Blade swing wing design method and H-type vertical axis wind turbine with blade swing wings
A design method and technology for wind turbines, which are applied to wind turbines, wind turbines, motors and other directions at right angles to the wind direction, can solve problems such as difficulty in self-starting, and achieve reduced manufacturing costs, enhanced self-starting performance, and increased camber and chord length. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
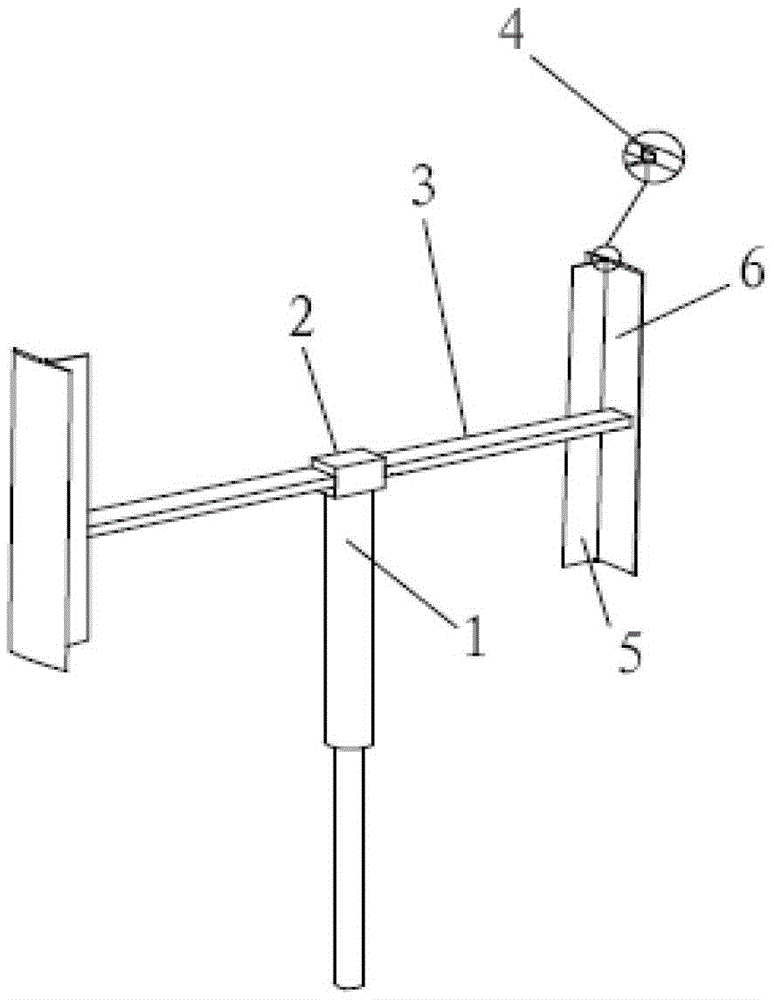
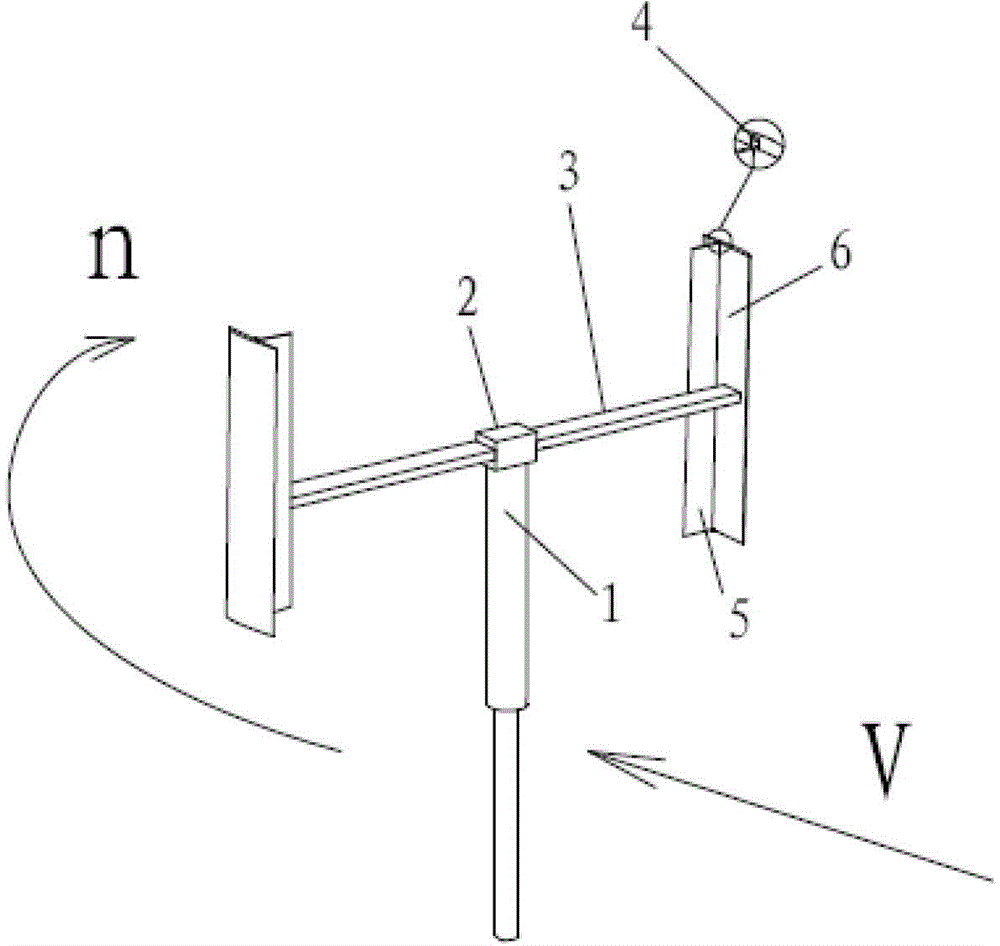
[0025]Specific embodiment one: blade swing wing design method in the present invention comprises following 7 steps:
[0026] 1. Determine the working wind speed of the wind turbine, the resistance moment when the wind turbine starts, the length of the blade, the chord length of the blade and the radius of rotation of the wind rotor;
[0027] 2. According to the working wind speed of the wind turbine, the length of the blades, the resistance moment of the wind turbine and the radius of rotation of the wind wheel to determine the mathematical model of the wind turbine startup;
[0028] 3. Determine the friction torque when the swing wing rotates, the density of the material used to process the swing wing, the thickness of the swing wing and the speed of the wind wheel when the swing wing is closed;
[0029] 4. According to the length of the blade, the friction torque when the swing wing rotates, the density of the material used to process the swing wing and the speed of the wind...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. In step 1, the working wind speed of the wind turbine is calculated according to the average wind speed of the wind condition in the area where the wind turbine is located; conditions and the technical data of the supporting generator, calculate the resistance moment that the wind turbine needs to overcome when it is aerodynamic; according to the specific geometric parameters of the wind turbine rotor that needs to be installed with blades, measure the length of the blade, the chord length of the blade and the radius of gyration of the wind wheel.
specific Embodiment approach 3
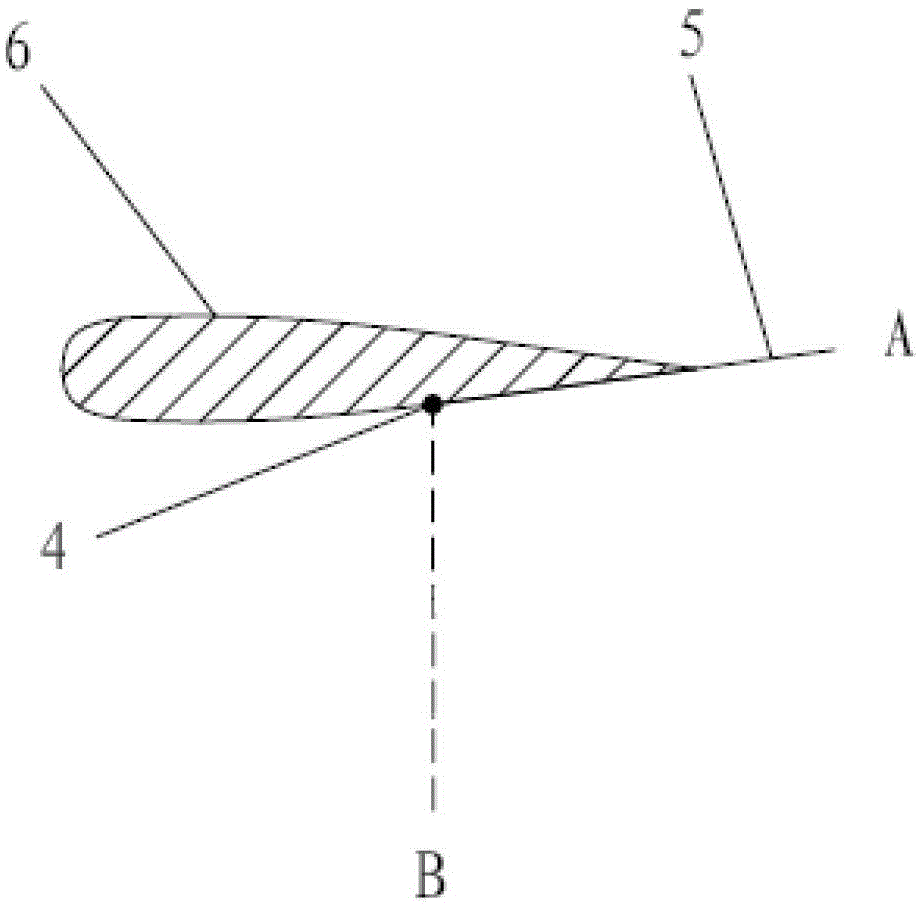
[0034] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode is a further description of specific implementation mode one or two, and the calculation formula of the wind turbine starting mathematical model described in step two is: ; where, M s is the resistance torque that needs to be overcome when the wind turbine starts, V a is the working wind speed of the wind turbine, C 1 is the width of the swing wing, H is the length of the blade, and R is the radius of gyration of the wind wheel.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com