OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) pixel arrangement structure
A pixel arrangement and pixel technology, which is applied in the field of OLED display, can solve the problems of difficult metal mask evaporation, obvious moiré effect, and deterioration of oblique sawtooth, and achieve the effect of saving process cost, reducing process difficulty, and increasing aperture ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
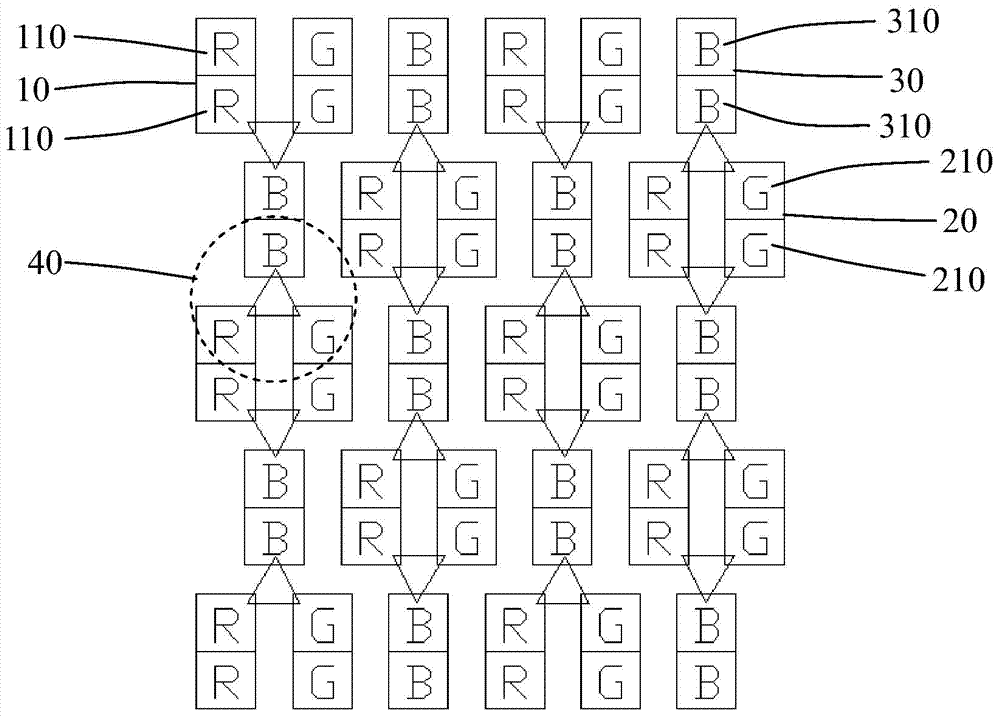
[0061] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the OLED pixel arrangement structure of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, in Embodiment 1, the first direction is the row direction (the X direction shown in the figure), and the second direction is the column direction (the Y direction is shown in the figure). In this embodiment, the OLED pixel arrangement structure includes:
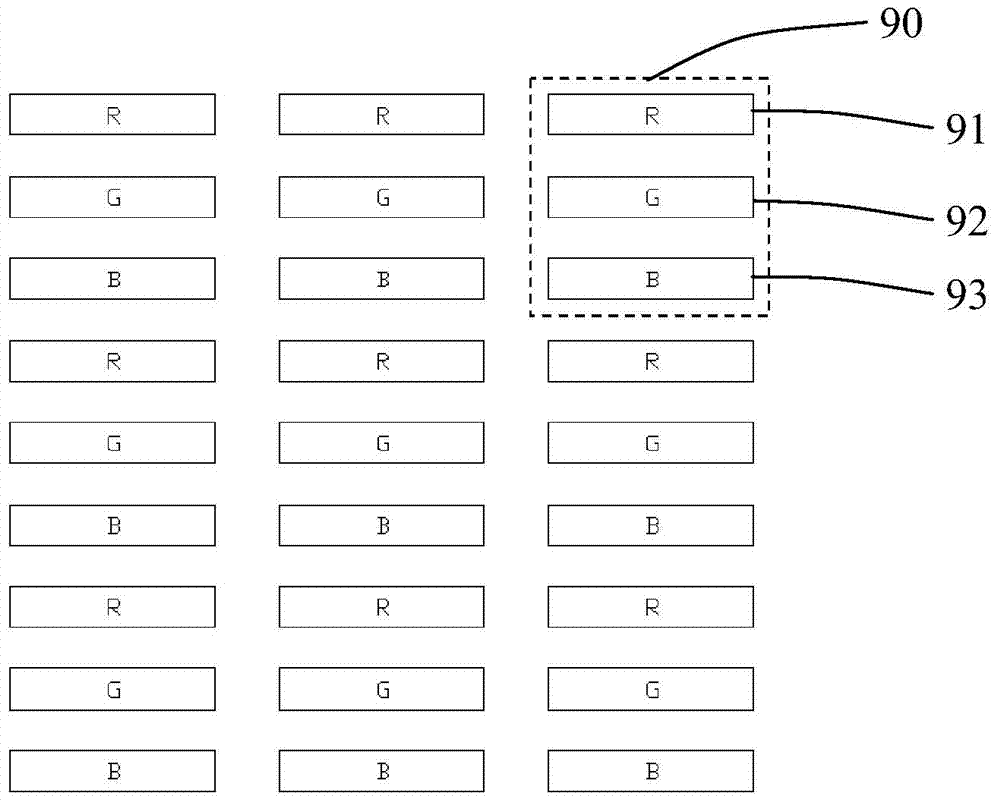
[0062] A plurality of first sub-pixel rows 50, the first sub-pixel row 50 includes a first R sub-pixel group 10a, a first G sub-pixel group 20a, and a first B sub-pixel group 30a arranged in sequence along the row direction;
[0063] A plurality of second sub-pixel rows 60, the second sub-pixel row 60 includes a second R sub-pixel group 10b, a second G sub-pixel group 20b, and a second B sub-pixel group 30b arranged in sequence along the row direction;
[0064] The first sub-pixel row 50 and the second sub-pixel row 60 are arranged at intervals, and the first R sub...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the OLED pixel arrangement structure of the present invention. Such as Figure 7 As shown, in Embodiment 2, the first direction is the column direction (the Y direction shown in the figure), and the second direction is the row direction (the X direction is shown in the figure). In this embodiment, the OLED pixel arrangement structure includes:
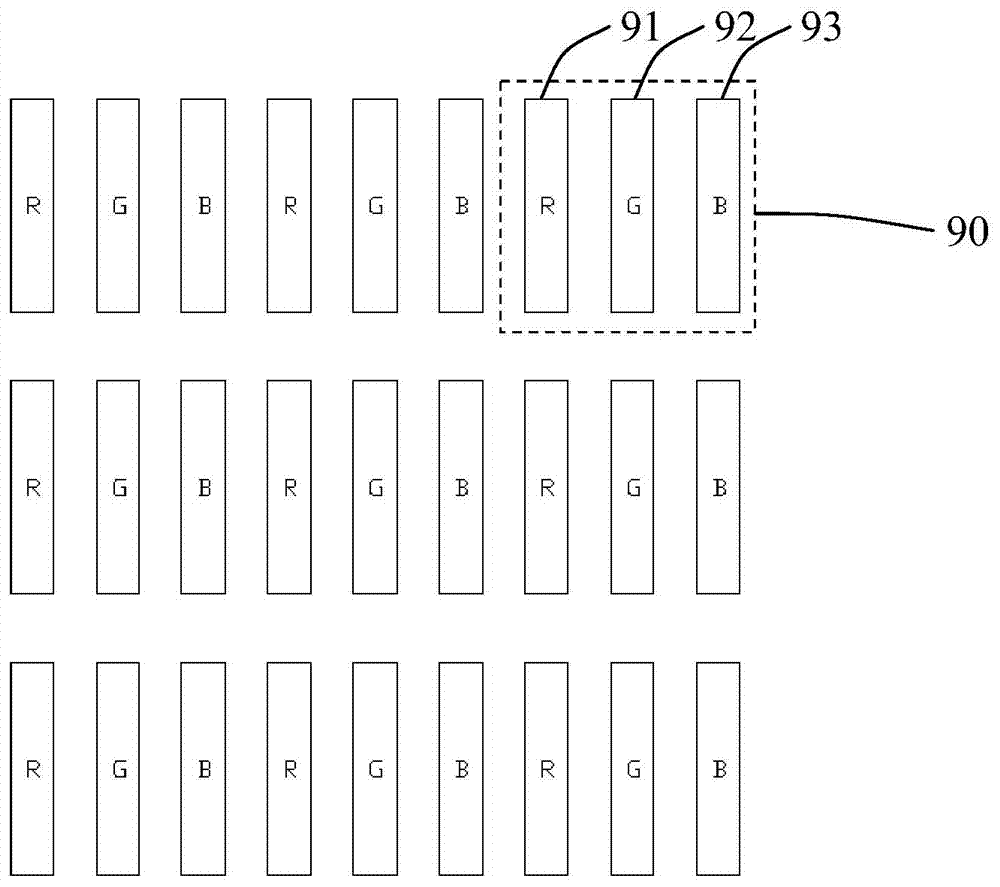
[0075] A plurality of first sub-pixel columns 70, the first sub-pixel column 70 includes a first R sub-pixel group 10c, a first G sub-pixel group 20c, and a first B sub-pixel group 30c arranged in sequence along the row direction;
[0076] A plurality of second sub-pixel columns 80, the second sub-pixel columns 80 include a second R sub-pixel group 10d, a second G sub-pixel group 20d, and a second B sub-pixel group 30d arranged in sequence along the row direction;
[0077] The first sub-pixel row 70 and the second sub-pixel row 80 are arranged at intervals, the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com