Disjunction method of semiconductor wafer
A semiconductor and wafer technology, applied in the field of semiconductor wafer cutting, can solve the problems of perfect cutting section, quality or yield reduction, intrusion, etc., to achieve the effect of effective use of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] In order to further explain the technical means and effects adopted by the present invention to achieve the intended purpose of the invention, the specific implementation, structure, Features and their functions are described in detail below.
[0037] Hereinafter, details of the method for dividing a semiconductor wafer according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
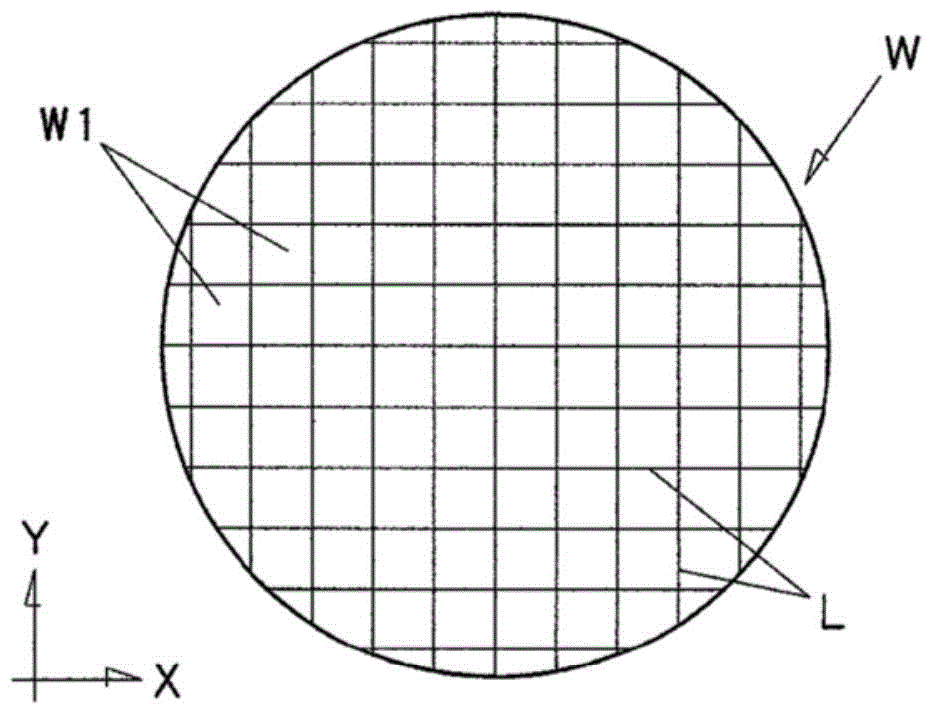
[0038] figure 1It is a plan view of a silicon wafer to be processed, and is divided along grid-like planned breaking lines L extending in the X-Y direction by the following breaking method to take out wafer-sized unit products W1. The silicon wafer W to be processed has a thickness of, for example, 100 to 300 μm before slicing, and is thinned to a thickness of 25 to 50 μm in a slicing process described below.
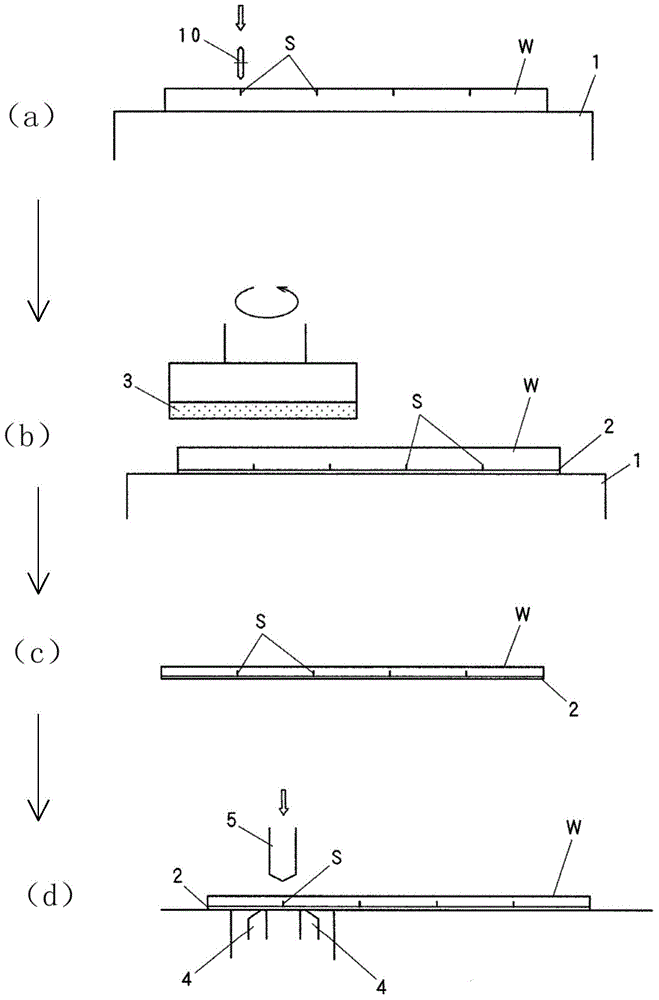
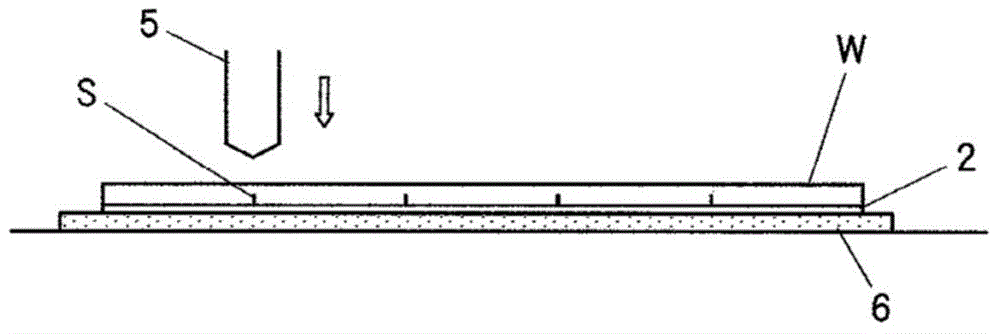
[0039] figure 2 An explanatory diagram showing an example of a method for breaking a silicon wafer (semiconductor wafer) W according to the present inventi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com