OLED displays fabricated by inkjet printing
An organic electronic device and a manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of OLED devices, can solve the problems of increasing processing time, increasing processing time, etc., to achieve the effect of improving processing time and avoiding processing problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
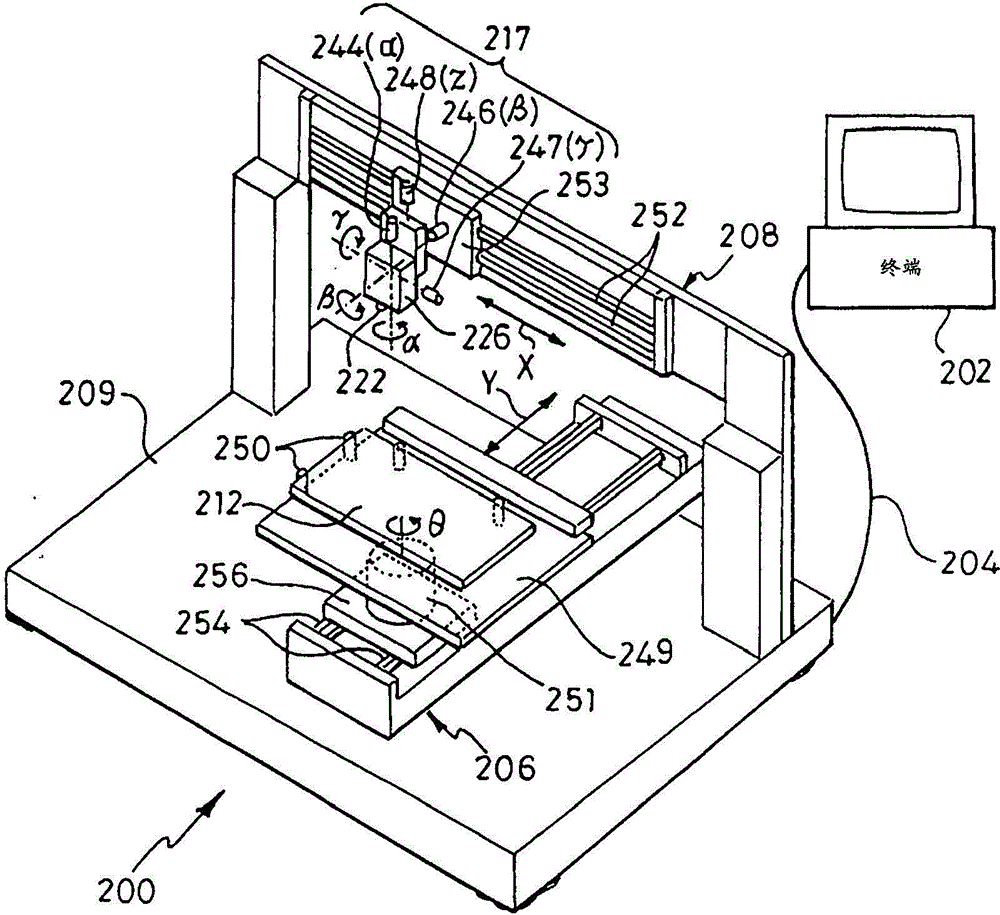
[0039] Examples of printers that we use for OLED fabrication are Litrex1408, Litrex142 and Litrex140P printers with Dimatix SX3 inkjet printheads (from Fujifilm Dimatix Inc.). Typically, the printhead prints successive swaths, say in the Y direction, stepping in the X direction between each swath. Optionally, the printhead can assume an angle Φ with respect to the X direction to reduce the dot pitch by a factor of cos Φ.
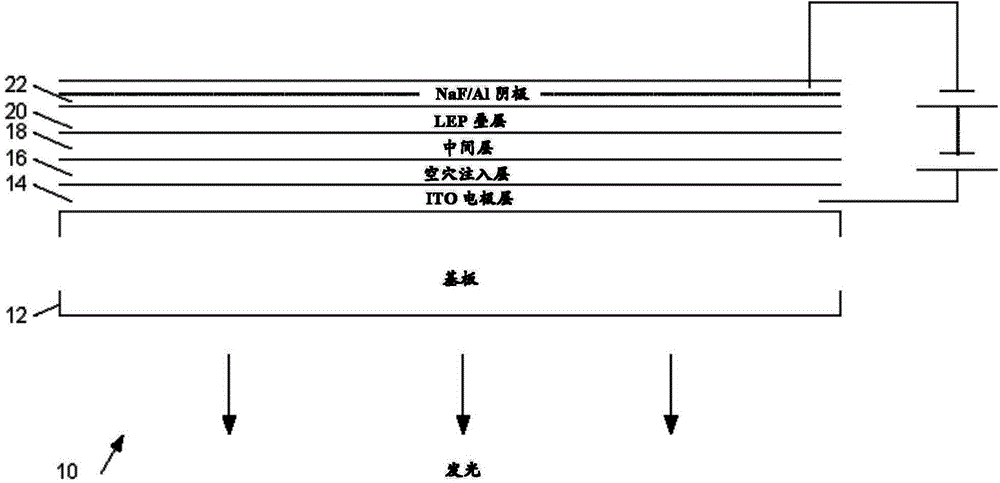
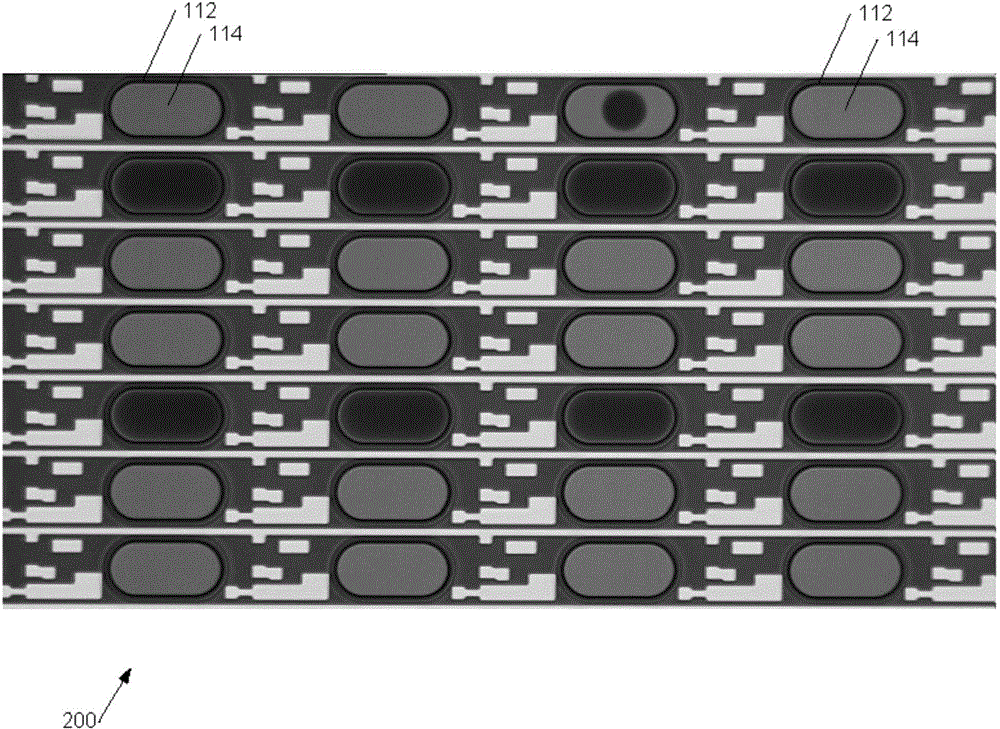
[0040] Figure 3a The passage of the scan head 222 over several pixels of a portion of a color OLED display is shown. The figure schematically represents the deposited droplets within a "polo" shaped annular bank 112 . In the figure, the red (R), green (G) and blue (B) sub-pixels respectively have separate wells based on the anode metal 14 . By way of example only, in a small flat panel display a pixel may have a width of 50 μm and a length of 150 μm to 250 μm, say a 10 μm or 20 μm wide bank; in a larger display more suitable for applications such as colo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com