Electrostatic protection circuit
An electrostatic protection and circuit technology, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, circuits, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of MOS transistor malfunction and poor internal circuit operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach )
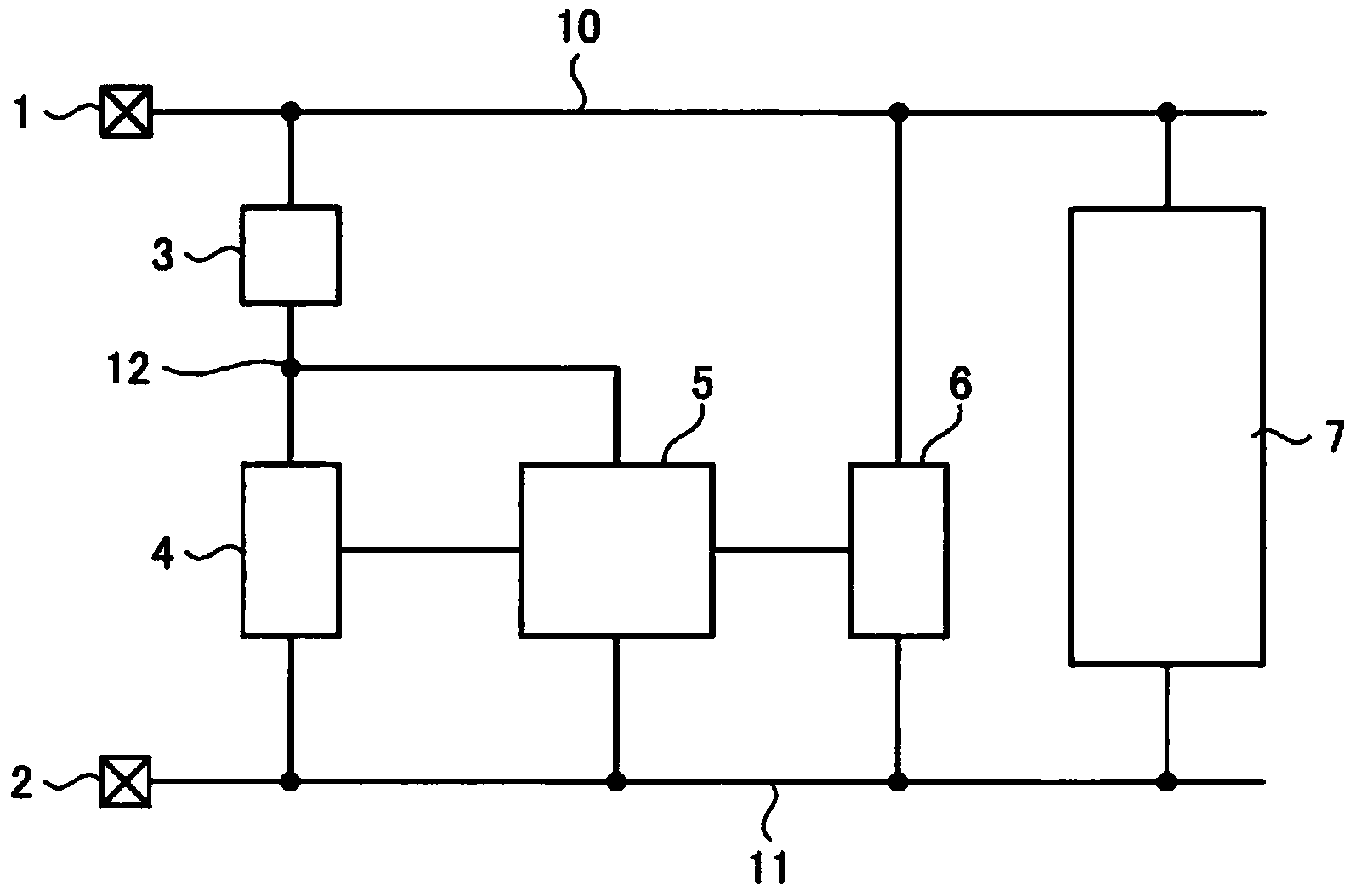
[0028] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the electrostatic protection circuit of 1st Embodiment. The electrostatic protection circuit of this embodiment has a clamp circuit 3 , a trigger circuit 4 , a snubber circuit 5 and a switch circuit 6 . The first power supply line 10 is connected to the first power supply terminal 1 , and applies, for example, a predetermined power supply voltage VCC to the first power supply terminal 1 to which a high potential side power supply voltage is applied. The second power supply line 11 is connected to the second power supply terminal 2 and is supplied with a low potential side power supply voltage. For example, a ground potential is applied to the second power supply terminal 2 as a low potential side power supply voltage. A clamping circuit 3 is connected between the first power line 10 and the first connection point 12 . For example, when a positive ESD surge is applied to the first power supply terminal 1 relative to the second power...
no. 2 approach )
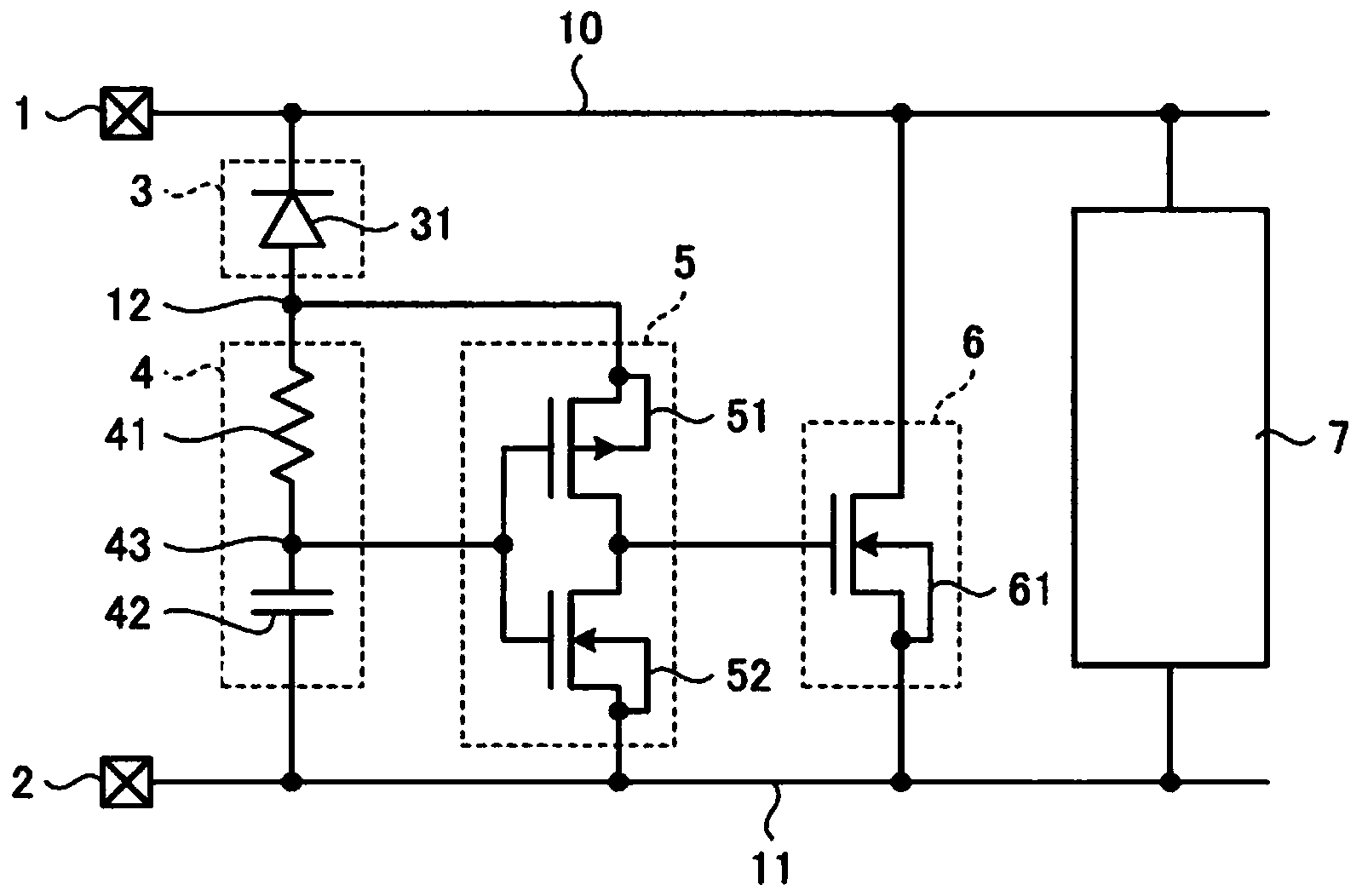
[0032] figure 2 It is a figure which shows the electrostatic protection circuit of 2nd Embodiment. Components corresponding to those of the first embodiment are assigned the same reference numerals, and description thereof will be omitted. In the present embodiment, the clamp circuit 3 has a diode 31 that is reverse-biased by the power supply voltage applied to the first power supply line 10 and the second power supply line 11 . The trigger circuit 4 connected between the first power line 10 and the first connection point 12 has a series circuit of a resistor 41 and a capacitor 42 . The common connection point 43 of the resistor 41 and the capacitor 42 becomes the output terminal of the trigger circuit 4 .
[0033] The buffer circuit 5 biased by the voltage between the first connection point 12 and the second power supply line 11 has a CMOS converter composed of a PMOS transistor 51 and an NMOS transistor 52 . The gate electrodes of the PMOS transistor 51 and the NMOS tran...
no. 3 approach )
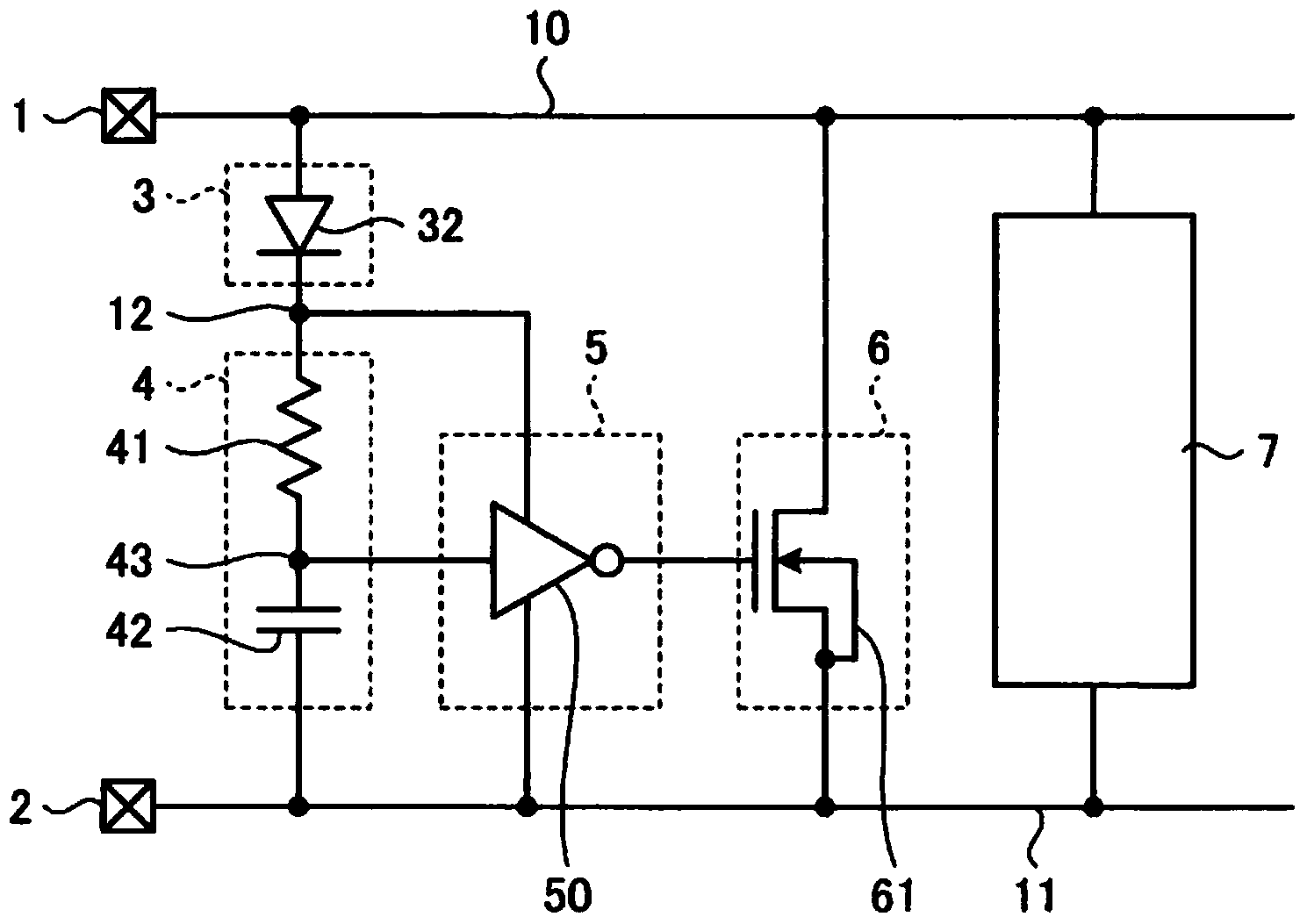
[0041] image 3 It is a figure which shows the electrostatic protection circuit of 3rd Embodiment. Components corresponding to the above-described embodiments are given the same reference numerals, and explanations thereof are omitted. In the electrostatic protection circuit of the present embodiment, the clamp circuit 3 connected between the first power line 10 and the first connection point 12 has the function of controlling the power supply voltage applied between the first power line 10 and the second power line 11. forward biased diode 32 . The common connection point 43 constituting the output terminal of the flip-flop circuit 4 is connected to the input terminal of the converter 50 constituting the buffer circuit 5 . The converter 50 is biased by the voltage between the first connection point 12 and the second power supply line 11 .
[0042] In a stable bias state where a predetermined power supply voltage is applied between the first power supply terminal 1 and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com