Oxidation and high salt stress resistant artificially synthesized sRNA and application thereof
An artificial synthesis and anti-oxidation technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of undetermined coding genes and functions, no anti-oxidation and high-salt stress resistance, and no host adversity stress, etc., and achieve a high survival rate. , the effect of improving oxidative stress resistance and salt stress resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
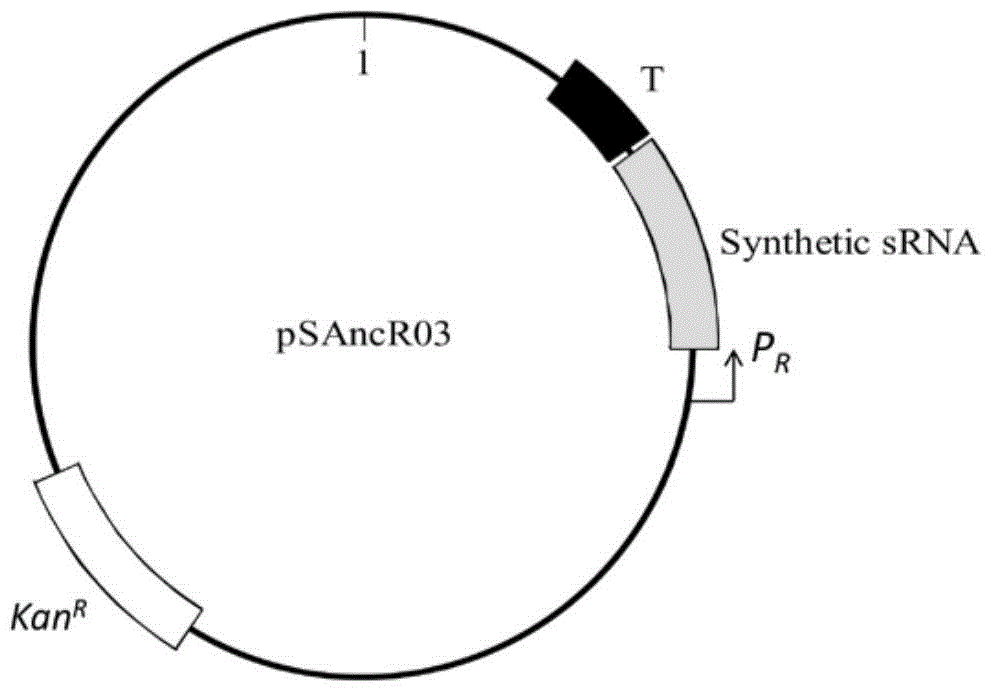
[0033] Example 1 Determination of specific binding sequence in artificially synthesized sRNA and construction of expression plasmid pSAncR03
[0034] 1. Determination of the specific binding sequence in artificially synthesized sRNA
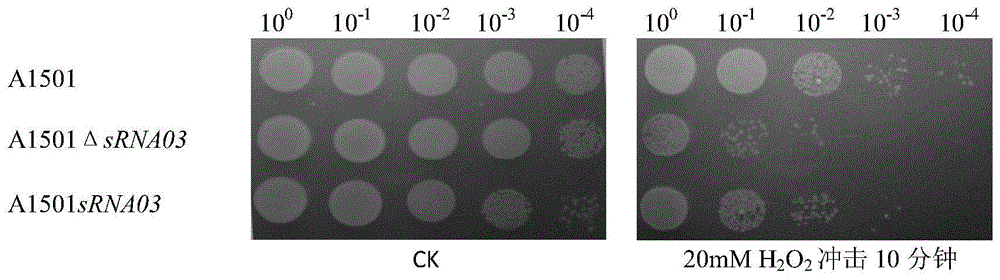
[0035] We found that non-coding sRNA03 from nitrogen-fixing Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 was involved in regulating some stress-resistant physiological processes of host cells. Experiments have shown that the loss of sRNA03 will lead to the reduction of the antioxidant and salt tolerance of cells, and the transfer of this sRNA into Escherichia coli will also significantly enhance its ability to survive in peroxidative and high-salt environments, which regulates the physiological process of cell stress resistance has been confirmed. In order to construct an sRNA with stronger regulatory ability, the specific binding sequence needs to be clarified first. For this reason, we analyzed sRNA03 through bioinformatics software and selected a 20bp fragment...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Construction of mutant strains and verification of their functions
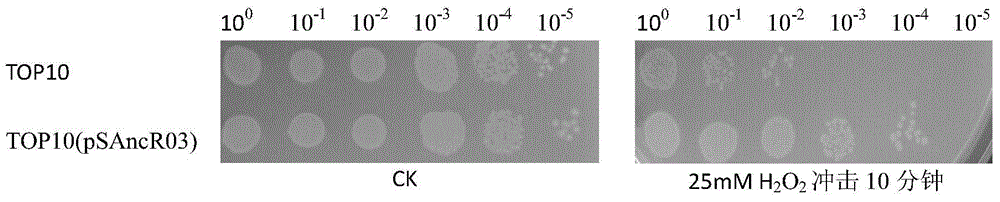
[0051] A method for improving oxidative stress resistance and / or salt stress resistance of Escherichia coli TOP10 strain by artificially synthesizing sRNA is used to construct mutant strains with oxidative stress resistance and / or salt stress resistance.
[0052] In this embodiment, the artificially synthesized sRNA gene is a non-coding sRNA gene transcribed from the nucleotide sequence DNA shown in the sequence listing.
[0053] In this example, the steps for constructing a recombinant strain of Escherichia coli TOP10 with oxidative stress resistance and / or salt stress resistance are: transforming the constructed pSAncR03 plasmid vector into the strain by heat shock transformation, constructing a recombinant expression The strain E. coli TOP (pSAncR03) is a recombinant Escherichia coli Top10 strain with high resistance to oxidative stress and / or salt stress.
[0054] Verification experiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com