SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marking method related to color character of Ulmus pumila cv.jinye. and application thereof
A Chinese golden leaf elm, molecular marker technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., to achieve accurate results, guaranteed accuracy, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
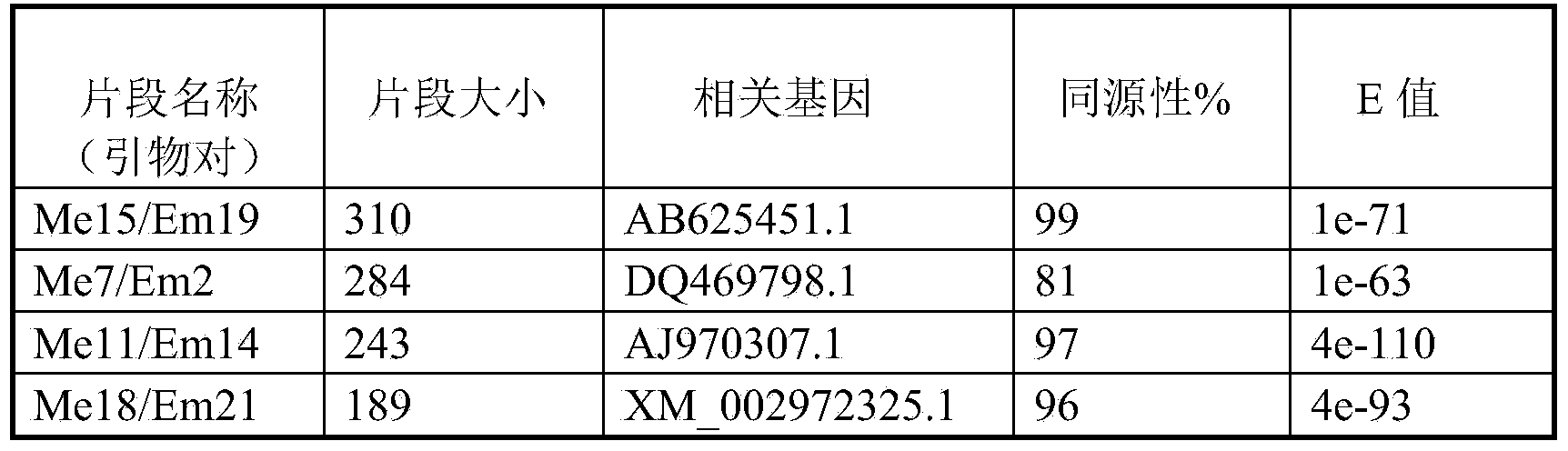
[0029] Example 1: Primer screening of SRAP molecular markers related to leaf color traits of Ulmus chinensis
[0030] The Ulmus sinensis used in this example was purchased commercially.
[0031] 1. Leaf collection and leaf color calibration of different leaf colors of Ulmus sinensis:
[0032] Select 10 healthy and healthy Ulmus sinensis plants of the same tree age, respectively numbered 1 to 10, the leaf color calibration adopts the international color standard color palette comparison, select healthy young leaves with the same color value, and collect #FFD700 golden leaves from each plant and #228B22 forest green leaves, immediately sealed and stored at low temperature;
[0033] 2. Extract the total RNA from #FFD700 golden leaves and #228B22 forest green leaves on each Ulmus sinensis plant respectively. The extraction method of total RNA adopts the modified Trizol method, and the specific method is as follows:
[0034] A. Take 0.2g of Ulmus chinensis leaves, remove the peti...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: According to the SRAP molecular marker system related to leaf color traits of Ulmus chinensis in Example 1, identify Ulmus chinensis with different leaf colors.
[0060] figure 1 It is the amplification result of the two traits of yellow leaves and green leaves by the primer pair Me15 / Em19, wherein Y1-Y5 is a yellow leaf plant, YMix is a mixed cDNA pool composed of Y1-Y5, G1-G4 is a green leaf plant, GMix is a mixed cDNA pool composed of G1-G4. The two kinds of leaf colors can be well distinguished by the SRAP molecular marker method of the present invention. The method of the invention has good repeatability, good polymorphism, clear bands and low background.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com