Low-power-consumption high-gain broadband frequency mixer
A mixer, high gain technology, applied in the field of low power consumption high gain wideband mixer, can solve the problems of mixer gain and bandwidth cannot be improved at the same time, the traditional structure cannot improve the gain, the bandwidth is narrow, etc. Gain, Power Reduction, Gain and Bandwidth Increase Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
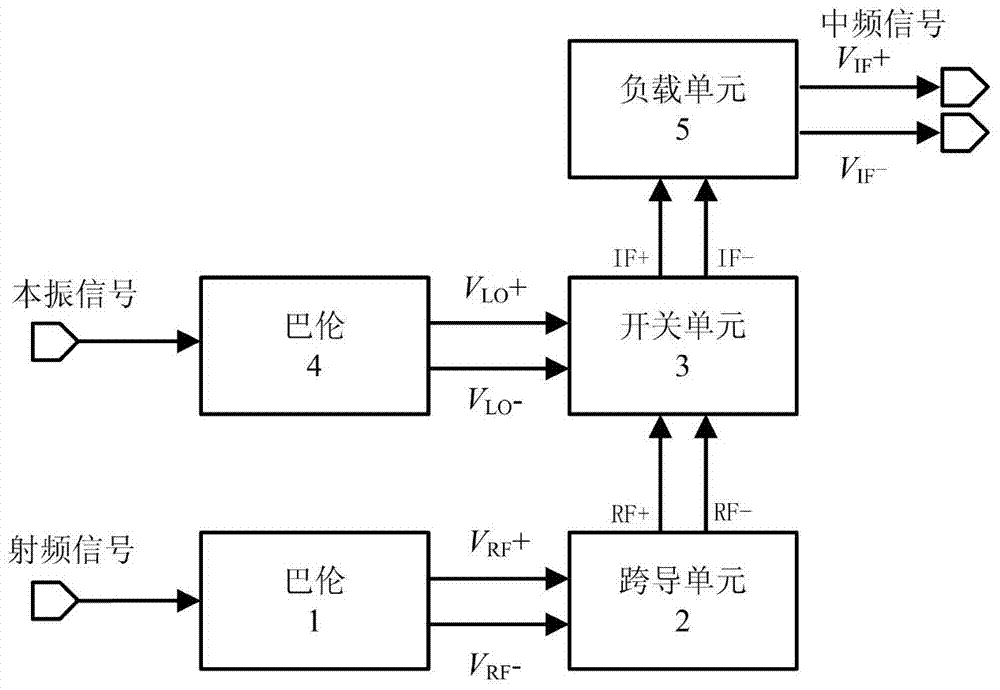
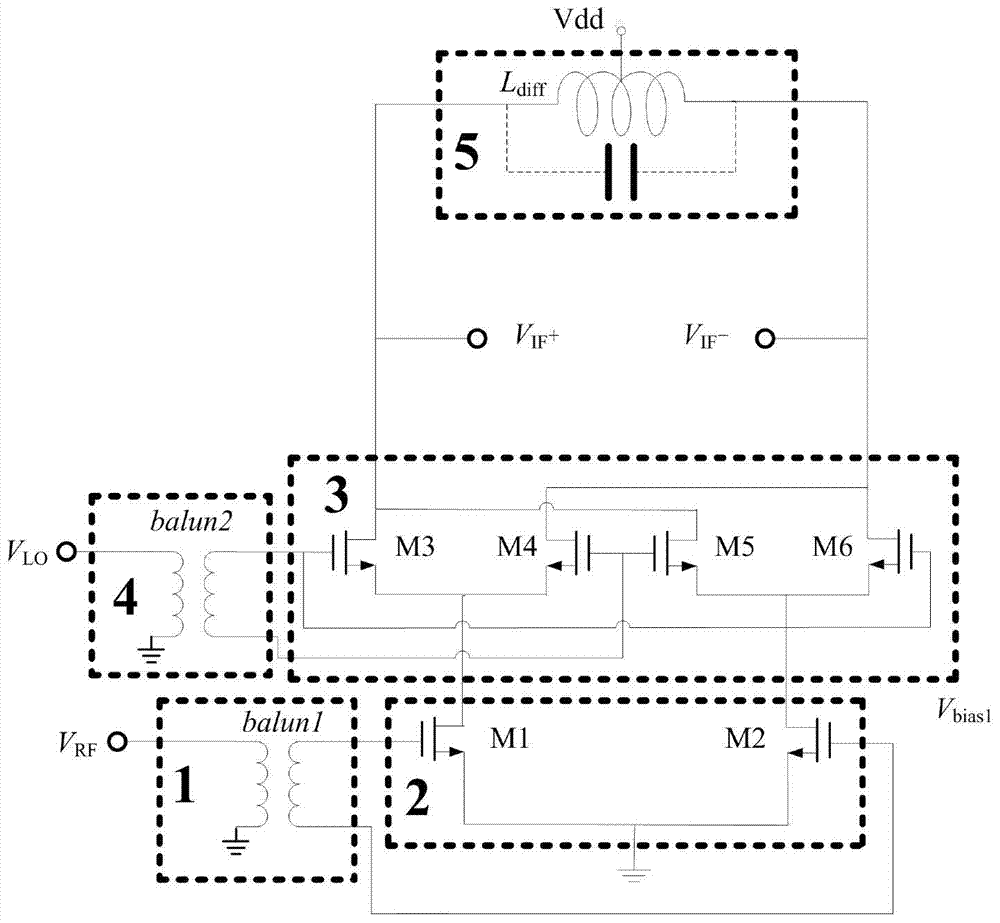
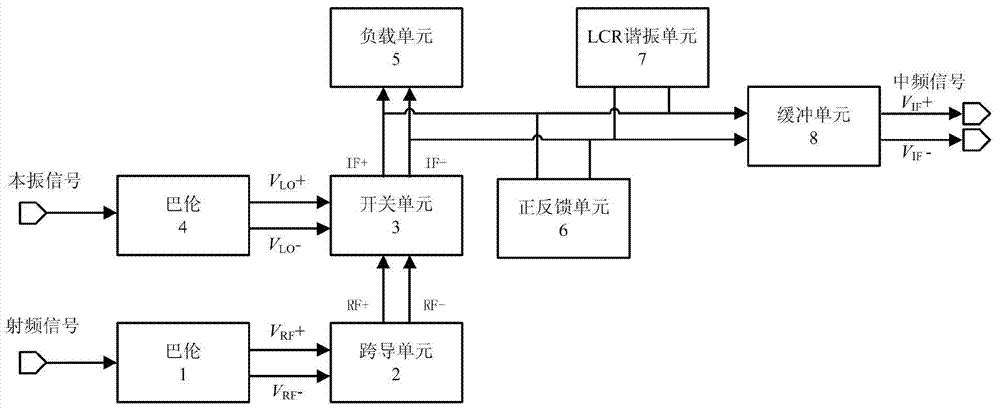
[0026] see image 3 , the radio frequency signal is converted into a differential voltage signal V by the radio frequency balun unit 1 RF + and V RF -Send into the transconductance unit 2, the transconductance unit 2 converts the input voltage signal into a current signal and sends it to the switch unit 3, while the local oscillator signal is converted into a differential voltage signal V by the balun unit 4 LO + and V LO - Afterwards, it is also added to the switch unit 3 to make it switch the radio frequency current at the local oscillator frequency. The switch unit 3 outputs the intermediate frequency differential current signals IF+ and IF- to be connected to the load unit 5 . The above part and the circuit block of the traditional Gilbert structure mixer figure 1exactly the same. The present invention adds a positive feedback unit 6, an LCR resonant unit 7 and a buffer unit 8 after the switch unit 3, and together with the load unit 5 they form a new load unit as the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com