Method for degrading sulfonamide antibiotics in water through intensifying singlet oxygen with cationic sufactant
A surfactant and cationic technology, applied in the field of water pollution treatment, can solve the problems that cannot meet the requirements of removing residual antibiotics, achieve good potential and application prospects, fast and efficient removal, and good oxidation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
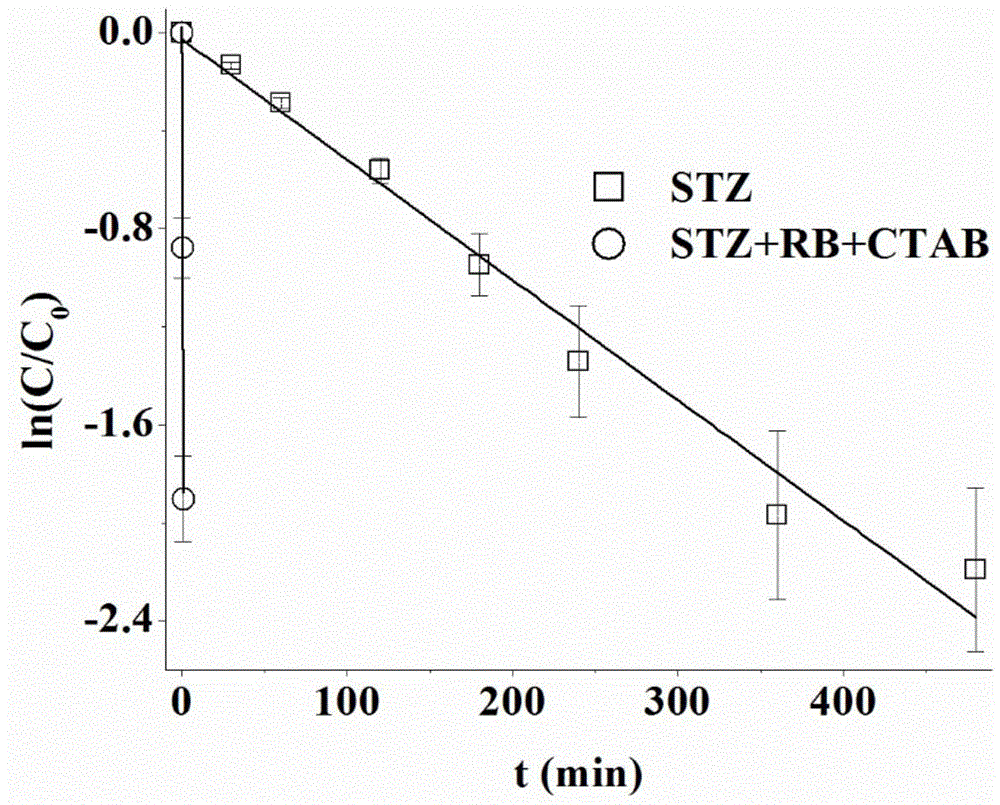
[0021] Oxidative degradation and concentration effect of five-membered ring-sulfathiazole (STZ):
[0022] (1) Oxidative degradation of sulfathiazole:
[0023] The four solutions containing STZ were placed under natural light, and the results were shown in Table 1 by HPLC detection and analysis. The half-life of STZ direct photolysis is 2.36h. After adding RB, that is, the half-life of STZ after photo-oxidative degradation was 0.16h, which was accelerated by 14.93 times. After the addition of CTAB, the photosensitive oxidation was enhanced by 26 times, and at the same time, it was promoted by 388.65 times compared with STZ's own photolysis, and the half-life was only 36s.
[0024] (2) Investigation of concentration effect
[0025]Three groups of the above-mentioned four solutions containing STZ were prepared, in which [CTAB]=1CMC, [STZ]:[RB] were 1:1, 10:1, 40:1 respectively in the three groups of solutions, and adjusted to pH=7 , place it in a photolysis tube, and place th...
Embodiment 2
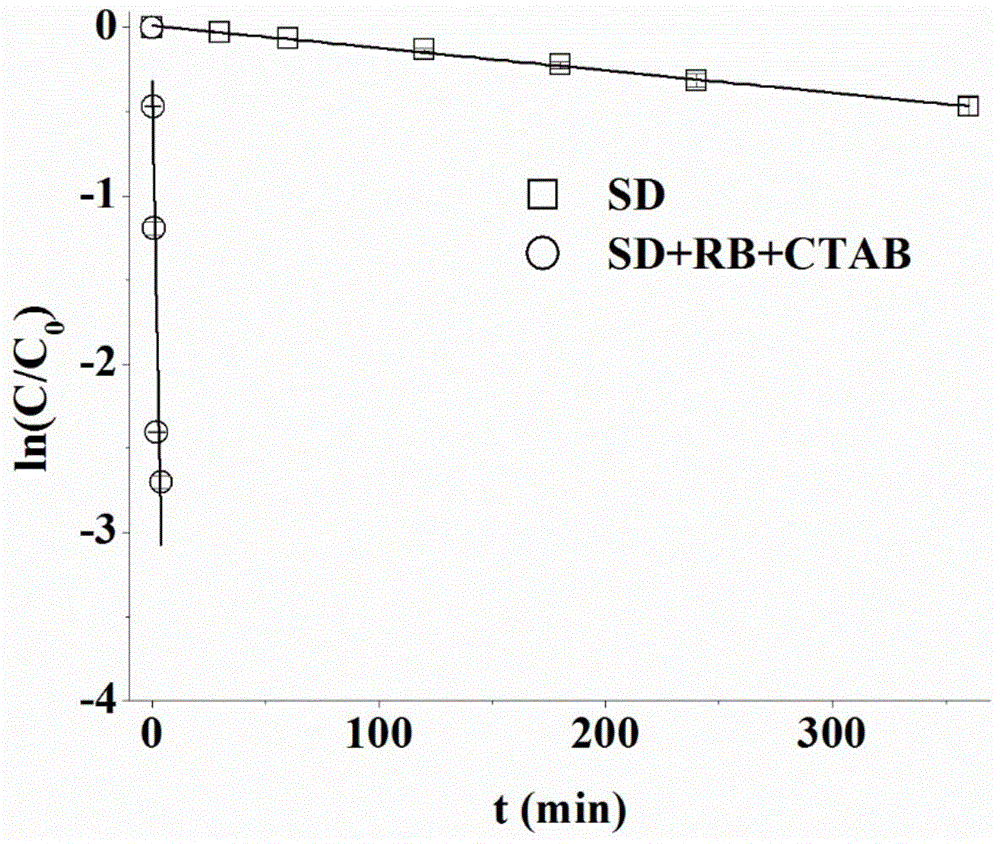
[0029] Oxidative degradation of six-membered ring-sulfadiazine (SD): The four solutions containing SD were placed under sunlight, and the results were shown in Table 1 by HPLC detection and analysis. Under sunlight, the half-life of SD direct photolysis was 9.63h. After adding RB, the half-life of SD after photosensitive oxidative degradation was 2.4 min, which was promoted by 234.41 times. After the addition of CTAB, the photosensitive oxidation was enhanced by 2.45 times, and at the same time, it was promoted by 574.68 times compared with the direct photolysis of SD self-photolysis, and the half-life period was only 72s.
Embodiment 3
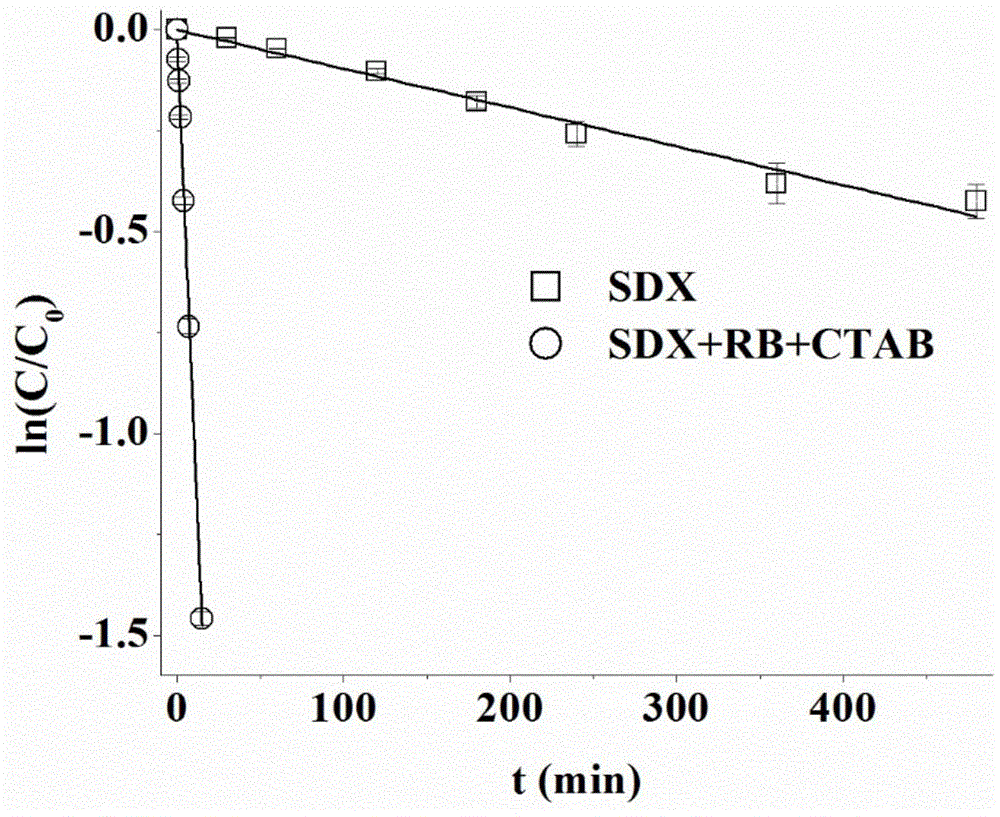
[0031] Oxidative degradation of six-membered ring-sulfadoxine (SDX): The four solutions containing SDX were placed in sunlight, and the results were shown in Table 1 by HPLC detection and analysis. Under sunlight, the half-life of SDX direct photolysis is 11.55h. After adding RB, that is, the half-life of SDX after photosensitive oxidative degradation was 36.6 min, a 19-fold improvement. After the addition of CTAB, the photosensitive oxidation was enhanced by 4.7 times, and at the same time, it was accelerated by 89.38 times compared with SDX self-photolysis, and the half-life was shortened to 7.8min.
[0032] Table 2 Photooxidation of sulfathiazole at different concentrations under simulated sunlight
[0033]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com