Protein matrix vaccine compositions including polycations
A protein matrix and polycation technology, applied in the field of protein matrix vaccines and vaccine administration, can solve problems such as complexity, production difficulties, and prevention of distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0171] Example 1: Vi-CRM197-αPLL PCMV
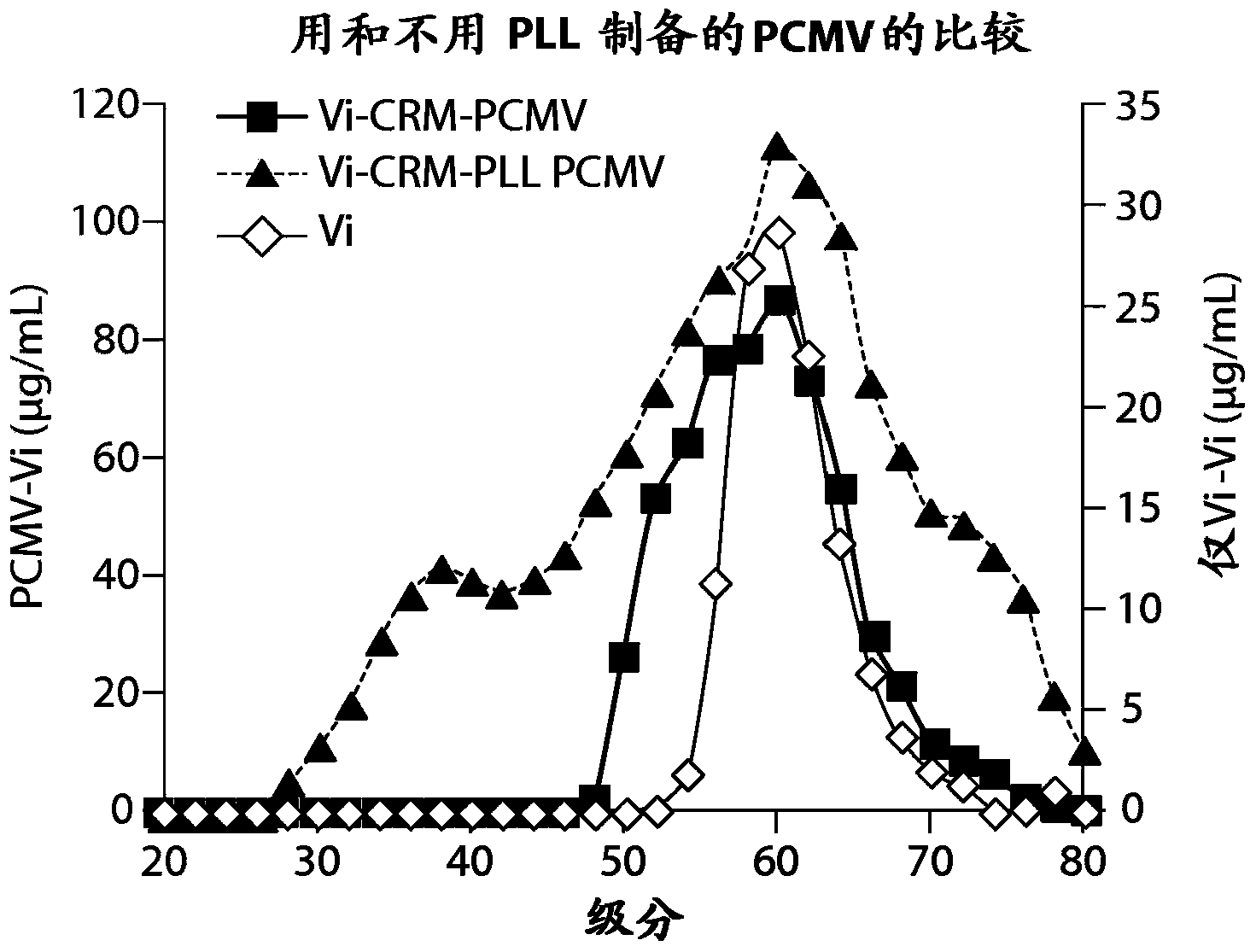
[0172] Use from Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi as antigen, use avirulent diphtheria toxin CRM197 as carrier protein (made in Matrivax Research and Development Corporation, Boston, MA, USA), and α-poly-L-lysine (Sigma- Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) as the polycation, investigated the effect of adding polycations to matrix vaccine compositions.
[0173] Vi is a highly anionic homopolymer composed of O-acetylated (α1-4)-D-GalANAc variable at C-3. One of the currently approved vaccines for typhoid fever is (Sanofi Pasteur SA) containing non-conjugated Vi polysaccharide as antigen. In the initial study, to test whether a protein matrix vaccine could be successfully used to deliver Vi antigen and elicit an immune response, PCMV was prepared in a reaction containing 4 mg / mL Vi as the antigen and 4 mg / mL CRM197 as the matrix-forming carrier protein . Matrix formation was initiated by adding glutaraldehyde as a crosslinker. After incubation...
Embodiment 2
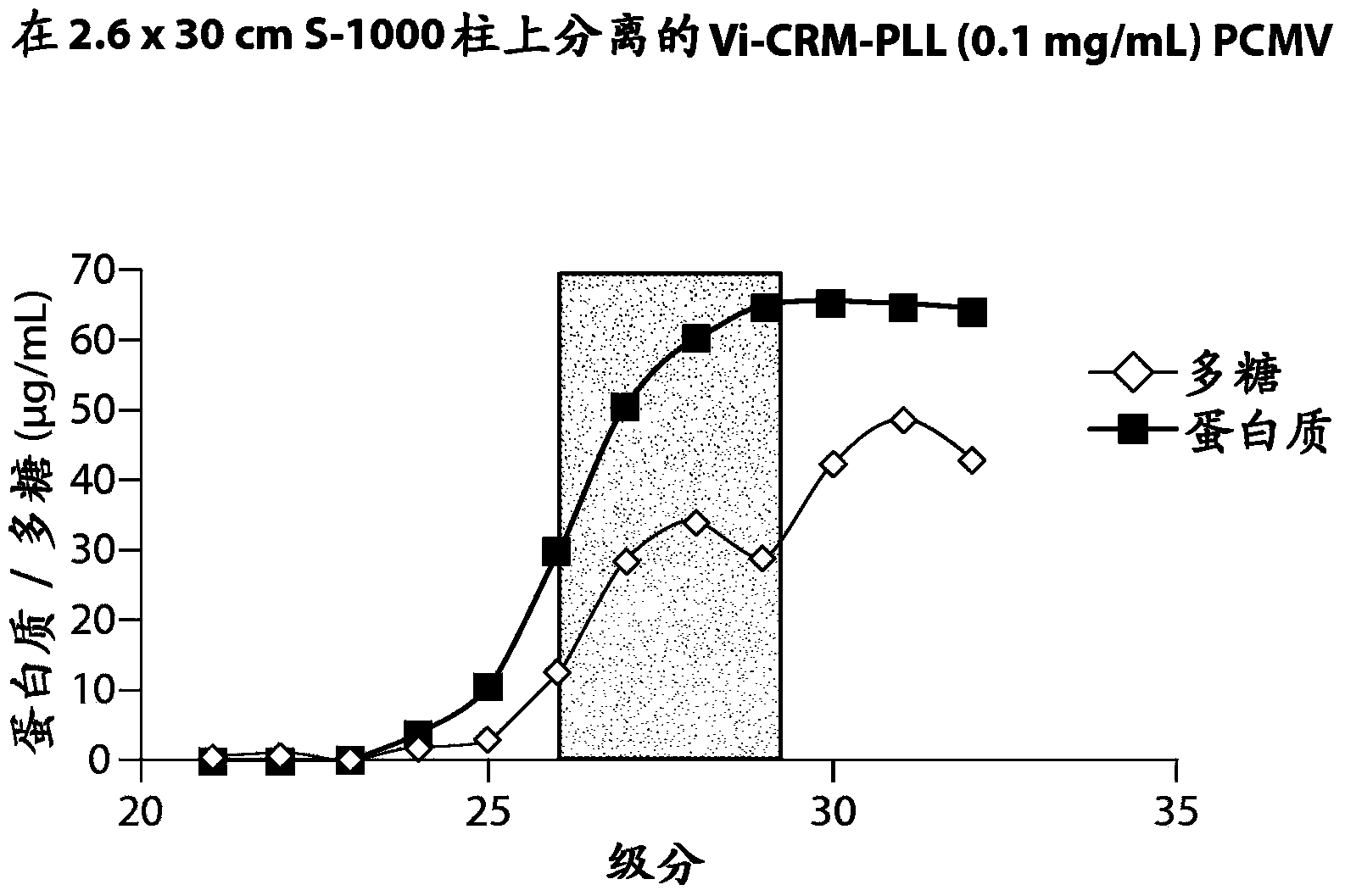
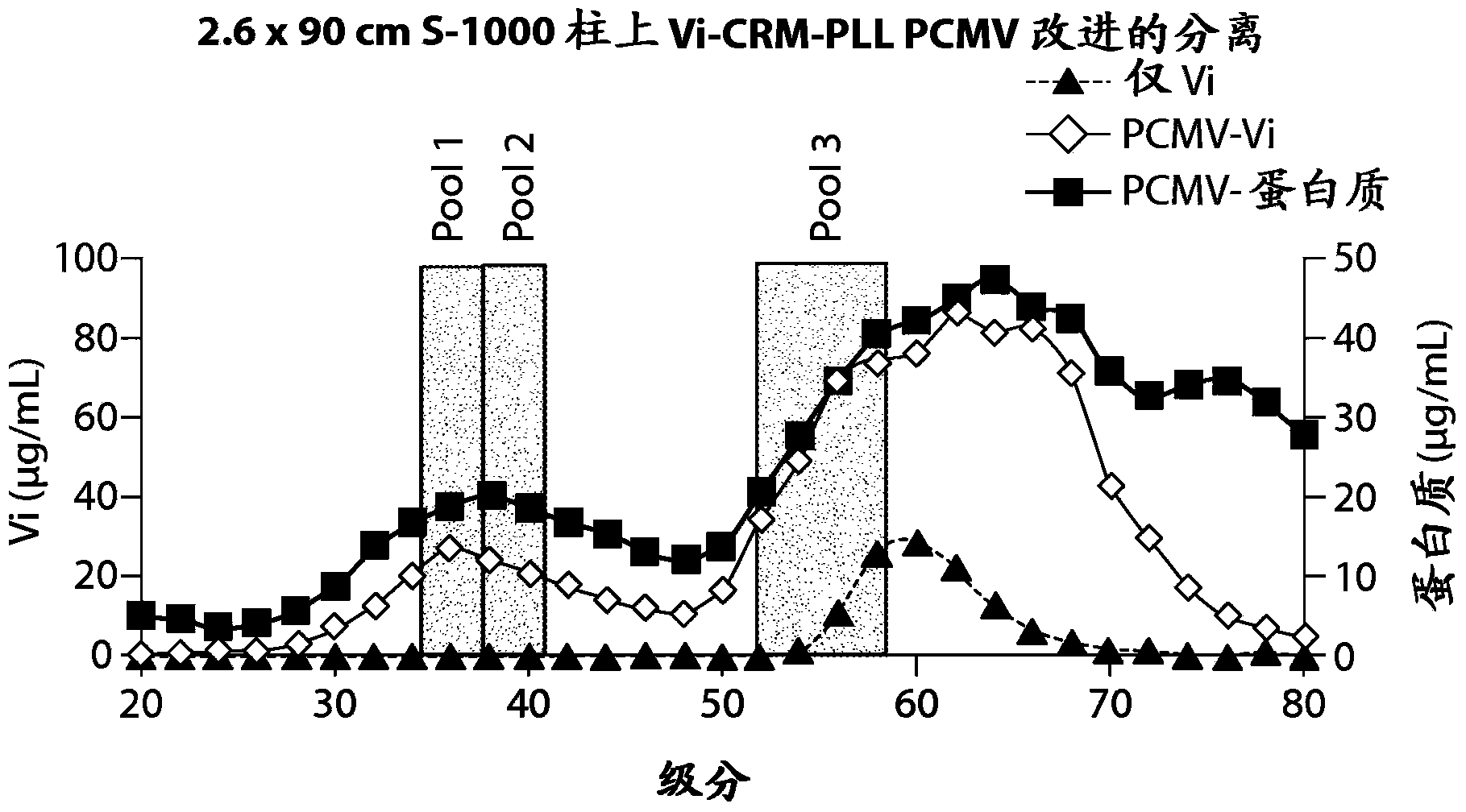
[0184] Example 2: Improved isolation of Vi-CRM197-αPLL PCMV
[0185] For better removal of low molecular weight species (presumably unentrapped, unconjugated antigen aggregates) from PCMV particles, a longer (90 cm) size exclusion column was used. Specifically, a PCMV crosslinking reaction mixture containing 4 mg / ml Vi, 4 mg / ml CRM197 and 0.01% α-poly-L-lysine (150-300 KDa) was prepared. Vi and αPLL were incubated for 15 min at room temperature with constant shaking before adding 0.25% glutaraldehyde and CRM197. Incubation was continued for an additional 10 minutes at room temperature with constant shaking, followed by 24 hours at 4°C with constant shaking. After separation of reaction products on SEC columns, protein and polysaccharide levels were determined by microBCA and stains-all assays, respectively. To determine whether the size or molecular weight of PCMV particles could affect its immunogenicity, fractions from 3 different elution points from the SEC column were ...
Embodiment 3
[0191] Example 3: PPS18C-CRM197-αPLL PCMV
[0192] In the case of improved Vi entrapment using α-PLL, we next tested whether α-PLL would improve entrapment of the less negatively charged pneumococcal polysaccharide PPS18C. Unlike Vi, where every sugar residue is negatively charged, PPS18C has only one negative charge for every five sugar residues. However, inclusion of 0.04% α-PLL (15–30 kDa) in the PCMV reaction resulted in a 35% shift of the polysaccharide from the lower molecular weight to the higher molecular weight fraction upon SEC separation ( Figure 4 ). Most of the CRM197 present in the PCMV reactions also co-localized with the high molecular weight fraction. It was shown by using a capture ELISA assay that the polysaccharides present in the high molecular weight fraction were all captured in the PCMV particles, which were bound to the ELISA plate by an anti-CRM197 antibody, and the polysaccharides were detected using serotype-specific antisera (data not shown )...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com