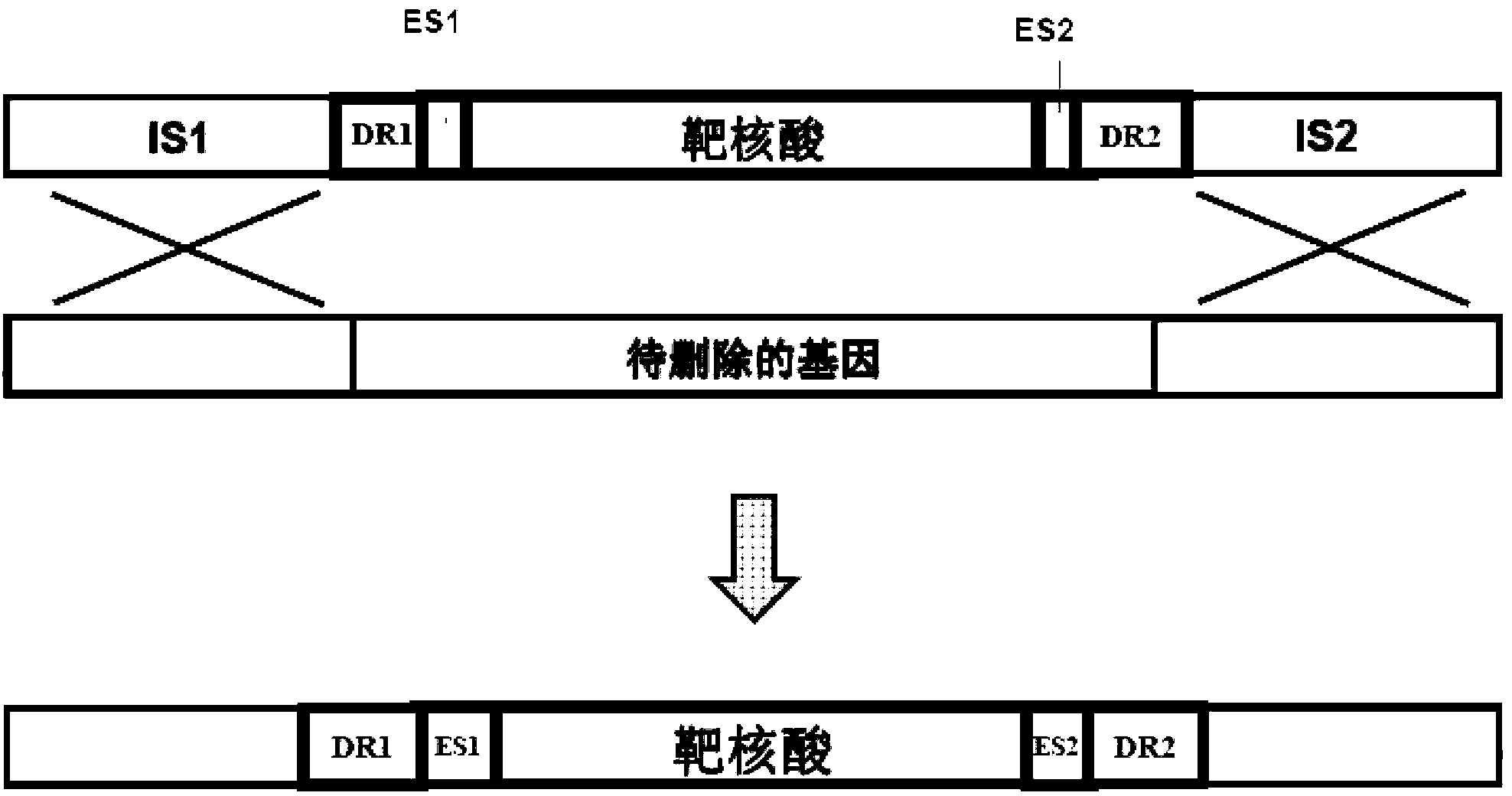
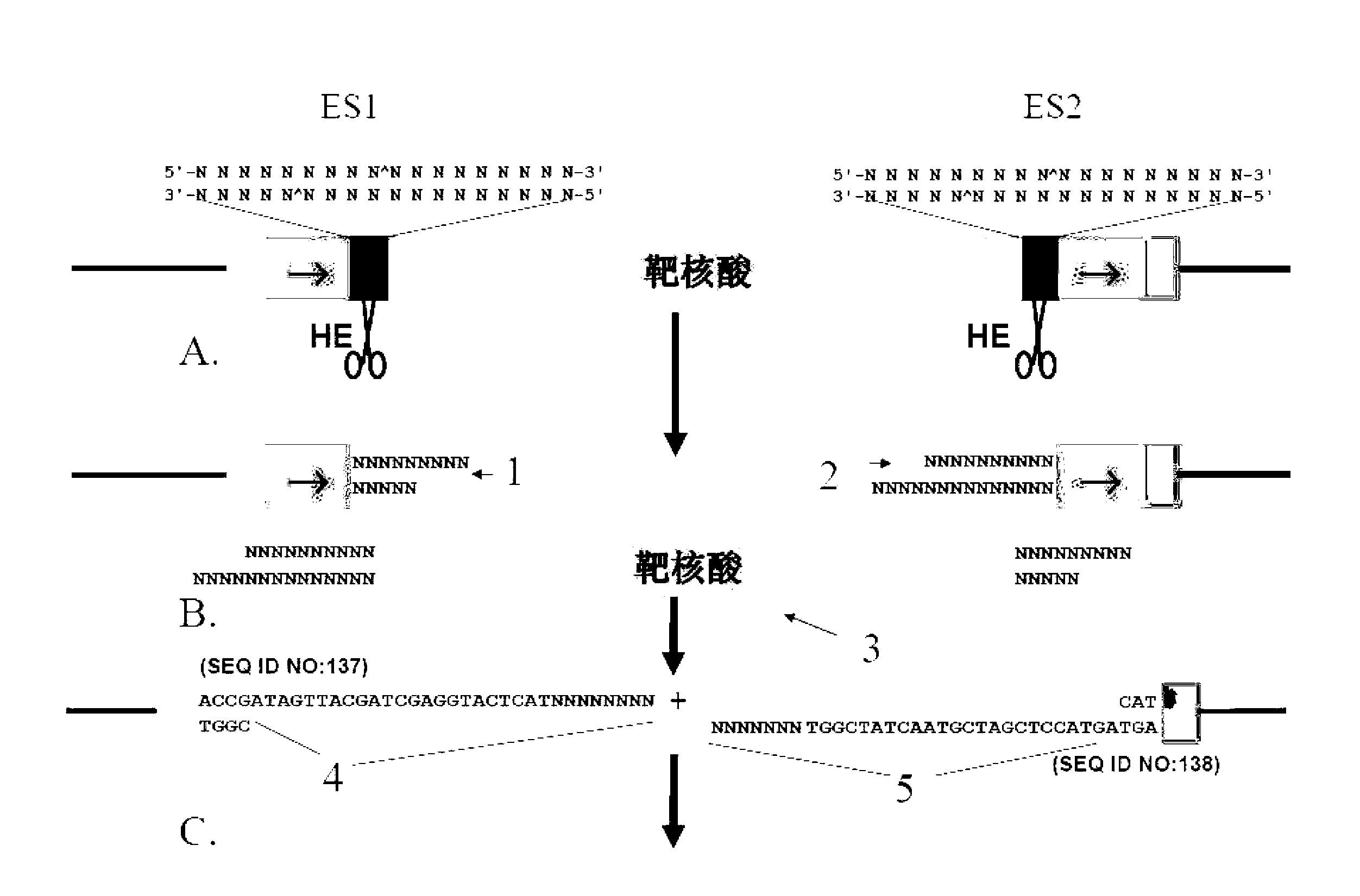
[0126] The compositions and methods described in this application are used to prepare and identify a series of resectable selectable markers for Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which are referred to as "x-markers" in this application. The first generation of markers uses I-SceI endonuclease, and the parameters of the DNA constructs tested are shown in figure 1 The parameters include: (1) the different lengths of the flanks of the forward repeat of the endonuclease site and (2) the comparison of one and two endonuclease sites. The second-generation marker uses the results of the first-generation test, which broadens the application of I-SceI endonuclease. The third-generation x-tag has been proven to be effective and can be extended to other endonucleases listed in Table 1 below.
[0127] Table 1: Recognition and cleavage sites of endonucleases.
[0128]
[0129] The reagents used in the experiment are described below, and the re...
Embodiment 2
[0191] 6.2 Example 2: Excision of chromosomal DNA selectable marker
[0192] This example demonstrates that the x-marker construct described in Example 1 can mediate the excision of the selectable marker from the chromosomal DNA of the host cell. As described below, transfer the constructs into cells, inoculate the cells in a medium selective for x-marking, and confirm the correct integration by colony PCR; the treatment of such strains is the same as any other preparations prepared with standard markers The strain is the same, the x mark can exist stably. Third, when the x-mark needs to be removed, a single copy (CEN.ARS) plasmid containing its own marker and a homing endonuclease gene expression construct is used to transform the strain, as described in the following section. After selecting the existing plasmids for several generations and inducing the expression of the homing endonuclease gene, the loss of the x mark in the strain is detected. Finally, the strain is grown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com