Preparation method of iron-tartaric acid-sodium complex
A tartaric acid and complex technology, which is applied in the field of complex preparation, can solve problems such as waste of raw materials and influence on the stability of complexes, and achieve the effects of small raw material consumption, simple preparation method, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
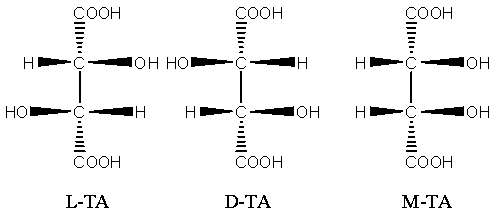
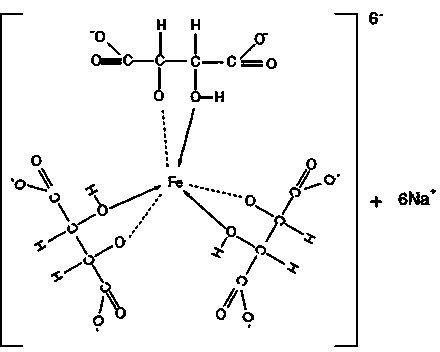
[0051] Add 3 kg of L-TA to the autoclave, H 2 O 3kg, heat up to 165°C, keep warm for 40h. Stop heating, stir and release the feed liquid after gradually cooling down. Detected content, meso form accounted for 45.6%, racemate accounted for 54.4%. Add 50% FeCl with stirring 3 Solution 6.5kg, after the complexation is uniform, add 50% NaOH solution 4.8kg under the condition of reflux with condensation. Stir evenly until a light green uniform iron-tartrate-sodium complex is formed, with a pH value of 2.2.
Embodiment 2
[0053] Add 4 kg of L-TA to the autoclave, H 2 O 2kg, heat up to 170°C, keep warm for 40h. Stop heating, stir and release the feed liquid after gradually cooling down. In the detection content, the meso form accounted for 51.7%, and the racemate accounted for 48.3%. Add 50% FeCl with stirring 3 Solution 9kg, after the complexation is uniform, add 50% NaOH solution 7.5kg under the condition of reflux with condensation. Stir evenly until a yellow-green uniform iron-tartrate-sodium complex is formed, with a pH value of 4.5.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Add 4 kg of L-TA to the autoclave, H 2 O 2kg, HCl (36% content) 0.5kg, heat up to 165°C, keep warm for 24h. Stop heating, stir and release the feed liquid after gradually cooling down. Detected content, meso form accounted for 58.4%, racemate accounted for 41.6%. Add 50% FeCl with stirring 3 Solution 9kg, after the complexation is uniform, add 50% NaOH solution 8.5kg under the condition of reflux with condensation. Stir evenly until a dark green uniform iron-tartrate-sodium complex is formed, with a pH value of 6.8.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com