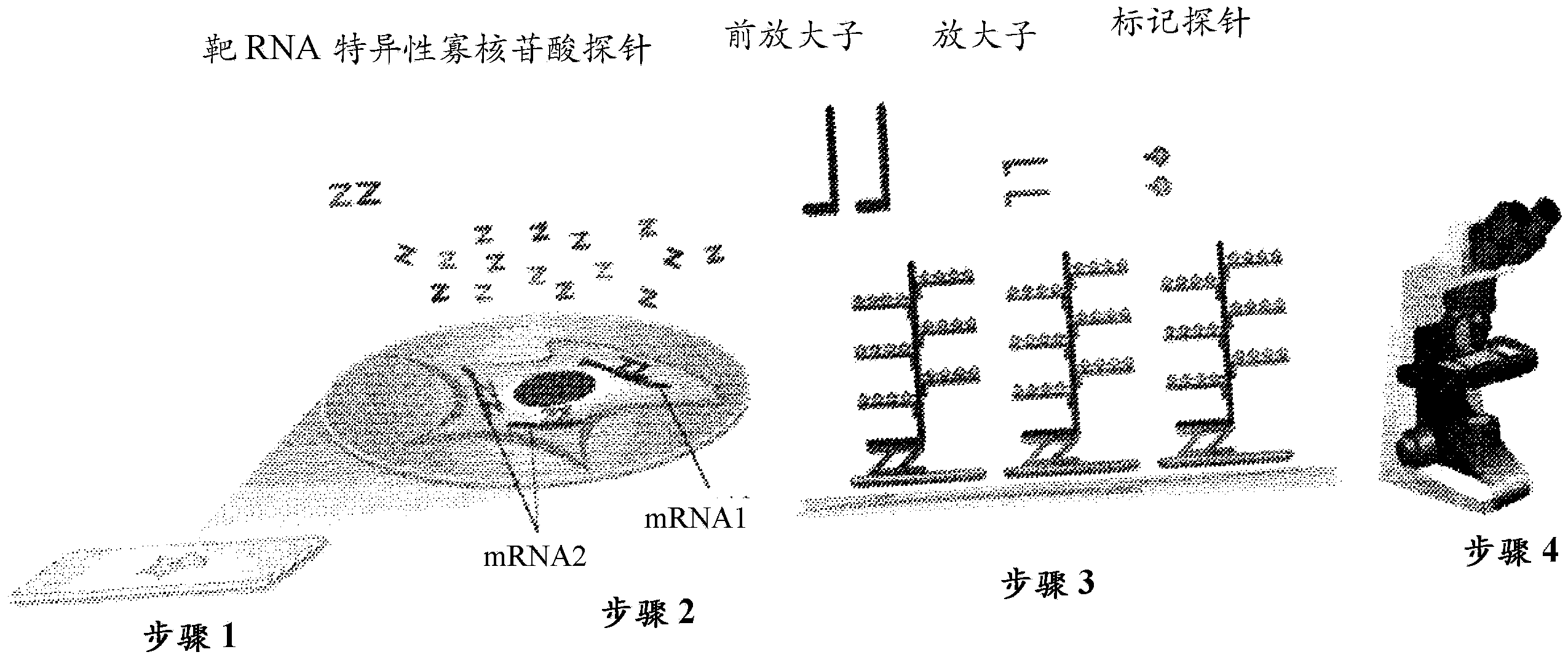
RNAscop (TM) HPV assay for determining HPV status in head and neck cancers and cervical lesions
A head and neck cancer, HPV-16 technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as unpredictable effects, difficult assay methods, unclear high-specificity properties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] RNAscope Protocol for HPV Assay
[0082] For each tumor sample, 5 micron tissue sections were cut and mounted on glass slides. Perform the following steps for each tumor sample:
[0083] 1. Obtain a sample from the subject. The sample may be a non-preserved tissue sample obtained from a patient or a tissue sample in a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue section.
[0084] 2. Optionally if the sample is in a FFPE tissue section, the sample can be treated first by heating the FFPE tissue section in citrate buffer followed by protease digestion.
[0085] 3. Perform RNAscope on the sample HPV assay, which includes the following tests:
[0086] i) a negative control using a target probe against the bacterial gene dapB;
[0087] ii) using a target probe for the human gene UBC to carry out a positive control;
[0088] iii) Assays are performed using HPV target probe sets containing pooled high-risk HPV subtypes or individual target probe sets specific to these subt...
Embodiment 2
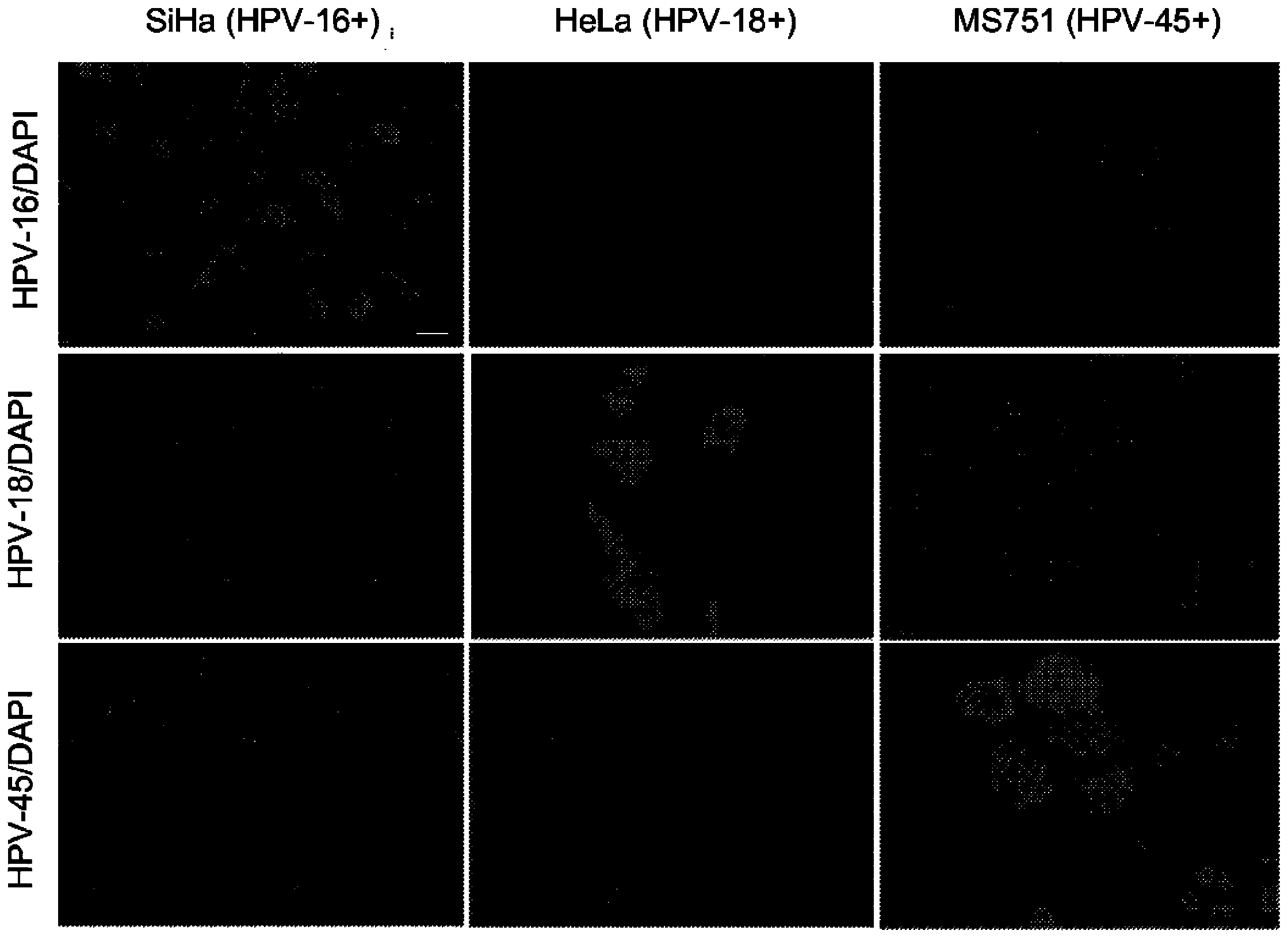
[0091] RNAscope of E6 / E7 mRNA of HPV subtypes in subtype-specific cell lines detection
[0092] To confirm RNAscope Feasibility of HPV Assays to Detect and Differentiate Different HPV Subtypes Experiments were performed to detect HPV subtypes in cell lines known to contain only specific HPV subtypes. Using the RNAscope described in Example 1 Protocol for HPV assay. Target probe sets specific to E6 / E7 mRNA of HPV-16, HPV-18 and HPV-45 were designed respectively. Hybridization of the probe set to its target is detected using an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated signal amplification system, followed by development with Fast Red, which produces a red fluorescent precipitate. Such as figure 2 As shown, the HPV-16 target probe set produced positive signals only in SiHa and CaSki cells, two cell lines bearing only the HPV-16 subtype. The HPV-18 target probe set produced a positive signal only in the HeLa cell line, which carries only the HPV-18 subtype. The HPV-45 target pro...
Embodiment 3
[0094] RNAscope of HPV subtypes in head and neck cancer tissue samples detection
[0095] The following experiments were performed to detect E6 / E7 mRNA of HPV high-risk subtypes in FFPE tissue samples obtained from HNC patients. In this experiment, the RNAscope described in Example 1 was used Protocol for HPV assay. Two sets of target probe sets were prepared. In one set, the target probe set contained only target probes that bound only to HPV-16. In another set, the target probe set contained target probes that bind to HPV-18, 31, 33, 35, 52, and 58 (referred to as the "HR-HPV probe set"). Multiple HNC patient samples diagnosed with cervical lesions were tested using each of the aforementioned panels of target probe sets. image 3 Exemplary results are shown. The results showed that positive E6 / E7 mRNA of HPV high-risk subtypes were detected in two patients. Two patients were known to have HPV-associated HNC. Therefore, the experiment confirmed that RNAscope with sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com