S-frequency-band monopulse self-tracking antenna system
An antenna system, monopulse technology, applied in the direction of antennas, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of complex feeder network, design time and poor performance, difficulty in achieving circular polarization processing, etc., to achieve good performance and reliability The effect of electrical performance and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following description.
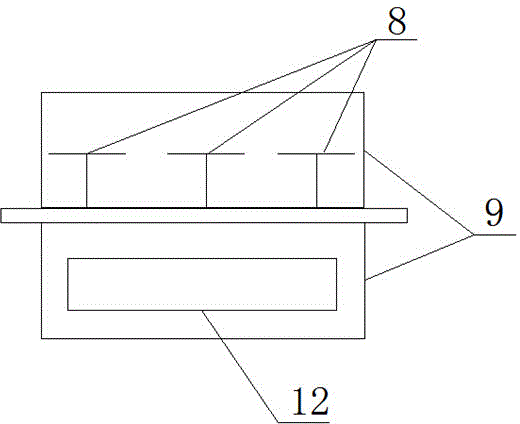
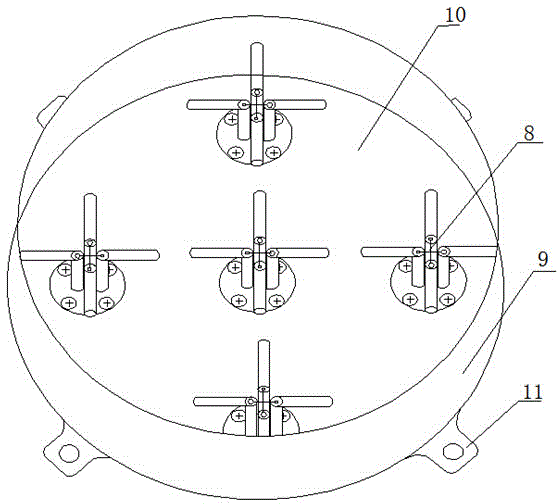
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the S-band monopulse self-tracking antenna system includes an antenna, a feed system and an antenna feed box 9, and the feed system includes an antenna feed source and a beamforming network 12, and the antenna feed box 9 There are two layers of structure, the upper and lower layers are separated by the base plate 10, the upper layer is used to install the antenna feed, and the lower layer is used to install the beam forming network 12.
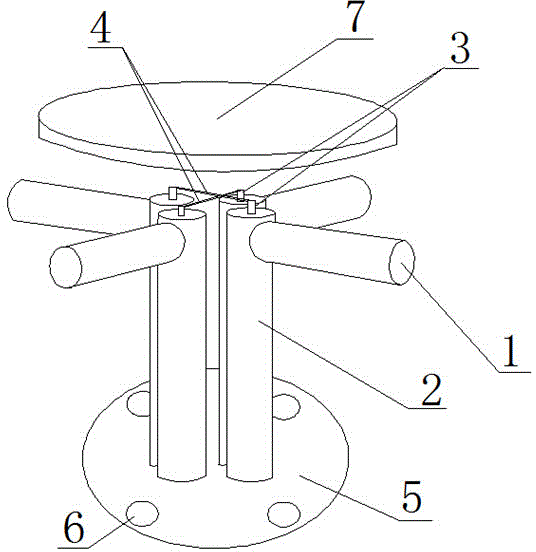
[0037] The antenna feed source includes five cross oscillators 8 arranged in a rhombus distribution structure, one of which is the central oscillator unit and is arranged on the diagonal intersection of the rhombus, and the other four cross oscillators 8 are the outer The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com