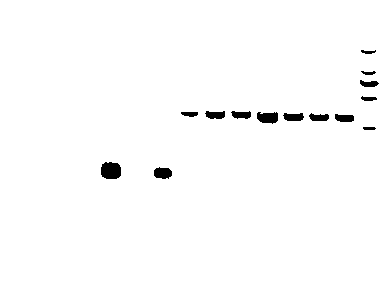
Method for enriching influenza virus through utilizing asialofetuin-containing magnetic bead
A fetuin and influenza virus technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of complex preparation process of monoclonal antibody and high price of monoclonal antibody, and achieve the effect of low cost and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Use a vortex to disperse the carboxylated magnetic microspheres by shaking for 10 minutes. The magnetic microspheres were washed twice with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, then resuspended in sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C for future use.
[0025] (2) Weigh 0.01g magnetic microspheres (about 0.5×10 6 ), use a magnetic separation rack to separate the magnetic beads from the solution, and resuspend the separated magnetic microspheres with 5ml sterile pH 4.5 PBS. Add 0.2 g of EDC to the suspension and react at 4° C. for 15 minutes, then add 0.05 g of NHS and react at 4° C. for 4 hours. After the reaction, the magnetic beads were separated from the liquid, washed three times with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, resuspended in 1ml of sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C. Use 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (English abbreviation: EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (English abbreviation: NHS) to carboxylate the carboxyl group of the magnetic beads Activate to obtain magnetic...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Use a vortex to disperse the carboxylated magnetic microspheres by shaking for 8 minutes. The magnetic microspheres were washed twice with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, then resuspended in sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C for future use.
[0030] (2) Weigh 0.01g magnetic microspheres (about 0.5×10 6 ), use a magnetic separation rack to separate the magnetic beads from the solution, and resuspend the separated magnetic microspheres with 5ml sterile pH 4.2 PBS. Add 0.22g of EDC to the suspension and react at 4°C for 15 minutes, then add 0.055g of NHS and react at 4°C for 4 hours. After the reaction, the magnetic beads were separated from the liquid, washed three times with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, resuspended in 1ml of sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C. Use 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (English abbreviation: EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (English abbreviation: NHS) to carboxylate the carboxyl group of the magnetic beads Activate to obtain magnetic bead...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Use a vortex to disperse the carboxylated magnetic microspheres by shaking for 12 minutes. The magnetic microspheres were washed twice with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, then resuspended in sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C for future use.
[0035] (2) Weigh 0.01g magnetic microspheres (about 0.5×10 6 ), use a magnetic separation rack to separate the magnetic beads from the solution, and resuspend the separated magnetic microspheres with 5ml sterile pH 4.5 PBS. Add 0.18 g of EDC to the suspension and react at 4° C. for 15 minutes, then add 0.45 g of NHS and react at 4° C. for 4 hours. After the reaction, the magnetic beads were separated from the liquid, washed three times with sterile pH 7.6 PBS, resuspended in 1ml of sterile pH 7.6 PBS, and stored at 4°C. Use 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (English abbreviation: EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (English abbreviation: NHS) to carboxylate the carboxyl group of the magnetic beads Activate to obtain magneti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com