Video compression method and system
A video compression and video signal technology, applied in digital video signal modification, electrical components, image communication, etc., can solve the problems of difficult pixel-level video real-time transmission, poor image effect, complex compression algorithm, etc., to simplify complexity, data The effect of reducing the volume, reducing the amount of data and the complexity of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] This embodiment provides a video compression processing method suitable for real-time sharing of Wi-Fi wireless networks, focusing on low-complexity real-time video signal compression, and the signal source of the video signal can be a small terminal device such as a smart phone or a tablet computer. video signal. In the transmission and processing of pixel-level video signals, the biggest problem is how to solve the problem of "moving" pixel-level high-definition video information of 2.8Gbps per second or higher resolution pixel-level video information above 2.8Gbps from one end of the network to the other. one end of the problem. For the current commonly used network bandwidth, a general-purpose 150M wireless network is not up to the job.
[0060] The purpose of the video compression method in this embodiment is to compress the obtained high-definition video signals so that they can adapt to the current Wi-Fi wireless network conditions after compression, such as the...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A video compression system implementing the above video compression method is provided in this embodiment, including:
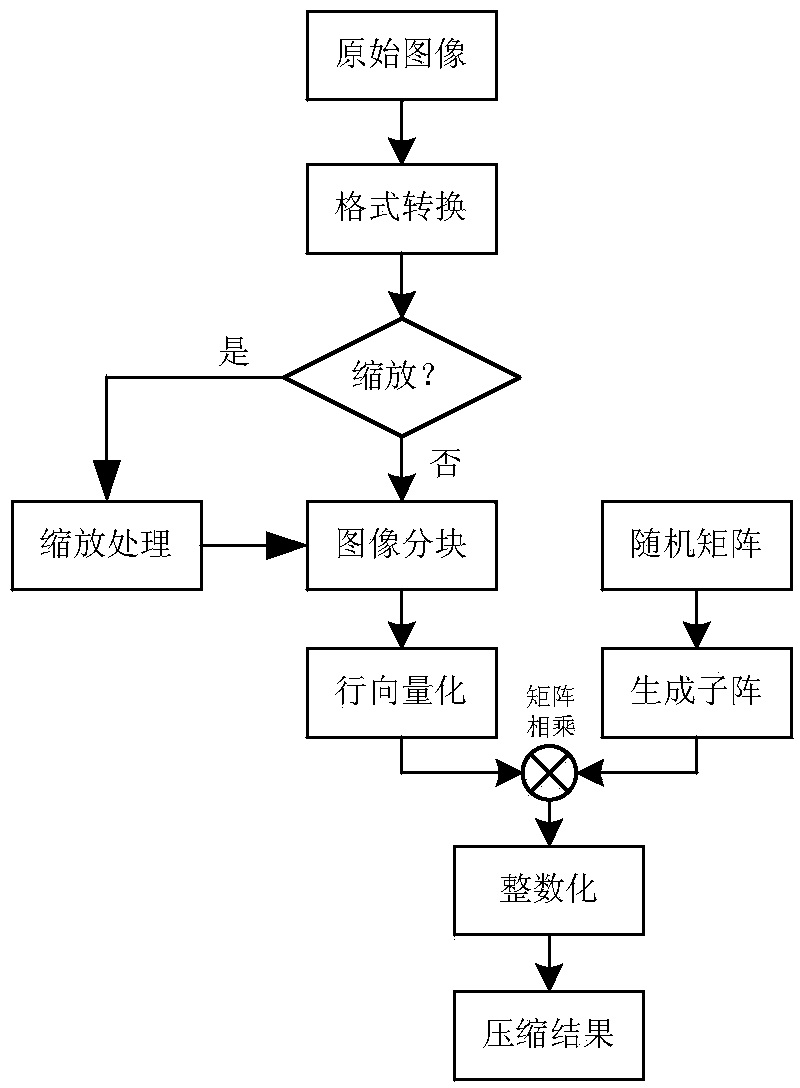
[0069]Format conversion module: obtain the format of the original video signal, and convert the original video signal of the non-YUV format into a video signal of the YUV format; Image block module: process the YUV video signal into blocks respectively to obtain image sub-blocks, wherein The size of the rows and columns of the sub-blocks of the U and V component images is half of the size of the rows and columns of the sub-blocks of the Y component image.
[0070] Row vectorization module: change the form of the image sub-blocks from the image sub-block matrix form to the row vector form according to the row scanning order, and the current line and the next line end-to-end, to obtain the row vector image sub-blocks.
[0071] Scaling judging module: judge whether the data volume of the video signal in the YUV format is greater than a preset threshold, i...
Embodiment 3
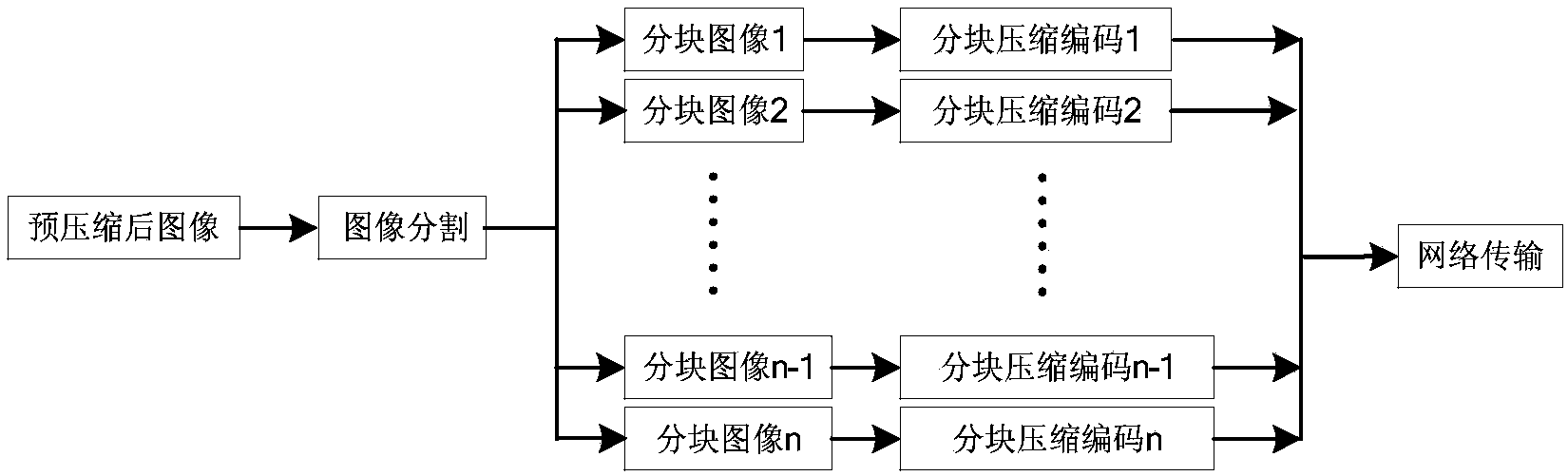
[0077] In this embodiment, a specific scaling example is provided. For a video signal with a resolution of 320x24060Hz, the amount of data I required for real-time transmission is 320x240x60x24bit / s or 110592000bit / s, although it can be realized under the current IEEE802.11n wireless network conditions The requirement for real-time transmission of a single video image signal, but a challenge for the parallel transmission of multiple video image signals.
[0078] The specific implementation steps of the video scaling method in this embodiment are as follows:
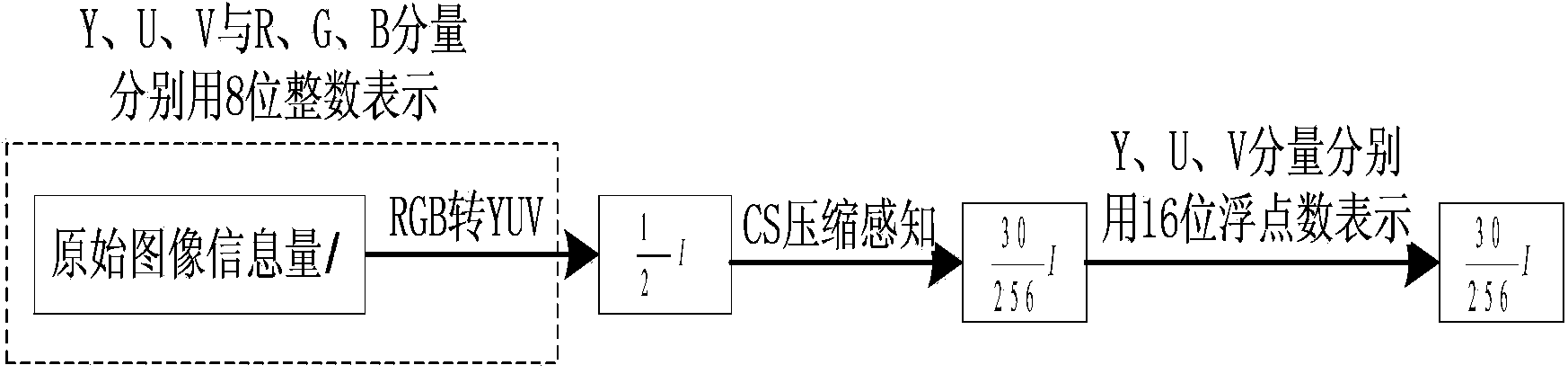
[0079] Step 1: Convert RGB format to YUV format. After format conversion, the amount of information I of the original video data is reduced to The video information is reduced to half of the original. In order to reduce the data volume and calculation complexity of image processing, the RGB format video signal is converted into YUV420 format before compression. Every 4 Y share a set of UV components. When compressing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com