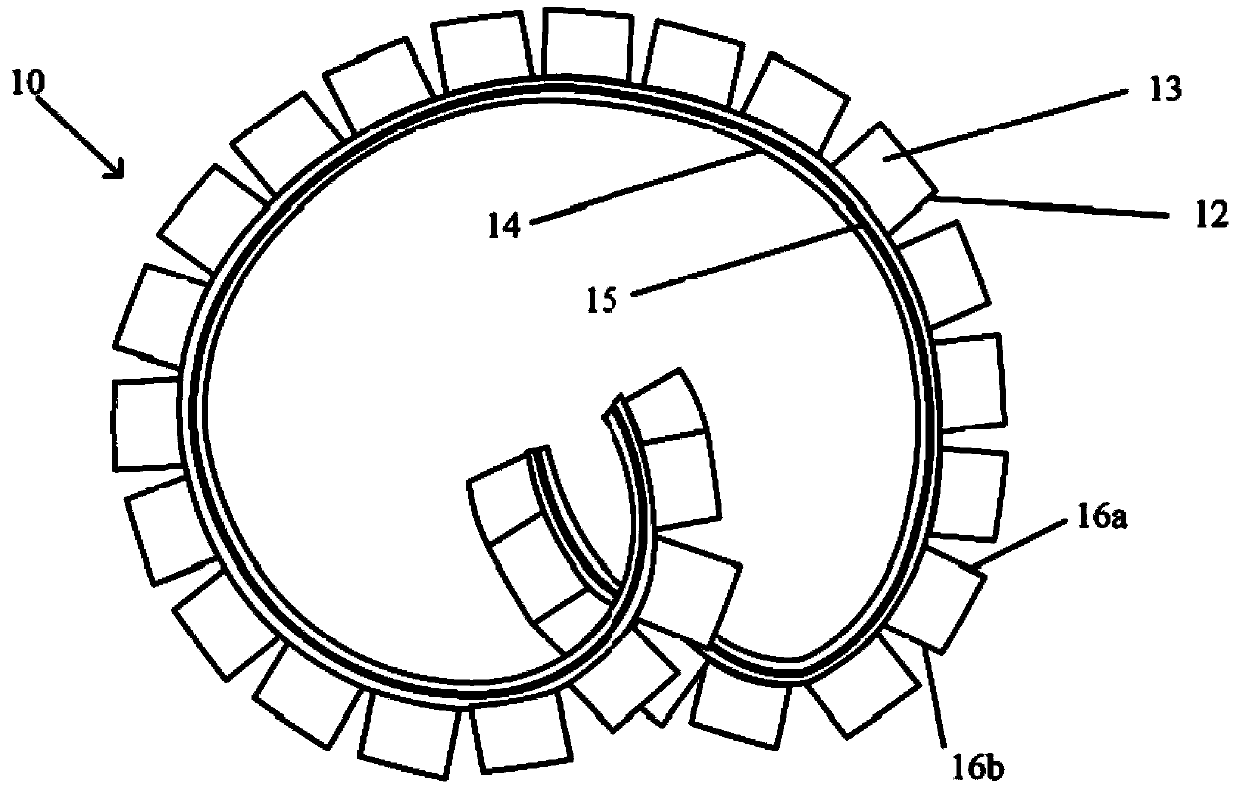
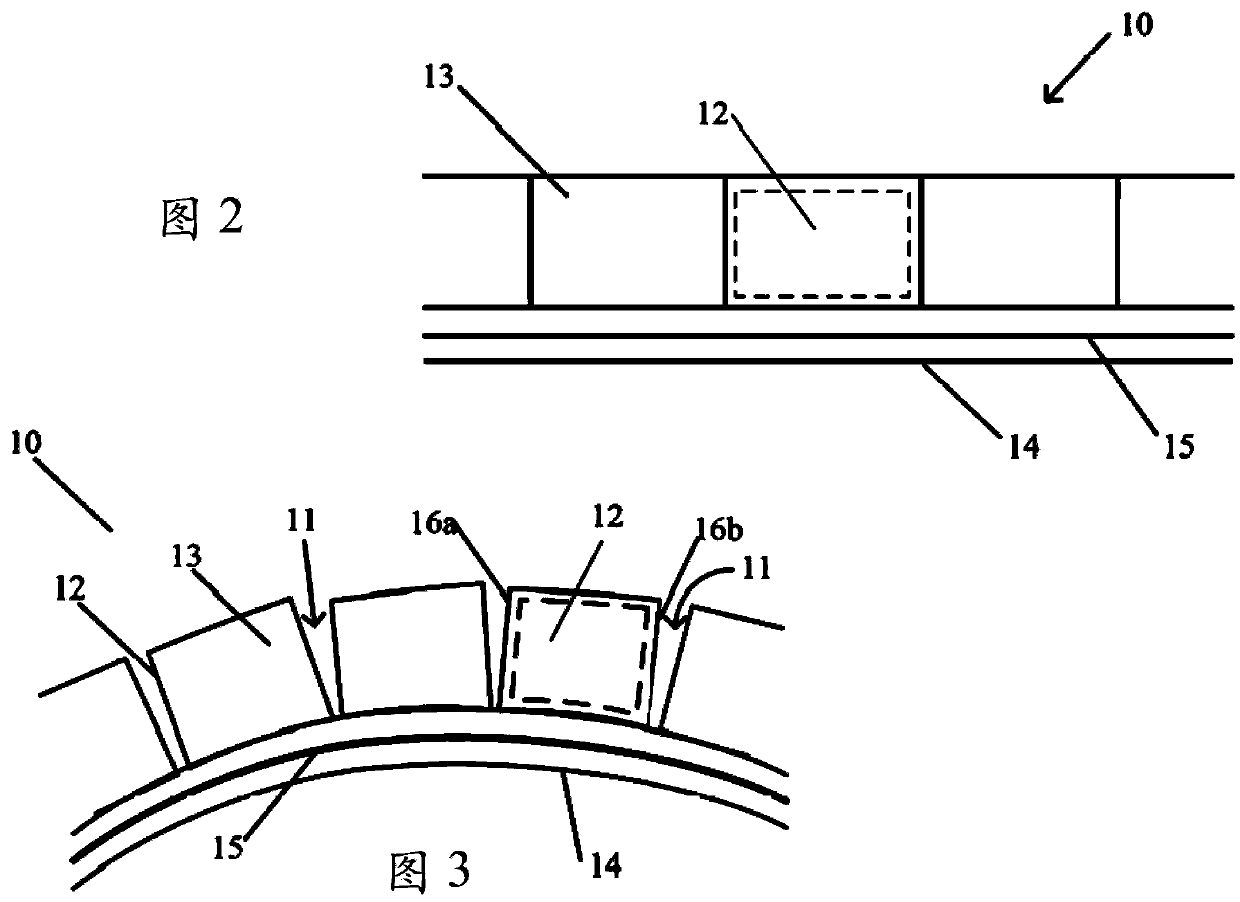
Implantable device for controlled release of low solubility drug
A drug and delivery device technology, applied in the field of implantable devices for controlled release of low-solubility drugs, can solve problems such as small discomfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0226] Example 1: Diffusion of Mitomycin C from Different Device Designs
[0227] A study was conducted to determine the feasibility of delivering mitomycin C ("MMC", a drug of low water solubility) from different capsid structures. A total of eight devices—two devices in four different configurations—are formed from 2.65mm ID ("600" tubing) silicone tubing and loaded with compressed tablets of MMC tablets to achieve a total of about 60 mg. payload.
[0228] The four configurations are (1) devices with a single open end presenting a single face of an MMC tablet; (2) devices with two opposing open ends presenting two faces of an MMC tablet; (3) devices with means of two opposing open ends and a slit in the channel between the two MMC tablets, thereby effectively presenting the four sides of the MMC tablet; Contains MMC tablet (ie, without shell). Two devices of each configuration were tested.
[0229] Each of the four configurations was placed separately in 100 mL of deioni...
example 2
[0232] Example 2: In vitro release of mitomycin C from capsid modules
[0233] Housing device modules loaded with mitomycin C (MMC) tablets were fabricated and the in vitro release of MMC was observed.
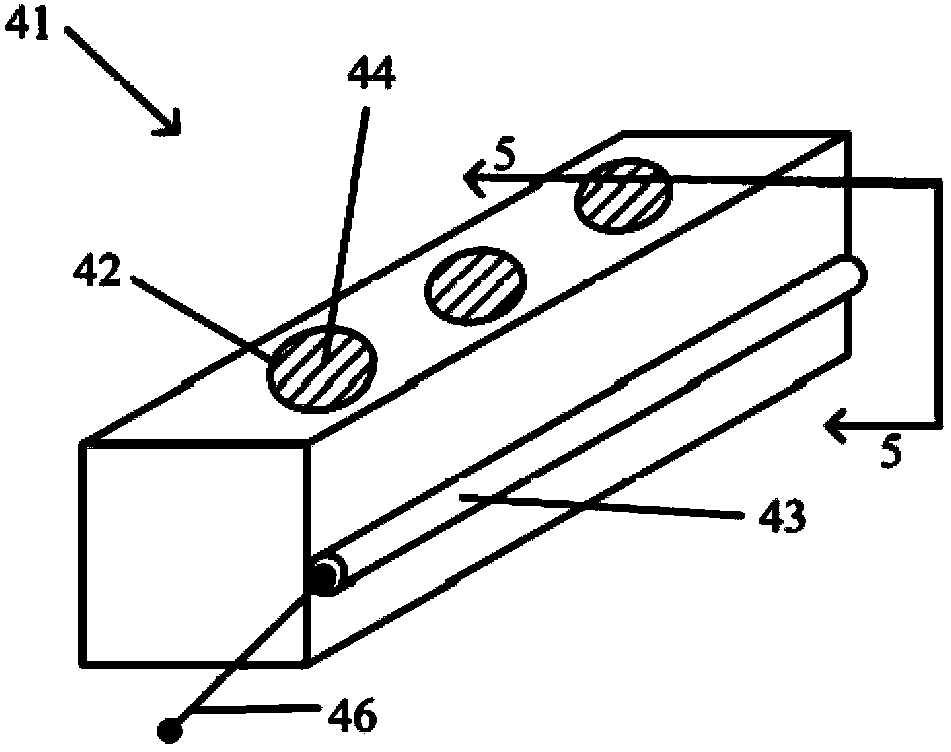
[0234] Tablets were made from 100% Mitomycin C powder using a Carver press. Tablets are 2.1 mm or 2.6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in height. The mass of the tablet is approximately 10 mg for a 2.1 mm diameter tablet and 16 mg for a 2.6 mm diameter tablet. exist Figure 42a An MMC tablet 402 is shown in .
[0235] The housing modules are fabricated from sections of silicone tubing and silicone adhesive. Figure 42b An assembled device module 400 is shown showing an MMC tablet 402 loaded into a housing module 404 . Surface 'b' of tablet 402 is surrounded by silicone tube 406 and surface 'c' is in contact with silicone adhesive 408 .
[0236] Surface 'a' of the MMC tablet 402 was exposed to the deionized water release medium for a test period of 8 days. Specifically, the housi...
example 3
[0238] Example 3: In vitro release of mitomycin C from capsid modules
[0239] The experiment described in Example 2 was repeated with modifications to the MMC tablet formulation in order to observe the effect of including excipients. use with Figure 43 Same configuration and experimental approach as in 'C'. By adding 5% (w / w) PVP (Plasdone K-29 / 32), PEO100K or PEG8K to 95% Mitomycin C powder, and then compressing the mixture to form tablets each having a mass of approximately 10 mg to make a 2.1 mm diameter tablet with a height of 2 mm. as in Figure 44 As shown in , with the addition of these excipients, an increased release rate was observed (n=3; error bars indicate standard deviation around the mean) (some error bars are not shown, i.e., when they were smaller than these symbols Time.).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com