Difference coplanar waveguide UWB (Ultra Wide Band) wide slot trapped wave antenna with high attenuation band characteristic
A coplanar waveguide and notch antenna technology, applied in slot antennas, radiating element structures, circuits, etc., can solve the problem that the antenna does not use the coplanar waveguide feeding method, the antenna radiation pattern is not very ideal, and the notch squareness It is not very good, etc., to achieve the effect of low cost, simple structure and good radiation pattern
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
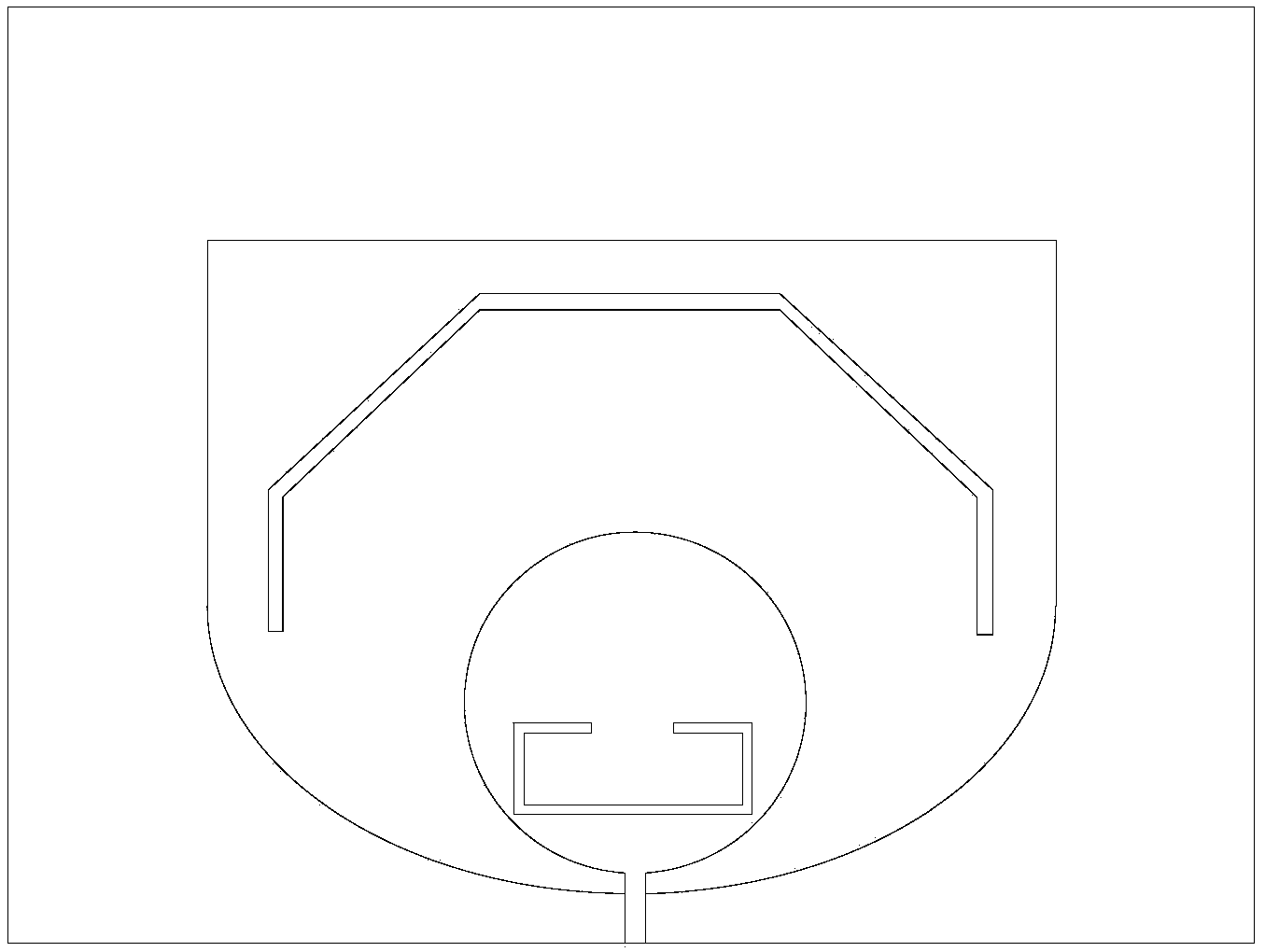
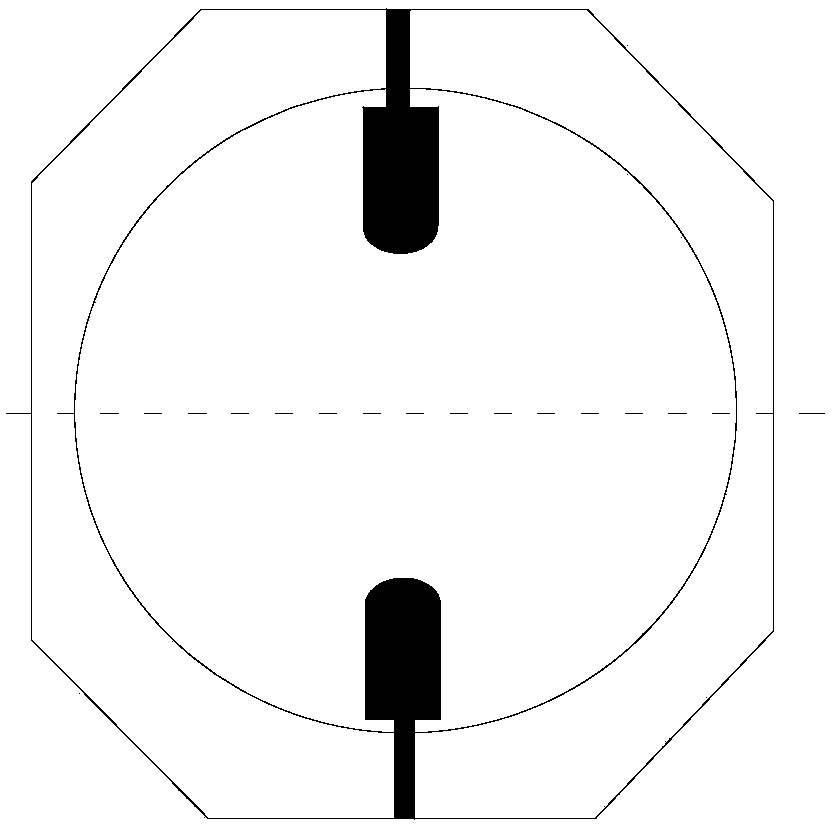
[0031] Such as Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, the differential coplanar waveguide UWB wide-slot trap antenna with high stopband characteristics of this embodiment includes a dielectric substrate, and the front side of the dielectric substrate is provided with a first feed circuit, a second feed circuit and a wide slot The ground structure 1, the first feeding circuit and the second feeding circuit are left and right symmetrical to form a differential coplanar waveguide feeding structure; the first feeding circuit includes a first feeding port 2, a first microstrip feeder 3, The first radiator 4 and the first via 5, the second feed circuit includes a second feed port 6, a second microstrip feeder 7, a second radiator 8 and a second via 9, the first The radiator 4 is connected to the first feeding port 2 through the first microstrip feeder 3, and the second radiator 8 is connected to the second feeding port 6 through the second microstrip feeder 7; the wide gap ground struct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com