Undervoltage release
A voltage and external power grid technology, applied in the direction of protection switch operation/release mechanism, etc., can solve problems such as undervoltage release misoperation, circuit breaker false opening, imperfection, etc., to avoid harmonic interference and reliable pull-in , the effect of small calorific value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
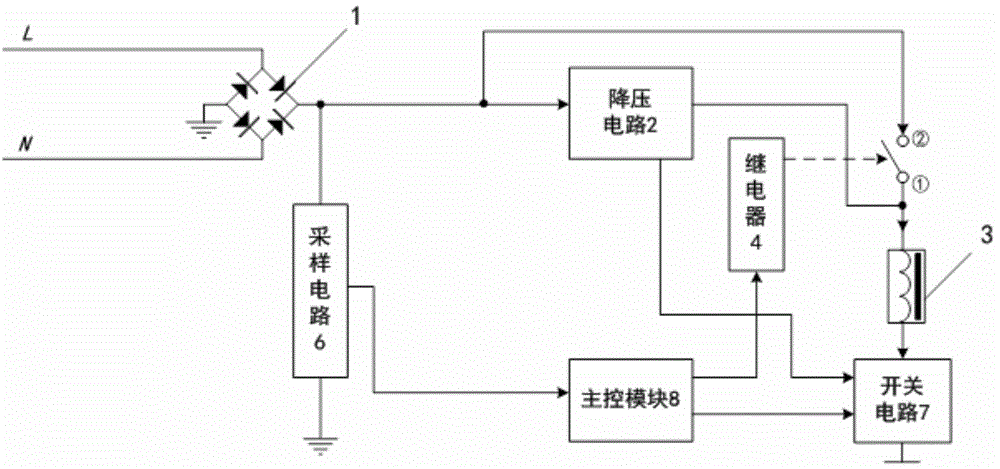
[0028] See figure 1 , an undervoltage release, comprising: a rectifier circuit 1 connected to an external power grid, an electromagnet coil 3, an armature controlled by the electromagnet coil 3; a step-down circuit 2, the input terminal of which is connected to the rectifier circuit 1 The positive output terminal of the relay 4 is connected with the current input terminal of the electromagnet coil 3, and its output terminal is connected with the current input terminal of the electromagnet coil 3, so as to provide a voltage for maintaining the armature pull-in; The output terminal is connected to the current input terminal of the electromagnet coil 3; the switch circuit 7 is connected to the current input terminal of the electromagnet coil 3; the sampling circuit 6 is used to detect the output pulsation of the rectifier circuit 1 DC voltage value; the main control module 8 stores the rated voltage Ue and the voltage value of the strong start, and is used to collect the output v...
Embodiment 2
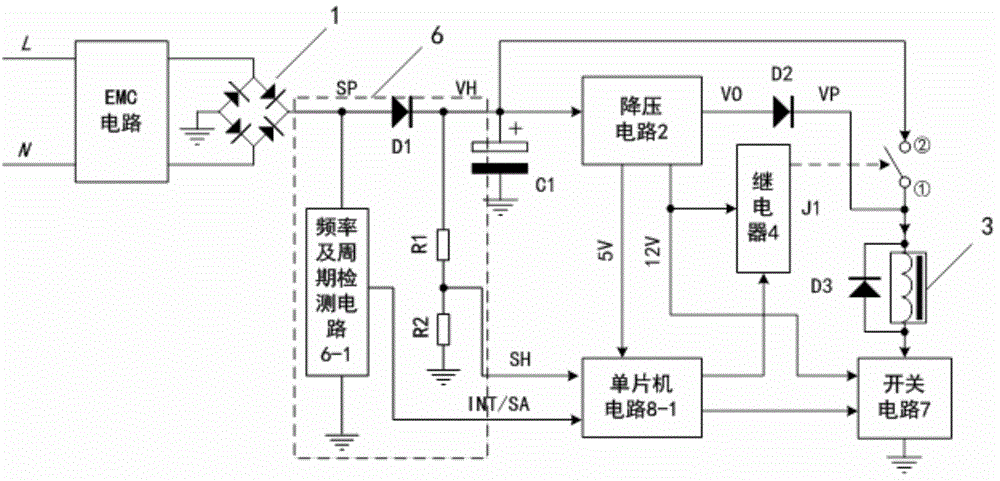
[0036] See Figure 1-2 , on the basis of Example 1, the implementation of the main part of the undervoltage release is described.
[0037] The full-wave pulsating voltage is isolated by the isolation diode D1 from the voltage VH charged to the strong start-up capacitor C1 without affecting the pulsating voltage SP. The VH voltage is stepped down by a step-down circuit 2 to provide working power for the relay 4 and the switch circuit 7 of the main control module 8. The voltage VO formed by the step-down circuit 2 is isolated by the diode D2 and the voltage VP is the electromagnet coil. 3 power supply. The resistors R1 and R2 form a sampling circuit of VH, and the sampling signal SH is sent to the main control module 8 . The pulsating voltage after full-wave rectification, frequency and period detection circuit 6-1 forms INT / SA signal, the main control module 8 analyzes the INT signal to obtain the grid cycle time (frequency), samples SA several times in one cycle, and applies...
Embodiment 3
[0045] See Figure 1-2 On the basis of the embodiment 1-2, taking 220V voltage and the main control module 8 using the single-chip microcomputer circuit 8-1 as an example, the implementation mode of the main part of the anti-harmonic and full-frequency undervoltage release is described.
[0046] The grid voltage is connected to the two input ends of the rectification circuit 1 after EMC bidirectional filtering. The positive end of the rectification circuit 1 is defined as (VH), and the negative end is grounded (GND).
[0047] After power-on, the rectifier circuit 1 rectifies the AC voltage into a DC pulsating voltage SP, charges the strong start-up capacitor C1 through the isolation diode D1, and the charging voltage VH is equal to the input AC voltage times (80% effective value, approximately equal to 248V). The charging voltage has a voltage sampling circuit 6 composed of R1 and R2 in series, and the production sampling signal SH is sent to the single-chip microcomputer. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com