Dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image tensor domain non-local mean denoising method
A magnetic resonance image, non-local mean technology, applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of noise effects of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
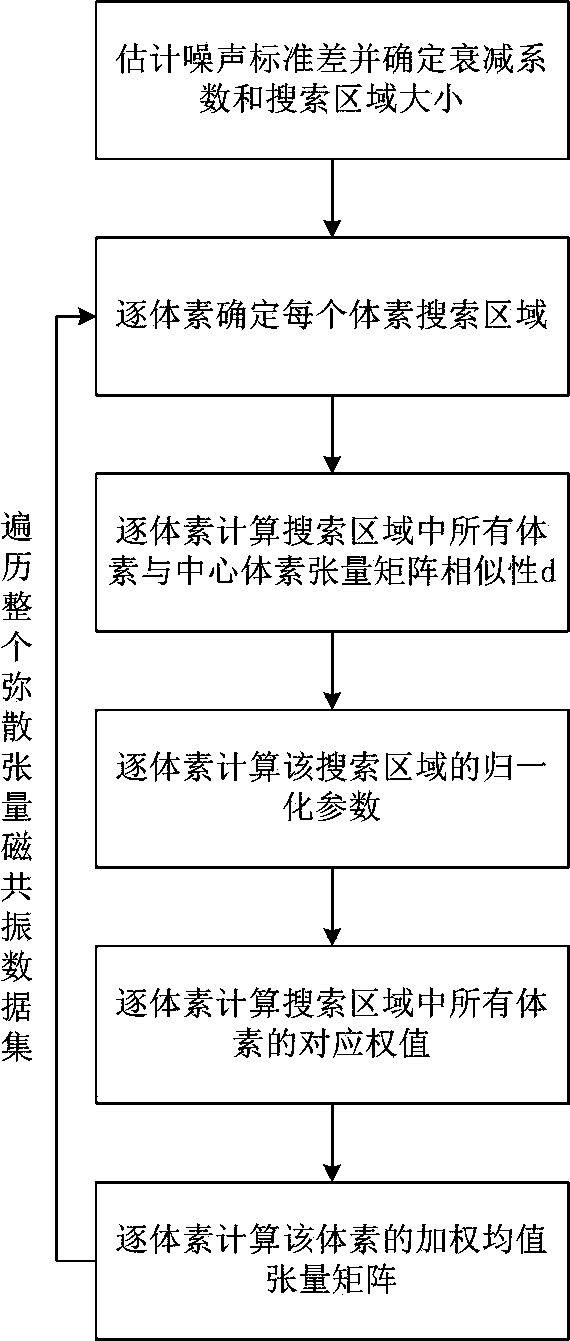
[0047] Step 1: In the background area, calculate the grayscale histogram of the background area, and use the Gaussian function to fit the grayscale histogram, determine the noise standard deviation according to the variance of the Gaussian function, and set the attenuation coefficient h to 1.2 times the noise standard deviation , the search area radius Ω is 10% of the larger value of the entire image length compared to its width.
[0048]Step 2: According to the noise standard deviation, attenuation coefficient h and search area radius Ω, traverse all voxels in the diffusion tensor magnetic resonance image dataset with a resolution of 128 rows, 128 columns and 53 layers in turn, and use each voxel traversed As the center, set a square search area Q with a radius of Ω, and the square search area Q is a cube with 13 rows, 13 columns and 13 floors.
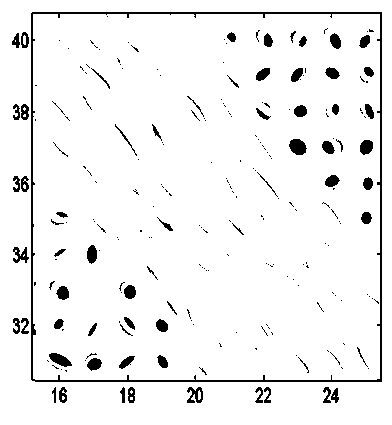
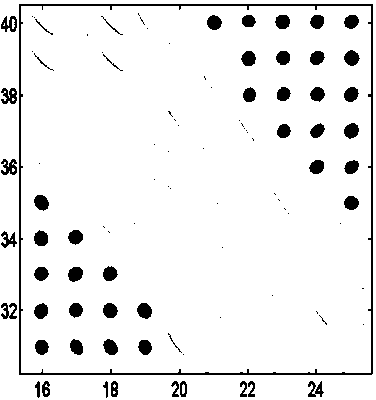
[0049] Step 3: Compare all voxels in the square search area Q with the central voxel in turn for tensor matrix similarity, and use ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Step 1: In the background area, calculate the grayscale histogram of the background area, and use the Gaussian function to fit the grayscale histogram, determine the noise standard deviation according to the variance of the Gaussian function, and set the attenuation coefficient h to 1.2 times the noise standard deviation , the search area radius Ω is 10% of the larger value of the entire image length compared to its width.
[0063] Step 2: According to the noise standard deviation, attenuation coefficient h and search area radius Ω, traverse all voxels in the diffusion tensor magnetic resonance image dataset with a resolution of 128 rows, 128 columns and 53 layers in turn, and use each voxel traversed As the center, set a square search area Q with a radius of Ω, and the square search area Q is a cube with 13 rows, 13 columns and 13 floors.
[0064] Step 3: Compare all voxels in the square search area Q with the central voxel in turn for tensor matrix similarity, and use...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Step 1: In the background area, calculate the grayscale histogram of the background area, and use the Gaussian function to fit the grayscale histogram, determine the noise standard deviation according to the variance of the Gaussian function, and set the attenuation coefficient h to 1.2 times the noise standard deviation , the search area radius Ω is 10% of the larger value of the entire image length compared to its width.
[0077] Step 2: According to the noise standard deviation, attenuation coefficient h and search area radius Ω, traverse all voxels in the diffusion tensor magnetic resonance image dataset with a resolution of 128 rows, 128 columns and 53 layers in turn, and use each voxel traversed As the center, set a square search area Q with a radius of Ω, and the square search area Q is a cube with 13 rows, 13 columns and 13 floors.
[0078] Step 3: Compare all voxels in the square search area Q with the central voxel in turn for tensor matrix similarity, and use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com