Broad spectrum monoclonal antibody for identification of influenza virus hemagglutinin protein HA1 structural domains
A monoclonal antibody, hemagglutinin protein technology, applied in the direction of antiviral immunoglobulins, antibodies, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problem that the neutralization activity is limited to a few strains of each subtype.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: Preparation of anti-H1 subtype influenza virus HA monoclonal antibody (mAb)
[0088] (1) Preparation of virus:
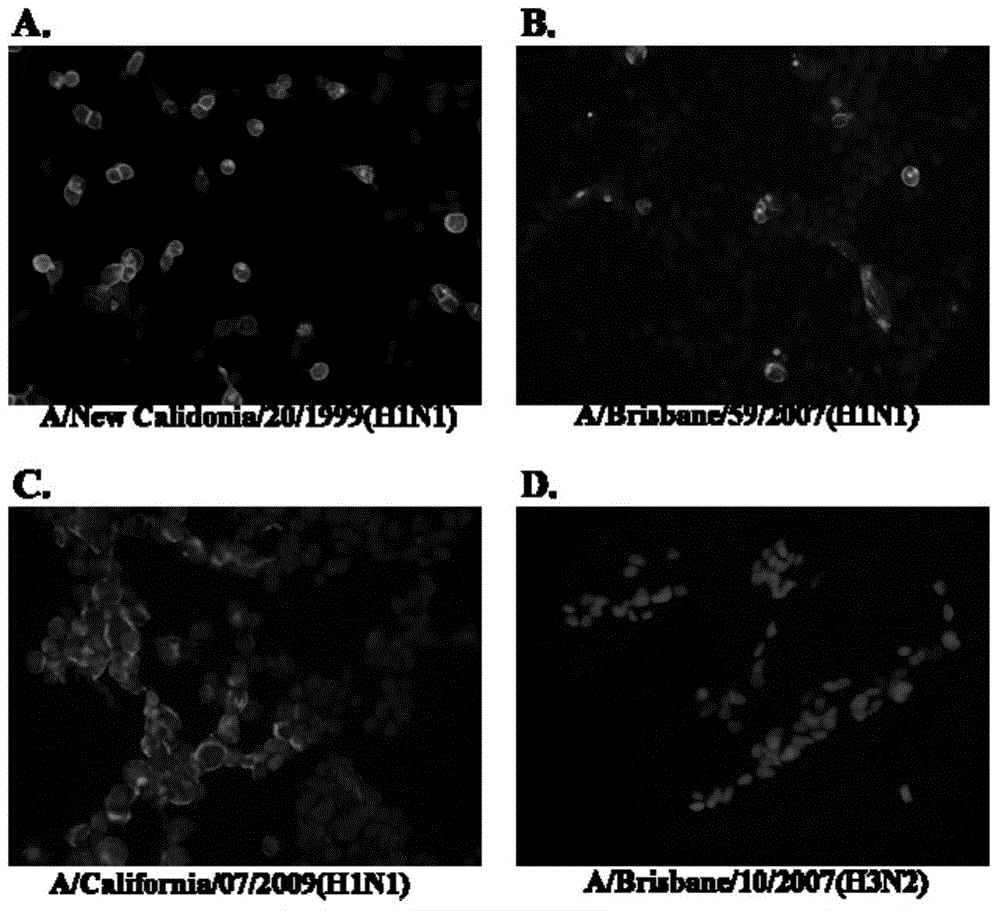
[0089] Three seasonal H1N1 influenza virus strains A / New Calidonia / 20 / 1999 (H1N1), A / Xiamen / 3118 / 2006 (H1N1), A / Xiamen / N585 / 2009 (H1N1), a new influenza A H1N1 Virus strain A / California / 04 / 2009 (H1N1) was inoculated into MDCK cells, and after incubation at 37°C for 2 days, the supernatant was collected to obtain the amplified virus. Collect the live virus and inactivate it with 0.03% formalin at 4°C. The inactivated virus is detected by HA to determine the titer of the inactivated virus solution (Note: For the specific methods of HA titer determination and HI detection, refer to WHO operation Guide, A / California / 04 / 2009 was donated by the Department of Microbiology, University of Hong Kong, A / New Calidonia / 20 / 1999, A / Xiamen / 3118 / 2006, A / Xiamen / N585 / 2009 are all strains preserved in our laboratory).
[0090] (2) Experimental mice:
[0091] 6-week...
Embodiment 2
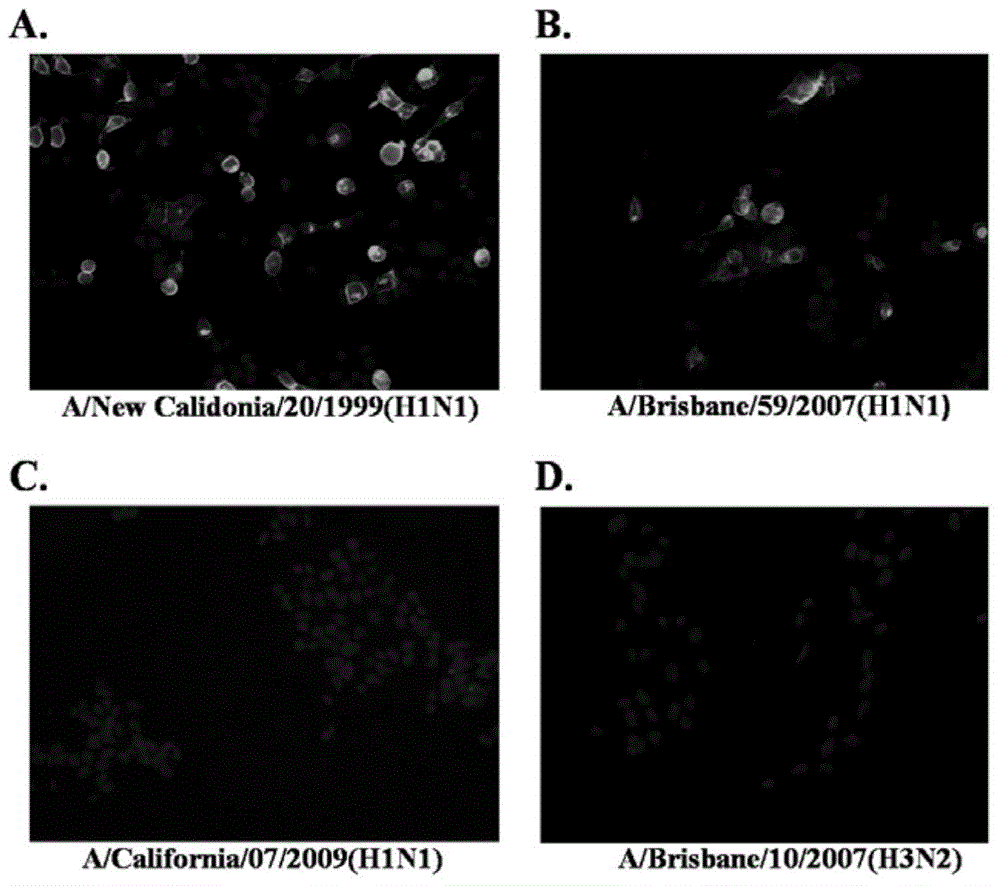
[0106] Example 2: The hemagglutination inhibition test method identifies the broad-spectrum reactivity of the H1 / H5 subtype hemagglutinin broad-spectrum monoclonal antibody
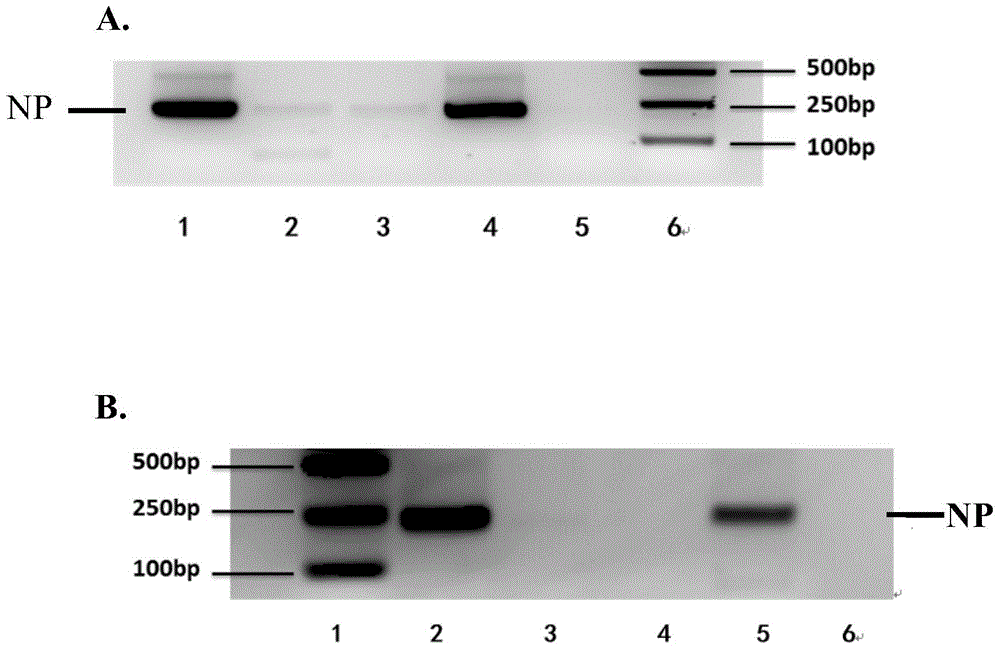
[0107] Select representative strains of seasonal H1N1 influenza virus, representative strains of new type A H1N1 influenza virus, representative strains of highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus and representative strains of seasonal H3N2 influenza virus isolated from different times, different regions, and representing different mutation types, The cross-reactivity of the monoclonal antibody ascites of the above 25 monoclonal antibody strains to different H subtype influenza viruses was identified by hemagglutination inhibition assay (HI). According to the reactivity of mAbs with various influenza virus strains, three broad-spectrum mAbs across H subtypes, 12H5, G10D10, and 8F11, which can simultaneously recognize H1 and H5 subtype influenza viruses, were identified (Table 1). Monoclonal antibody 1...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3. Microwell cell neutralization assay method to identify broad-spectrum neutralization activity (Neutralization titer) of broad-spectrum monoclonal antibody across H1 / H5 subtype hemagglutinin
[0113] Neutralizing activity is an important indicator to evaluate whether a monoclonal antibody has therapeutic potential. The neutralization activity of the monoclonal antibodies 12H5, G10D10 and 8F11 against H1N1 and H5N1 subtype influenza virus representative strains was detected by microwell cell neutralization assay (Hulse-Post et al., PNAS.2005, 102:10682-7), and the results (Table 2) shows that the results of the neutralization test of monoclonal antibodies are basically consistent with the results of the hemagglutination inhibition test, and the three monoclonal antibodies (12H5, G10D10 and 8F11) all have broad-spectrum cross-neutralizing activities against H1N1 and H5N1 viruses.
[0114] Table 2 Neutralization test activity of broad-spectrum monoclonal antibody...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com