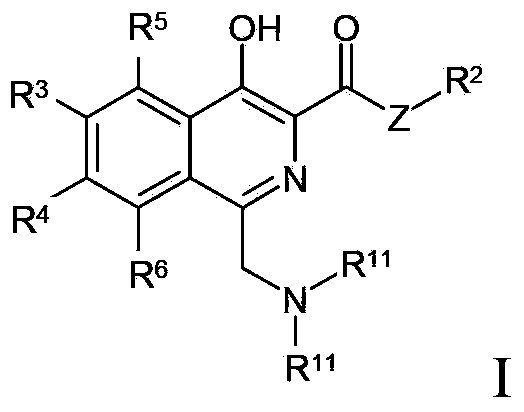
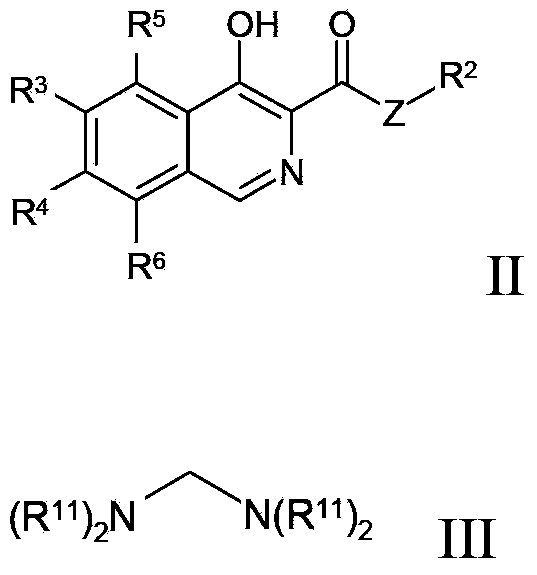
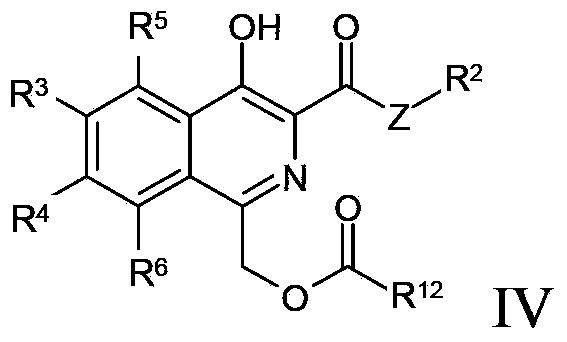
Method for preparing isoquinoline compounds
A technology of compounds and mixtures, used in organic chemistry, drug combinations, extracellular fluid diseases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0578] Preparation of 2-(4-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxamido)acetic acid
[0579] a) Preparation of methyl 1-((dimethylamino)methyl)-4-hydroxy-5-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxylate (1b)
[0580]
[0581] A round bottom flask equipped with a thermocouple and condenser can be charged with 1a and acetic acid (approximately 7 molar equivalents ± 5%). The suspension of 1a in acetic acid can be vigorously stirred with a magnetic stirrer (note: for larger scale processing, overhead stirring should be performed). A slight excess of bis-dimethylaminomethane (approximately 1.25 molar equivalents) can then be slowly added to this mixture [Remark: The reaction is slightly exothermic, a temperature rise of 15-20°C can be observed]. After the addition is complete, the mixture can be heated to 55±5° C. for at least 8 h. The reaction can then be evaluated by HPLC. If the amount of 1a is greater than 0.5%, the reaction can be stirred for an additional 2 hours at 55±5°C a...
Embodiment 2
[0595] Preparation of 2-(4-hydroxy-1-methyl-6-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxamido)acetic acid
[0596] a) Preparation of methyl 1-((dimethylamino)methyl)-4-hydroxy-6-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxylate (2b)
[0597]
[0598] A round bottom flask equipped with a thermocouple and condenser can be charged with 2a and acetic acid (approximately 7 molar equivalents ± 5%). The suspension of 2a in acetic acid can be vigorously stirred with a magnetic stirrer (remark: for larger scale workup, overhead stirring should be used). A slight excess of bis-dimethylaminomethane (approximately 1.25 molar equivalents) can then be slowly added to the mixture [Remark: The reaction is slightly exothermic, a temperature rise of 15-20°C can be observed]. After the addition is complete, the mixture can be heated to 55±5° C. for at least 8 h. The reaction can then be evaluated by HPLC. If the amount of 2a is greater than 0.5%, the reaction can be stirred at 55±5°C for 2 hours and re-evaluated by HPL...
Embodiment 3
[0612] Preparation of 2-(4-hydroxy-1-methyl-7-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxamido)acetic acid
[0613] a) Preparation of 5-phenoxybenzofuranone
[0614]
[0615] DMF (68Kg) was charged to the reactor and stirring was started. The reactor was then charged with phenol (51 Kg), acetylacetone (8 Kg), 5-bromobenzofuranone (85 Kg), copper bromide (9 Kg) and potassium carbonate (77 Kg). The mixture was heated above 85°C and held until the reaction was complete, then cooled. Add water. The solid was filtered and washed with water. The solid was dissolved in dichloromethane and washed with aqueous HCl and then water. The solvent was removed under pressure, and methanol was added. The mixture was stirred and filtered. The solid was washed with methanol and dried in the oven to yield 5-phenoxybenzofuranone (yield: 72%, HPLC: 99.6%).
[0616] b) Preparation of methyl 2-chloromethyl-4-phenoxybenzoate
[0617]
[0618]Toluene (24Kg) was charged to the reactor and stirring was st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com