A self-absorption correction processing method for fluorescence exafs data
A technology of self-absorption effect and processing method, which is applied in the field of self-absorption effect correction processing of fluorescence EXAFS data, and can solve problems such as multi-layer film correction method, oscillation structure attenuation, incident light refraction and multiple reflection effects not considered
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
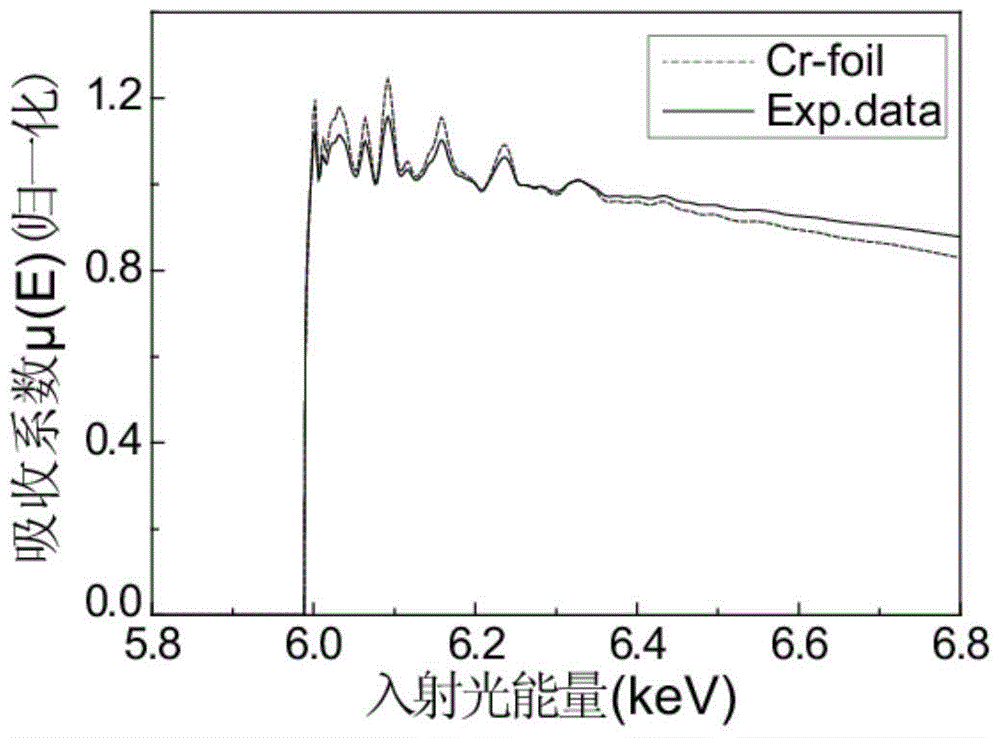
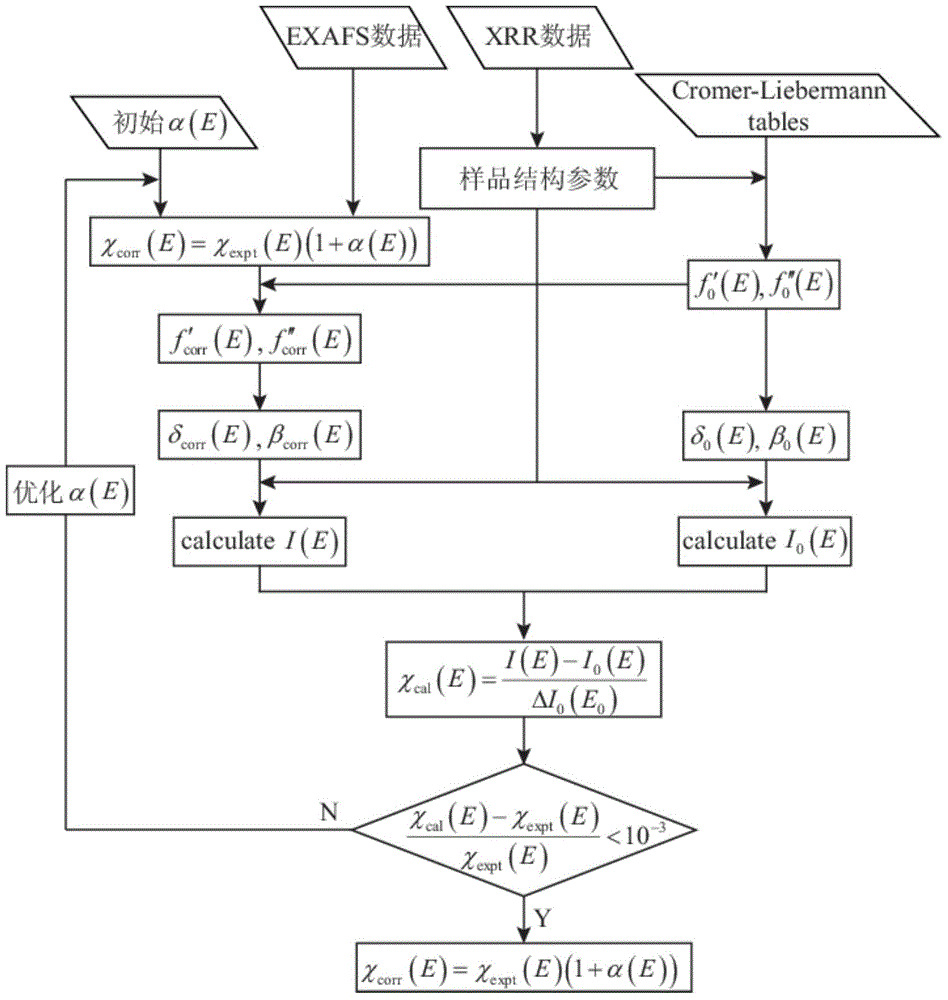
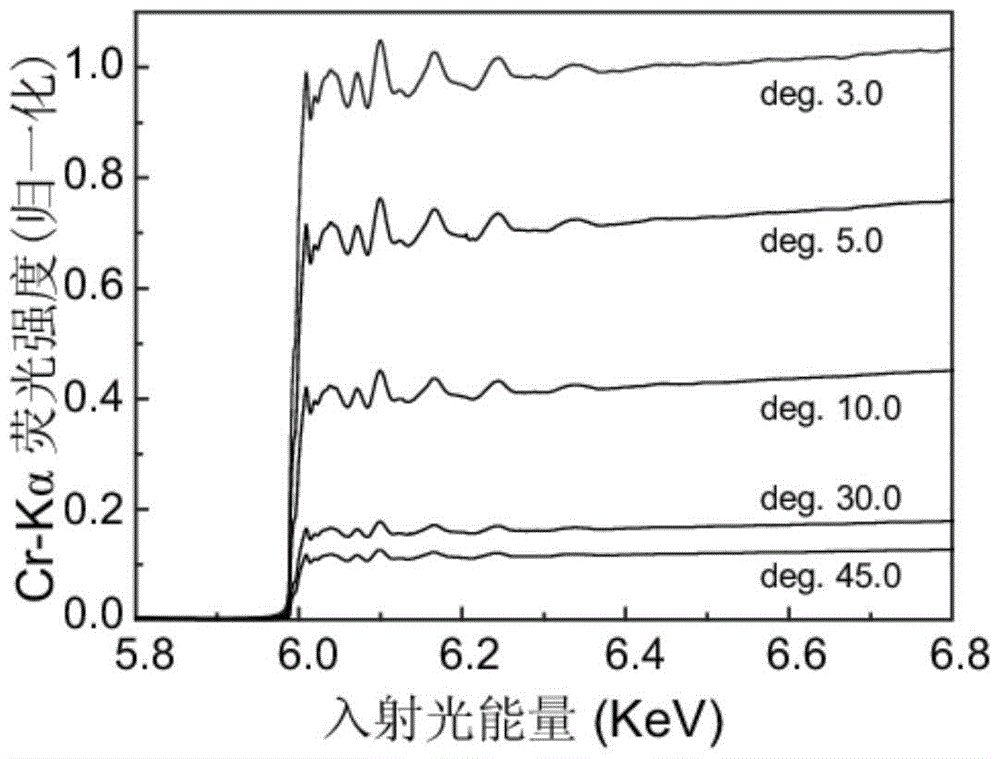
[0050] Take [Cr(20nm) / C(10nm)] 5 multilayer film as a sample, for Cr-K α Fluorescent EXAFS method measurements were performed. When a beam of light intensity is I 0 When the X-ray irradiates the sample with a total thickness of t at a grazing incidence angle θ, the X-ray passes through the sample layer with a thickness of x and reaches B, and its light intensity attenuation is use μ a (E) represents the absorption coefficient of the element to be measured to X-rays, μ other (E) represents the absorption coefficient of other elements to X-rays, then the probability of the element...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com