Light emitting device
A light-emitting device and a technology of light-emitting diodes, which are applied in the direction of lighting devices, light sources, and components of lighting devices, can solve problems such as open circuit or leakage current, locking screws and electrode arc effects, and use safety concerns, so as to prevent arc effects , Improve the number of high-voltage tests passed, and avoid short-circuit effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
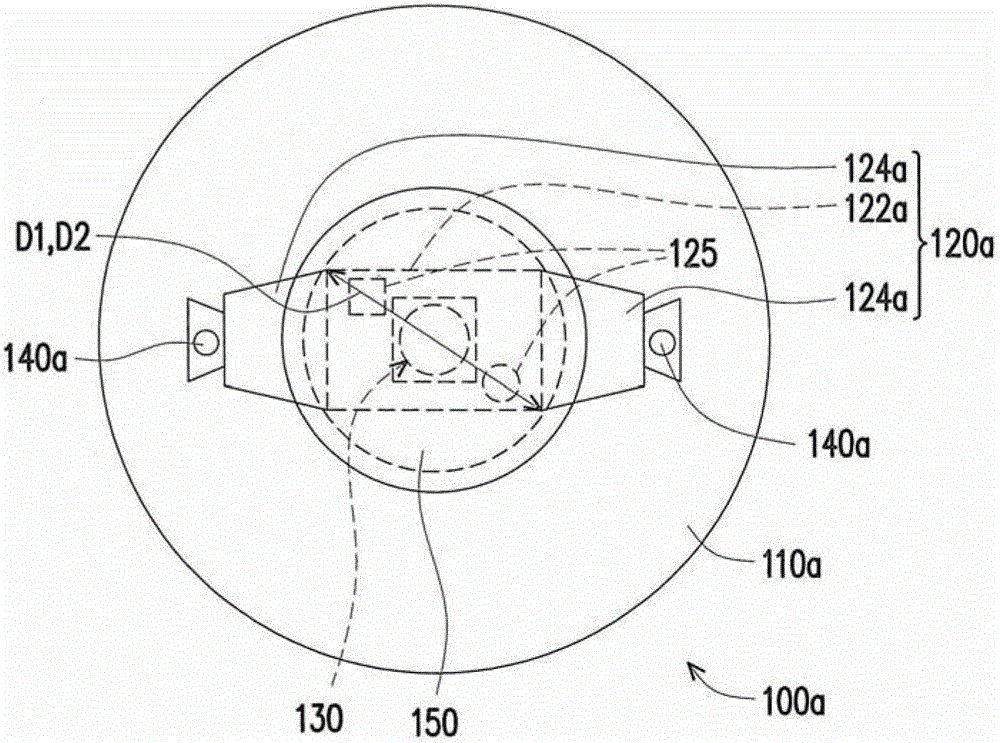
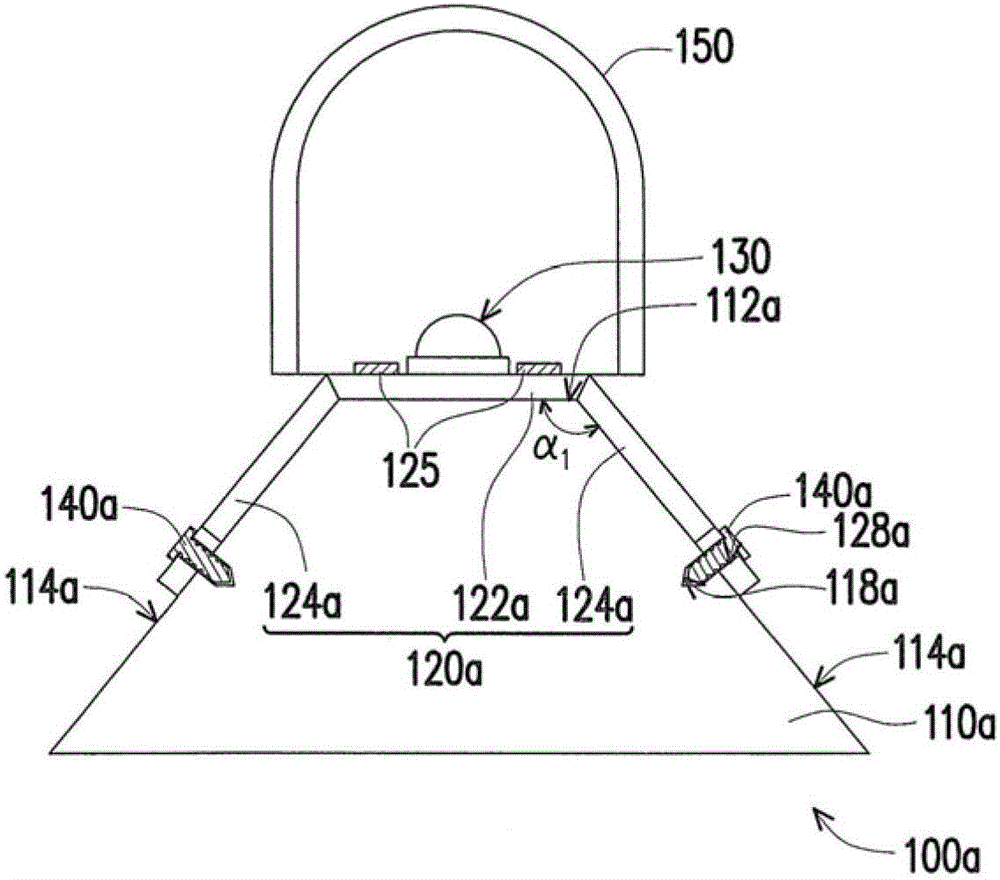
[0039] figure 1 It is a schematic top view of a light emitting device according to an embodiment of the present invention. figure 2 for figure 1 A schematic cross-sectional view of the light-emitting device shown. Please also refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , in this embodiment, the light emitting device 100a includes a carrier 110a, a substrate 120a, at least one electrode pair 125 ( figure 1 and figure 2 A pair is schematically shown in), at least one light emitting diode 130 ( figure 1 and figure 2 One is schematically shown in ) and at least one positioning member 140a ( figure 1 and figure 2 Two are schematically shown in ).
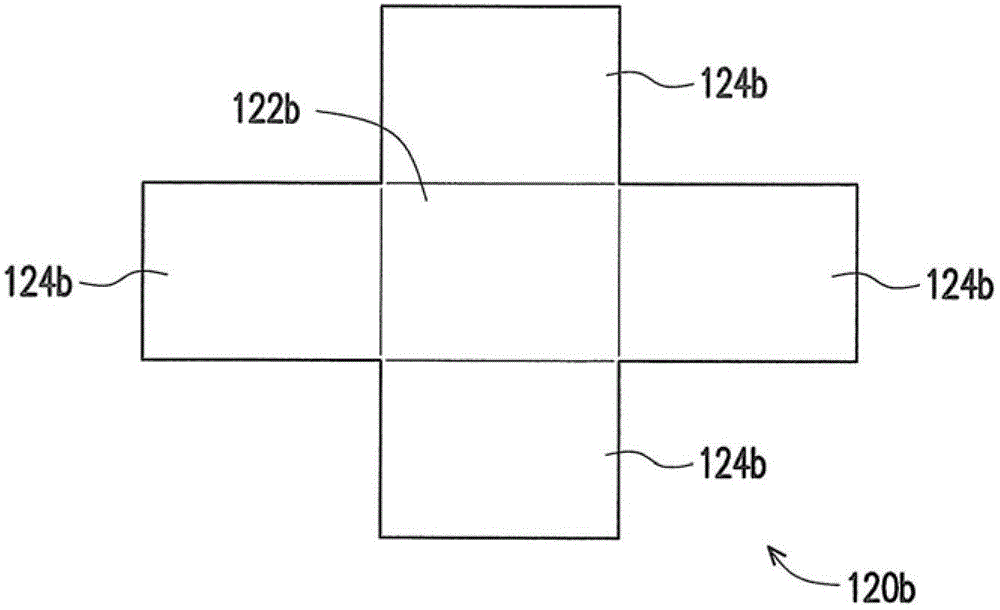
[0040] In detail, the substrate 120a is disposed on the carrier 110a, and has a body portion 122a and at least one bending portion 124a ( figure 1 Two are schematically shown in ), wherein the bent portion 124a is connected to the body portion 122a. In particular, the bent portion 124a is not coplanar with the body portion 122a. The ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com