Simulation method of real-time embedded system
A technology of embedded system and simulation method, which is applied in the cross field of software engineering, model-driven engineering and system simulation, and can solve problems such as finding no solution and affecting software complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
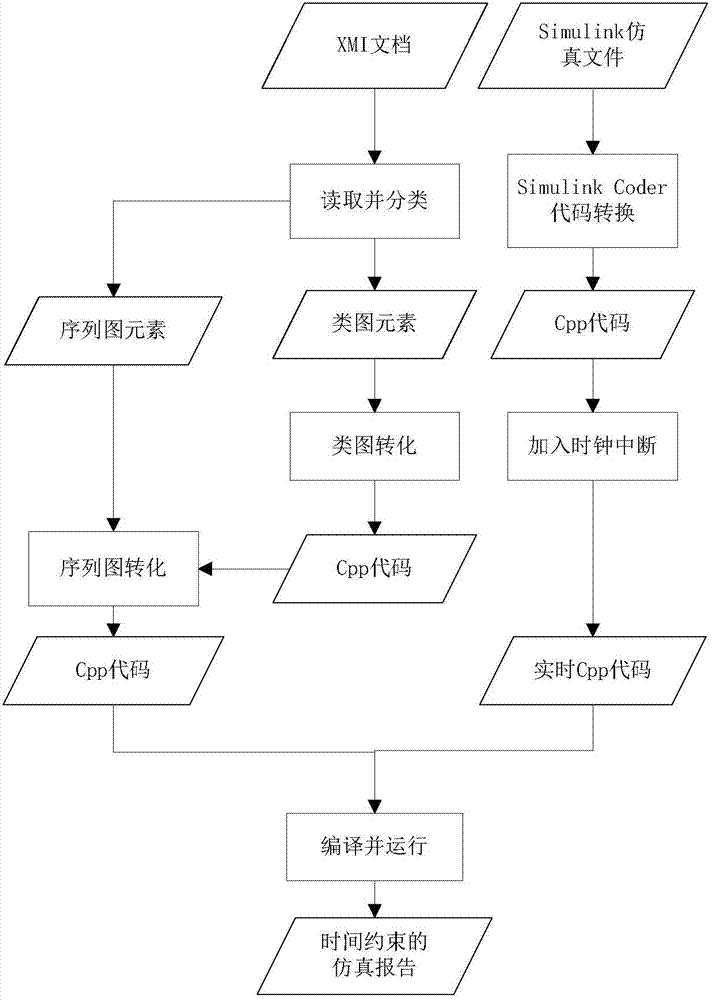
[0065] Combine below figure 1 Specific embodiments of the present invention are described in more detail.
[0066] 1. Reading and conversion
[0067] Use the XmiReader class in org.eclipse.xtend.typesystem.emf to read XMI documents. Use Xpand for model-to-code conversion. Xpand started out as part of the openArchitectureWare project before becoming a component of Eclipse. Xpand is a statically typed templating language. It has the following features: polymorphic calling templates, aspect-oriented programming, functional extensions, a flexible type system abstraction, model conversion, model verification, etc.
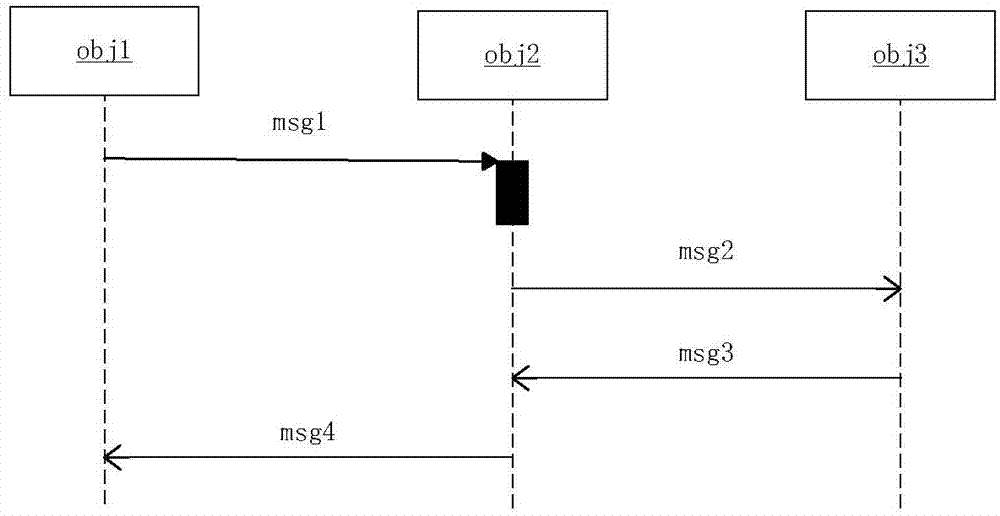
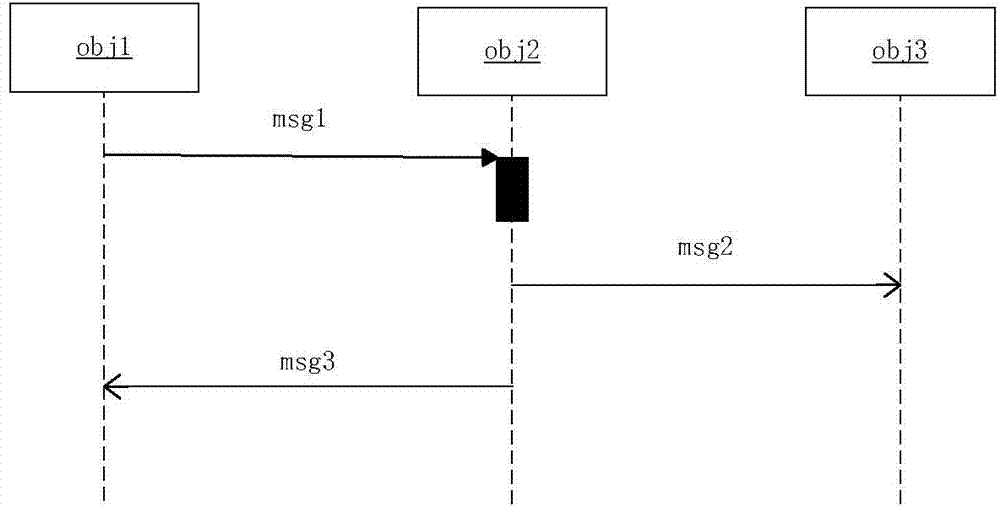
[0068] Second, the conversion class diagram
[0069] In the specific implementation, two versions (Stereotype) will be provided: >、>, at most one operation of one of the applications and classes can be used. A codeSegment attribute in > is used as the specific code of the current operation, targetName is used to specify the file location that implements...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com