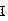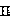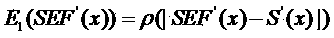Registering method of breast dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance image (DCE-MRI) sequence
A magnetic resonance image and dynamic enhancement technology, applied in the field of medical medical image registration, can solve problems such as the inability to guarantee time continuity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A registration method for breast dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance image sequences, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0054] (1) Read the image data of all time frames in the same layer of the DCE-MRI image sequence;
[0055] (2) Use affine transformation to roughly register the images before and after enhancement, and obtain the initial estimate of the deformation field;
[0056] (3) Perform motion compensation on the DCE-MRI image sequence from the currently estimated deformation field, and calculate the enhancement field at each time point;
[0057] (4) Use K-means clustering to discretely divide the enhanced fields of time series into finite types for the enhanced fields at all time points obtained in step (3), and then use Markov random field to model the enhanced fields of time series , use the Fast-PD algorithm to optimize the discrete Markov random field energy to solve the time series enhanced field;
[0058] (5) Use the time series...
Embodiment 2
[0088] The method of the present invention is described with a specific embodiment.
[0089] In this embodiment, the image size is 384×384×56, the pixel size is 1×1×1 mm, and a total of nine images of the patient at different times are collected. The image at the first moment is the image before enhancement, and the images at other moments are the image after enhancement.
[0090] (1) Read in the images of the ninth layer at nine times respectively, with figure 2 Five breast DCE-MRI images with obvious gray scale changes in the selected images are shown.
[0091] (2) Taking the pre-enhanced image as a reference image and the post-enhancement image as a floating image, affine transformation is used to perform rough registration on the pre-enhancement and post-enhancement images, and the initial estimation of the deformation field is obtained.
[0092] (3) Perform motion compensation on the DCE-MRI image sequence by the currently estimated deformation field, according to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com