Brake pad
A technology of brake pads and brake pads, which is applied in the direction of friction linings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as thermoelastic instability, short life of brake discs, and poor braking performance, and achieve improved braking performance and improved heat flow. Consistent density and improved service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
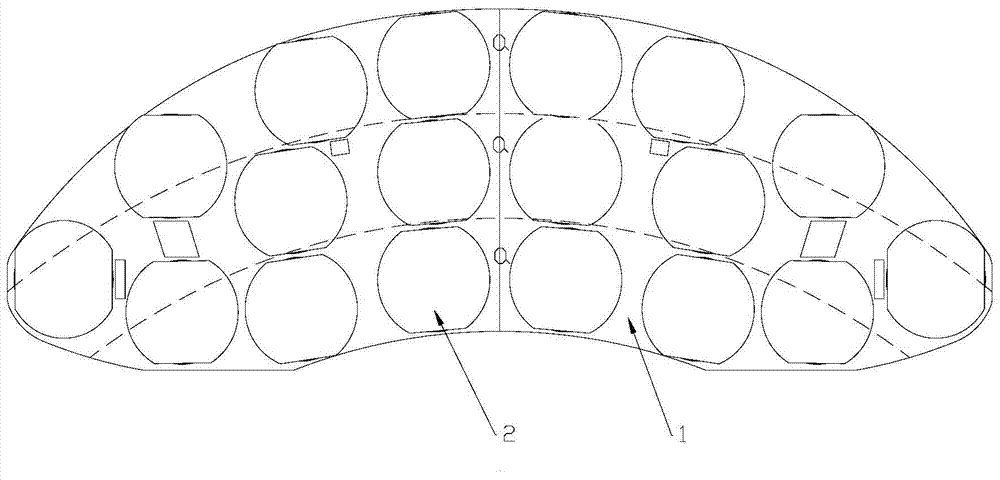
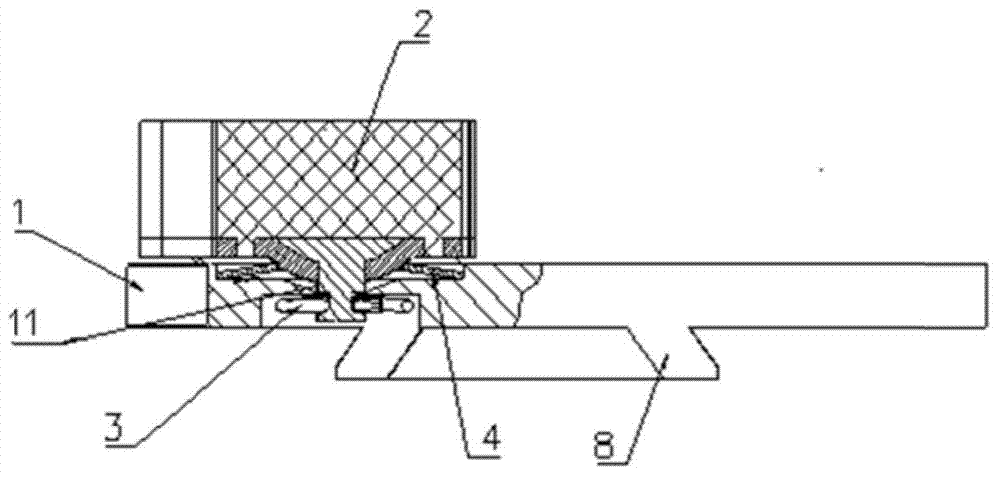
[0031] Figure 1-4 It is the brake pad of the present invention, which includes a back plate 1, two of which are spliced into a brake pad back plate; several friction blocks 2 arranged on the back plate 1; and the friction blocks 2 connected to the snap spring 3 on the backboard 1; as figure 1 As shown, taking the virtual center of the backplane 1 as the center, the backplane 1 is divided into three rings a, the lengths of the three rings a in the radial direction are equal, and each of the rings a The friction area of the friction block 2 inside is no more than 12% of the reference average friction area compared with the reference average friction area, that is, the friction areas of equidistant rings are approximately equal. The arrangement structure of the friction blocks can make the heat flux density of the back plate consistent, and the friction heat generated by the friction blocks during braking can be evenly distributed on the back plate, which avoids the back pl...
Embodiment 2
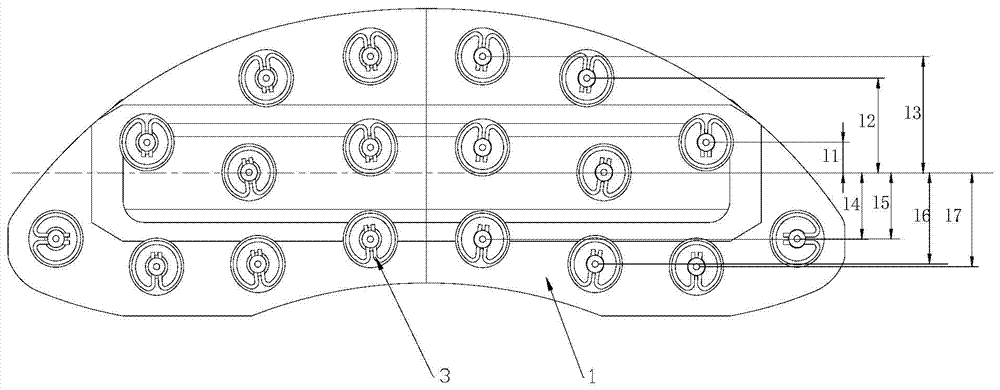
[0039] On the basis of Embodiment 1, in this embodiment, the distance between the friction blocks 2 on both sides of the brake pads and the stressed centerline of the brake pads is centered on the stressed centerline of the brake pads Compared with the reference distance, the sum does not exceed 10% of the reference distance. Such as Figure 5 As mentioned above, since the brake pad A is installed on the brake pad support D, and the brake caliper B and the brake pad support D are connected through the joint C, the axis of the joint C constitutes the joint of the present invention. Brake force center line.
[0040] For the brake pads in this embodiment, since the friction block is arranged symmetrically on the back plate 1, the sum of the distances from the friction block 2 to the force center line of the brake pad can be passed through the left side or The friction block on the right is calculated as figure 2 As shown, among the five friction blocks on the right side, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 2, the difference is that in this embodiment, the outer contour of the friction block 2 is located inside the outer contour of the back plate 1 or is in line with the outer contour of the back plate 1 cut.
[0044] In other embodiments, the brake pads take the center of the brake disc as the center to divide the back plate 1 into several equidistant rings a, and the friction blocks in each ring a The friction areas of 2 are equal; with the center line of the brake pad as the center, the sum of the distances between the friction blocks 2 on both sides and the center line of the brake pad is equal; the above scheme is the ideal state of the present invention. Considering the processing cost of the brake pad comprehensively, the brake pad takes the center of the brake disc as the center, divides the back plate 1 into a plurality of equidistant rings a, each of the rings a The friction area of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com