Low voltage ride through control method and device of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
A low-voltage ride-through and control method technology, which is applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, photovoltaic power generation, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as current fluctuation distortion, neglect control, and influence on output power quality, so as to improve reliability and prevent voltage transients. The effect of small drop and current fluctuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
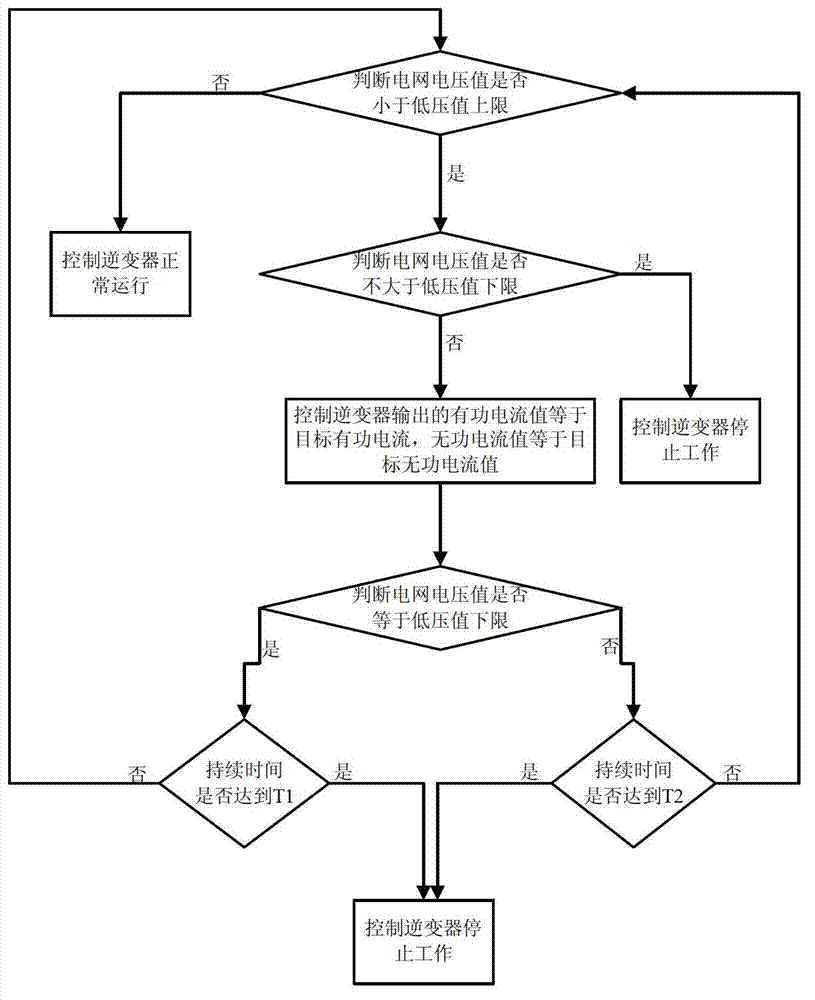
[0061] The low-voltage ride-through control method of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0062] Step S1: Determine whether the grid voltage value is less than the upper limit of the low voltage value, usually the upper limit of the low voltage value is 0.9 times the rated voltage,
[0063] If not, control the normal operation of the inverter. If the effective voltage value of the grid is greater than or equal to the upper limit of the low voltage value, it means that there is no voltage sag in the photovoltaic grid-connected at this time, and it is in a normal working state, so the inverter normal operation of the device;
[0064] If yes, go to step S2;
[0065] Step S2: Determine whether the grid voltage value is not greater than the lower limit of the low voltage value; usually the lower limit of the low voltage value is 0.2 times the rated voltage
[0066] Yes, control the inverter to stop working; if the voltage va...
Embodiment 2
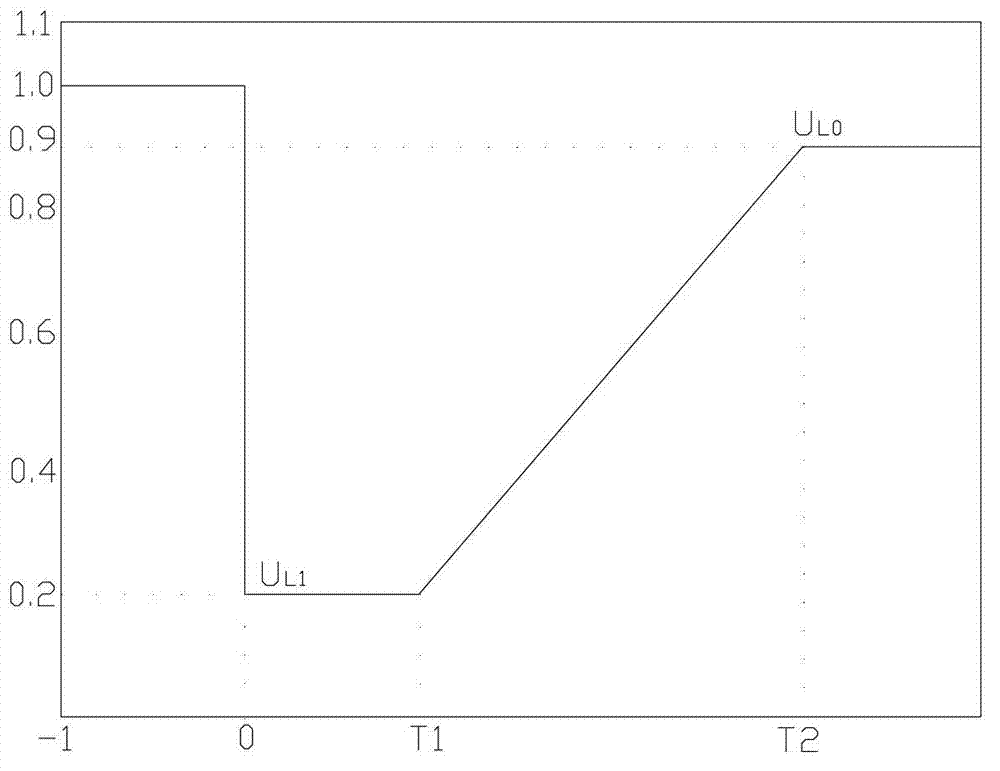
[0070] Such as figure 1 As shown, the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter certification testing standard "Technical requirements and test methods for grid-connected photovoltaic power generation inverters" CGC:2010 stipulates that medium and high voltage inverters specially suitable for large-scale photovoltaic power plants should have certain The ability to withstand abnormal voltage, to avoid disconnection when the grid voltage is abnormal, causing instability of the grid power supply, the following requirements are made;
[0071] Among them, U L0 is the low voltage upper limit for normal operation;
[0072] u L1 is the lower limit of low pressure that needs to be tolerated;
[0073] T1 is the voltage drop to U L1 The time required to maintain grid connection;
[0074] T2 is the voltage drop to U L0 The time required to maintain grid connection.
[0075] u L1 , T1, T2 values need to consider the protection and reclosing action time and other actual conditions, usu...
Embodiment 3
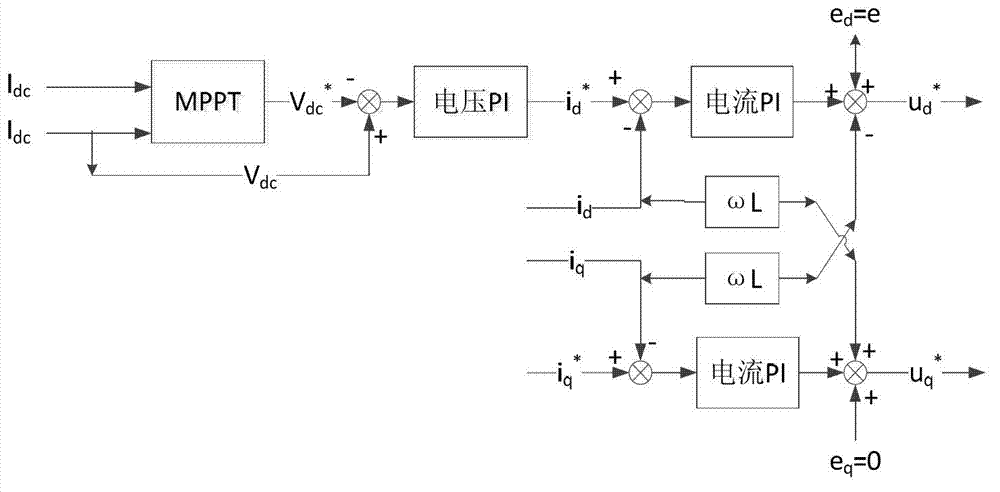
[0092] In this embodiment, on the basis of one of the above two embodiments, the low-voltage ride-through control method of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter further includes the steps of collecting voltage and current signals on the DC side and collecting voltage and current signals on the AC side power grid S0;
[0093] In the step S1, when the grid voltage is not less than the upper limit of the low-voltage value, the active current value normally output by the control inverter is equal to the normal target current obtained through the MPPT algorithm and voltage PI control based on the signal collected in step S0, and the reactive current value is zero. .
[0094] Step S1 can be before step S1 or after step S1, as long as it is guaranteed to be before step S2.
[0095] The control program or controller calculates the normal target voltage value of the inverter in normal operation through the MPPT: Maximum Power Point Tracking algorithm based on the DC voltage and DC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com