Preparation method for novel magnetic chitosan composite microsphere antibiotic adsorbent
A technology of composite microspheres and chitosan, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal compounds, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problems of poor mechanical properties, low density, small and wide application, etc. Simple preparation process, high adsorption capacity, good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Fe 3 o 4 / HNTs complex synthesis;
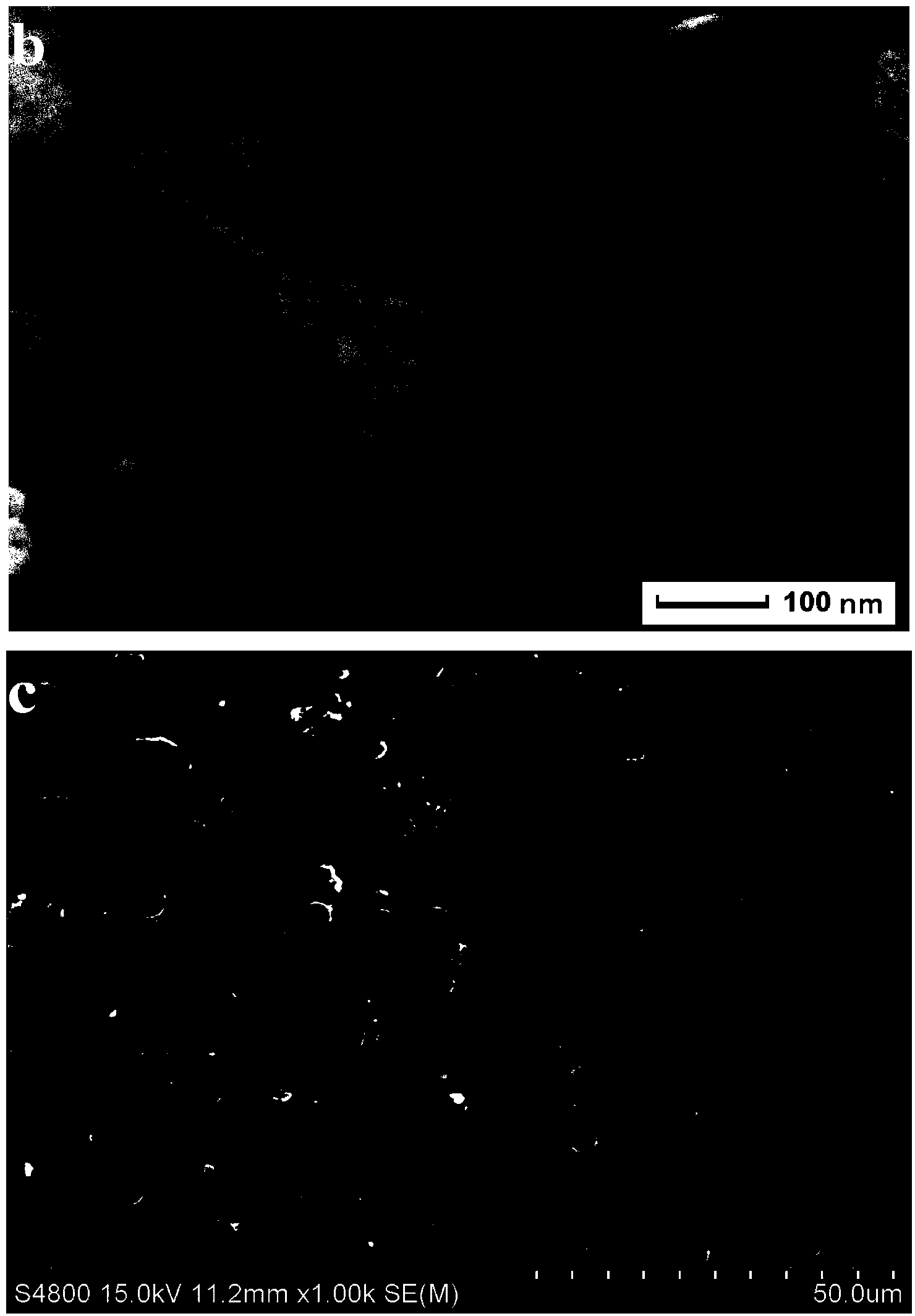
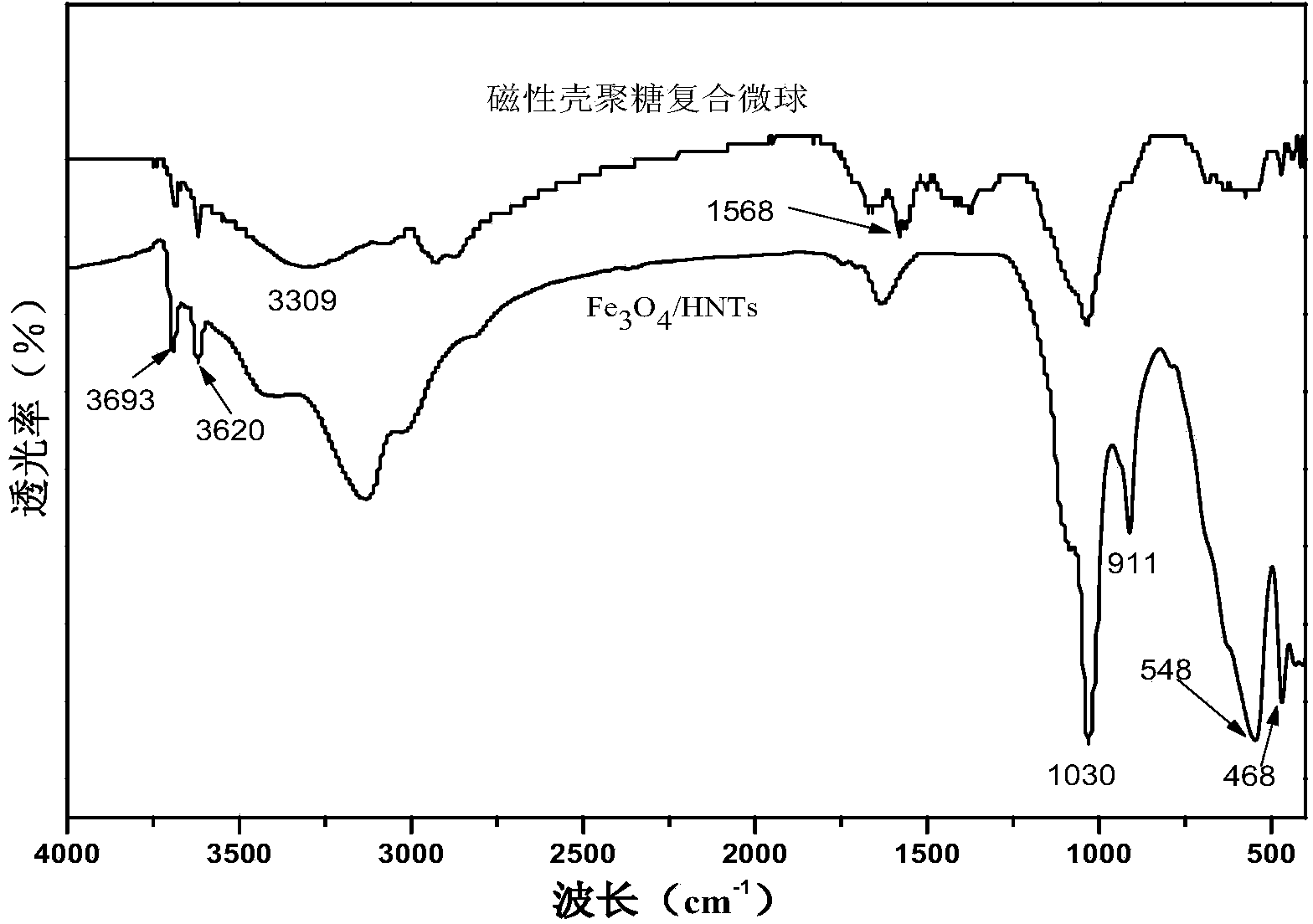
[0029] 4.77 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.35 g of halloysite nanotube powder were added to 138 mL of distilled water, and after ultrasonic dispersion for 30 min, mechanical stirring was continued for 3 h to obtain a stable suspension. Then in N 2 2.10 g FeCl under protection 2 4H 2 Add O to the above suspension, continue to stir the mixed solution vigorously for 30 minutes, then raise the temperature to 80°C, slowly add 10-15 mL of concentrated ammonia water, and react for 0.5-1.0 h under vigorous stirring, and permanently remove the black product with Nd-Fe-B Magnet separation, the product is fully washed with distilled water until neutral, vacuum dried at 50-60°C to obtain Fe 3 o 4 / HNTs complex; Figure 1-4 Characterization of physical and chemical properties of magnetic chitosan composite microspheres.
[0030] (2) Preparation of novel antibiotic adsorbents with magnetic chitosan composite microspheres;
[0031] 0.50 g of...
experiment example 1
[0036] Take 20 ml for an initial concentration of 100 mg L -1 The tetracycline solution was added to the colorimetric tube, and 20 mg of magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent was added, and the test solution was placed at 25 o Stand in the water bath of C for 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 and 80 min, respectively. After the standing time is completed, the supernatant is separated and collected by Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets, and the concentration of unadsorbed tetracycline molecules is measured by an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, and the adsorption capacity is calculated according to the results. Figure 5 It shows that the magnetic chitosan composite microspheres have good adsorption kinetics, and the adsorption equilibrium is basically reached within 80 minutes, and the adsorption rate is fast.
experiment example 2
[0038] Take 20ml and the initial concentration is 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, 180, 200 mg L -1 The tetracycline solution was added to the colorimetric tube, and 20 mg magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent was added respectively, and the test solution was placed at 25 o After standing in a water bath of C for 3.0 h, the supernatant was separated and collected by a Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet, and the concentration of unadsorbed tetracycline molecules was measured by a UV-visible spectrophotometer, and the adsorption capacity was calculated based on the results. Image 6 As shown, the saturated adsorption capacity of the magnetic chitosan composite microsphere adsorbent is 38.76 mg g -1 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com