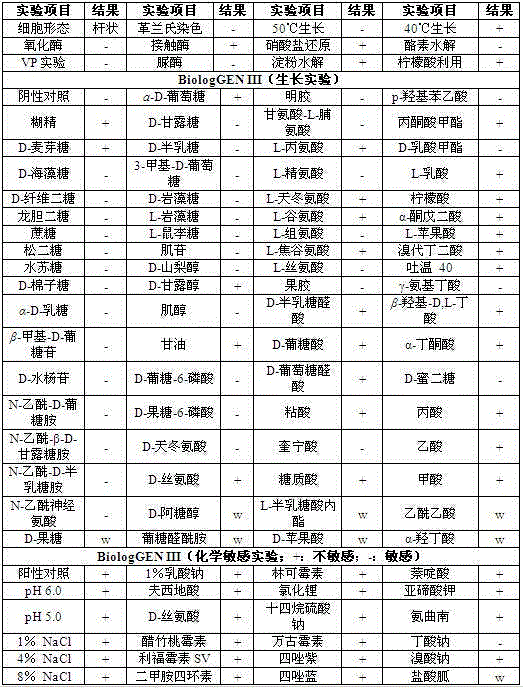
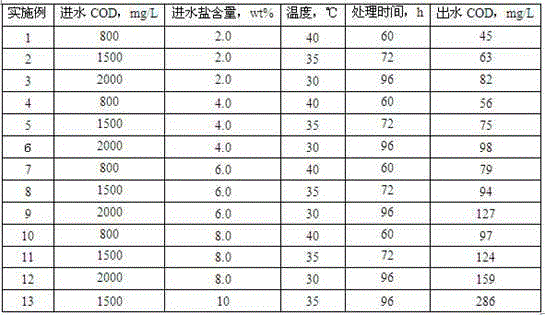
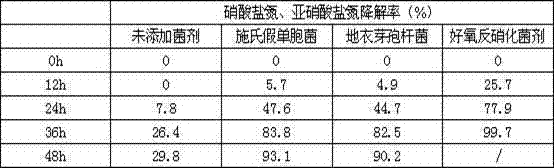
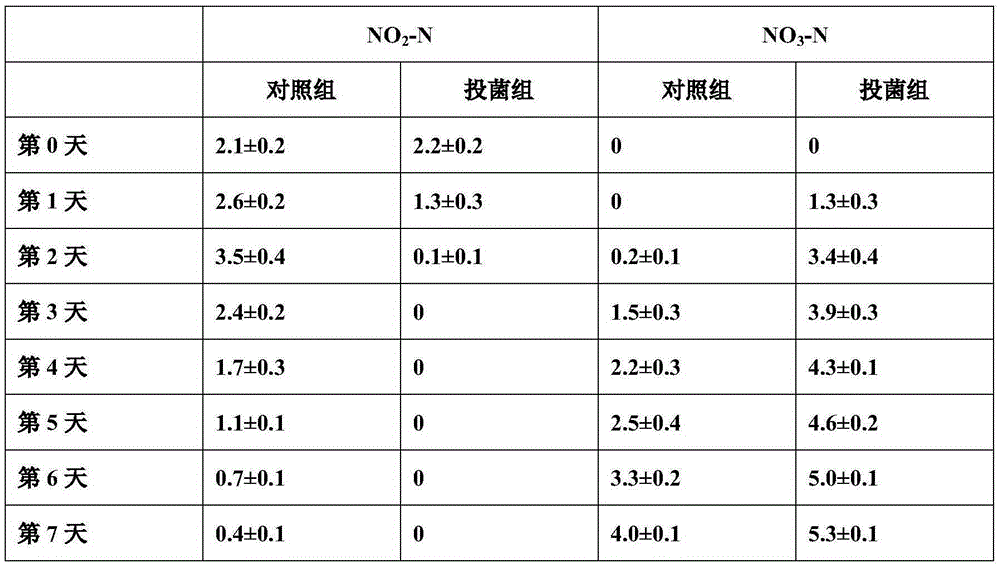
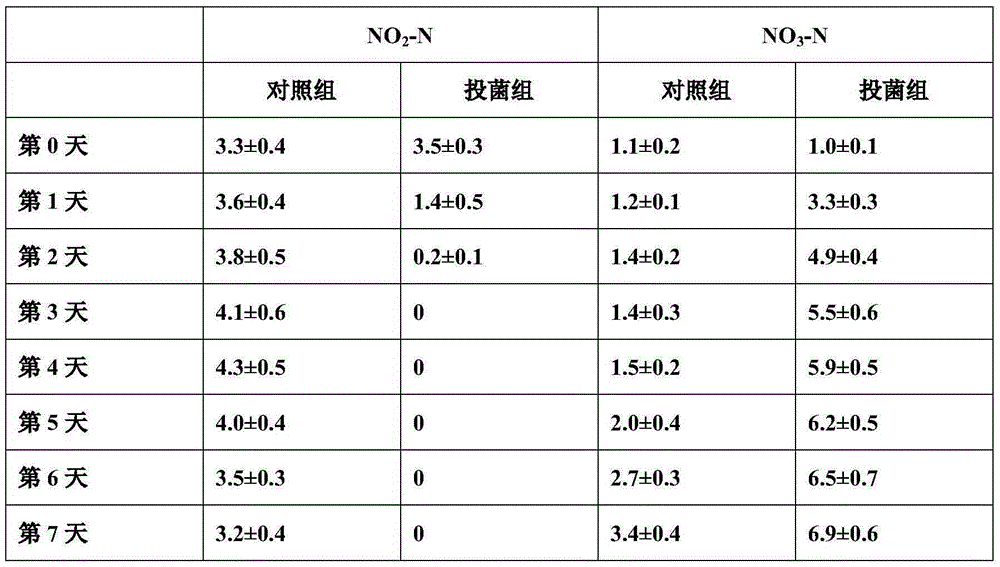
Patents
Literature
132 results about "Pseudosymblepharis schlimii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
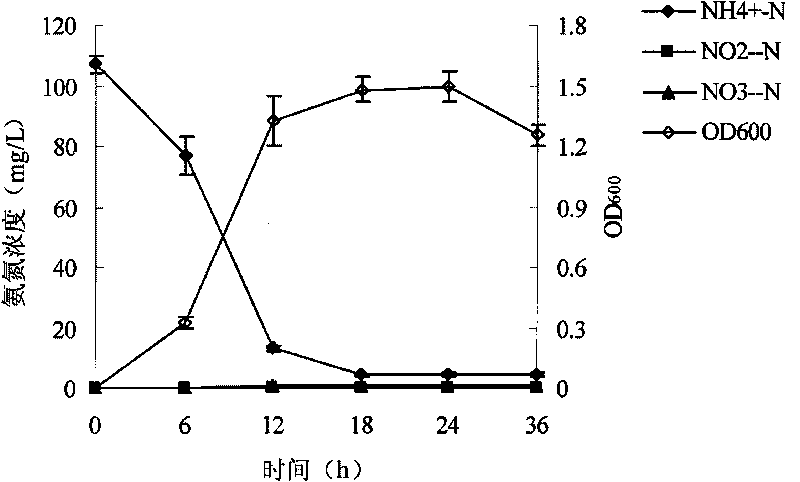
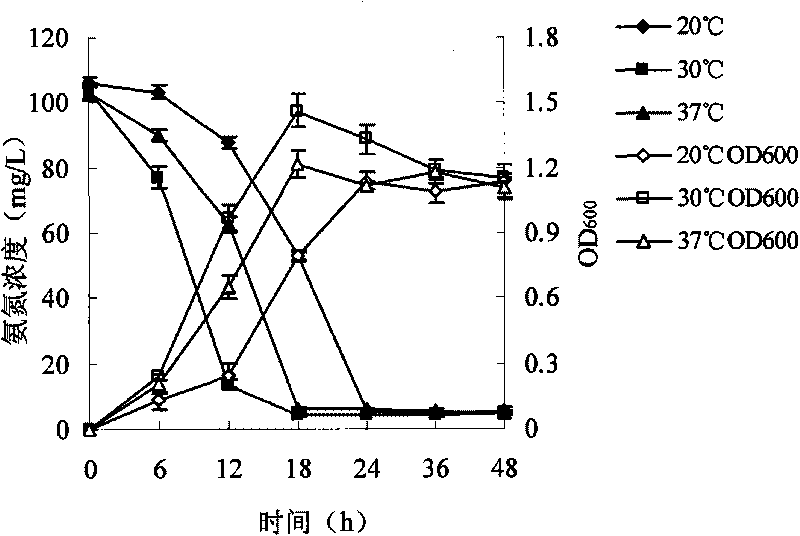
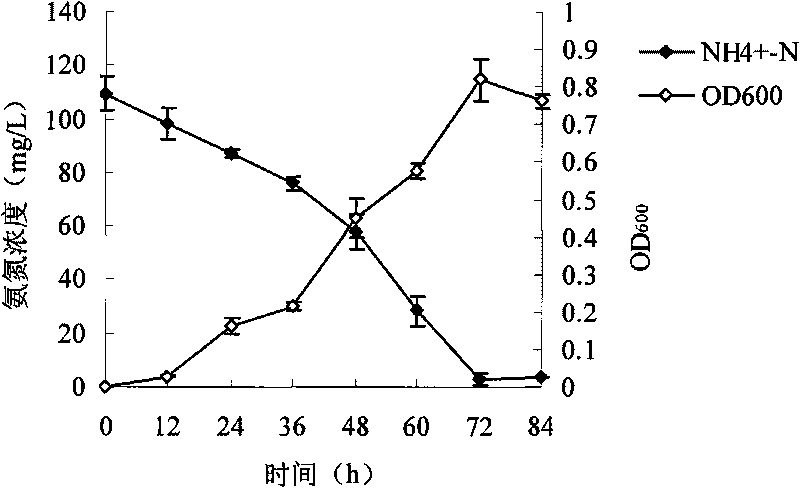
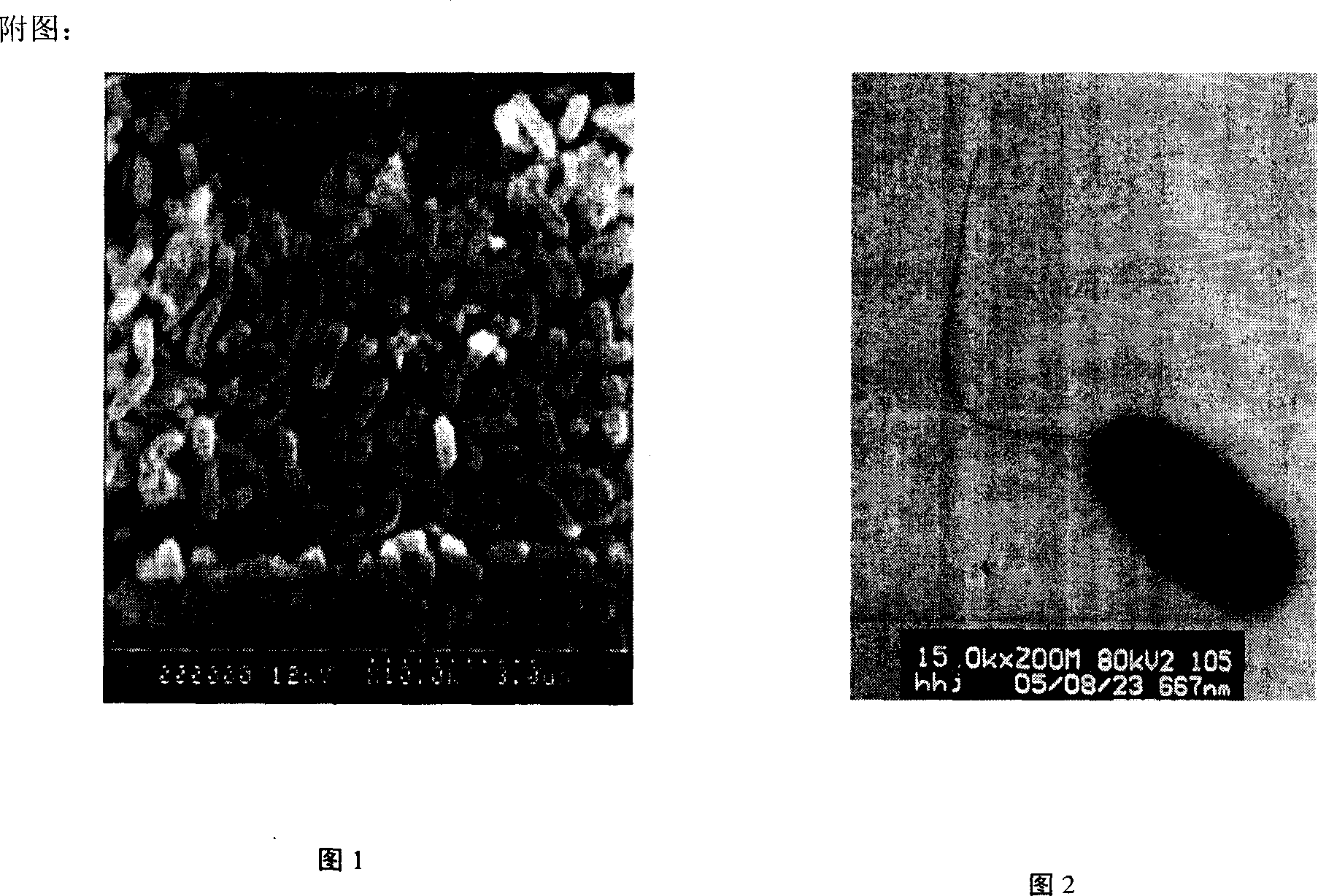
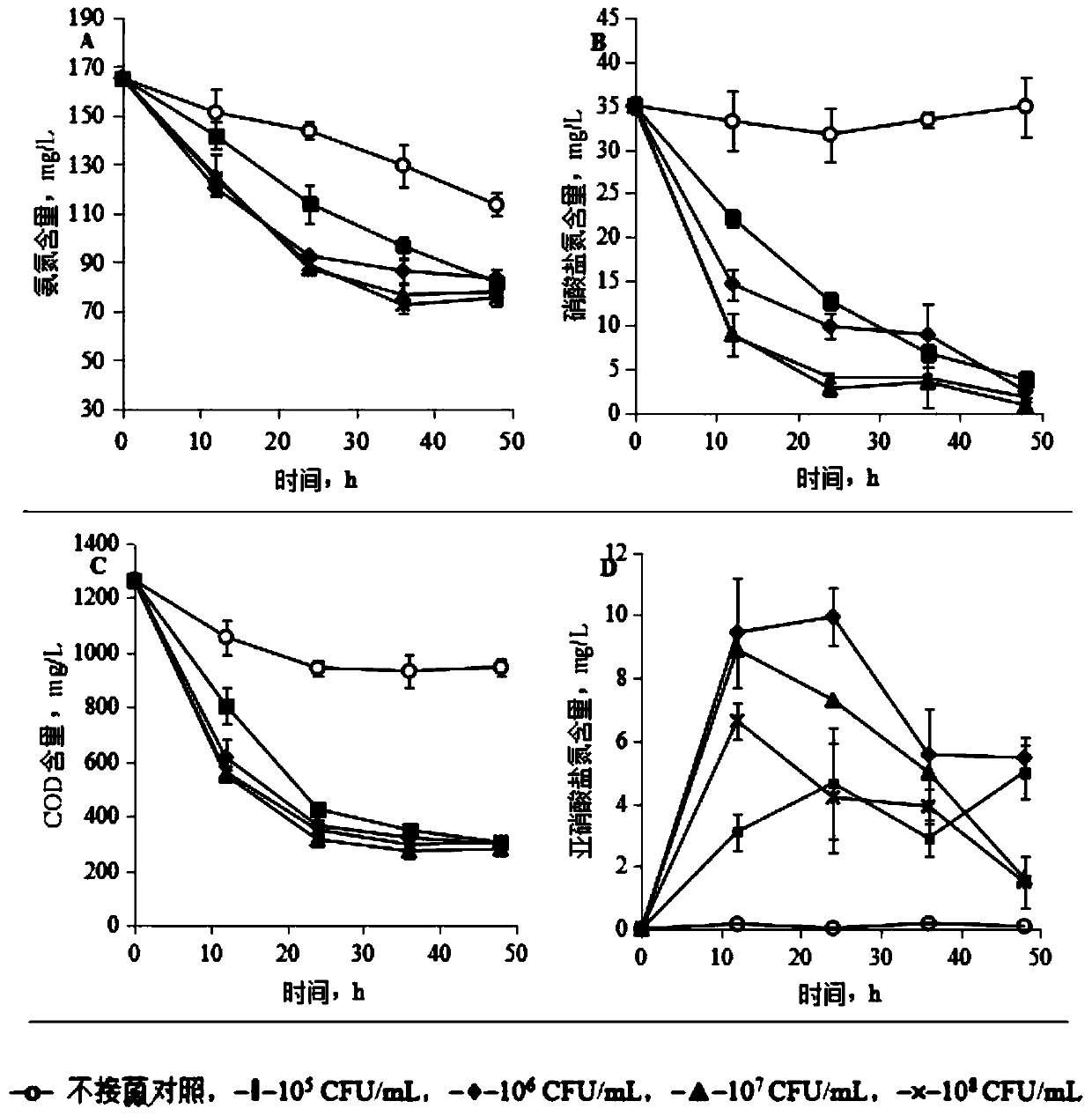
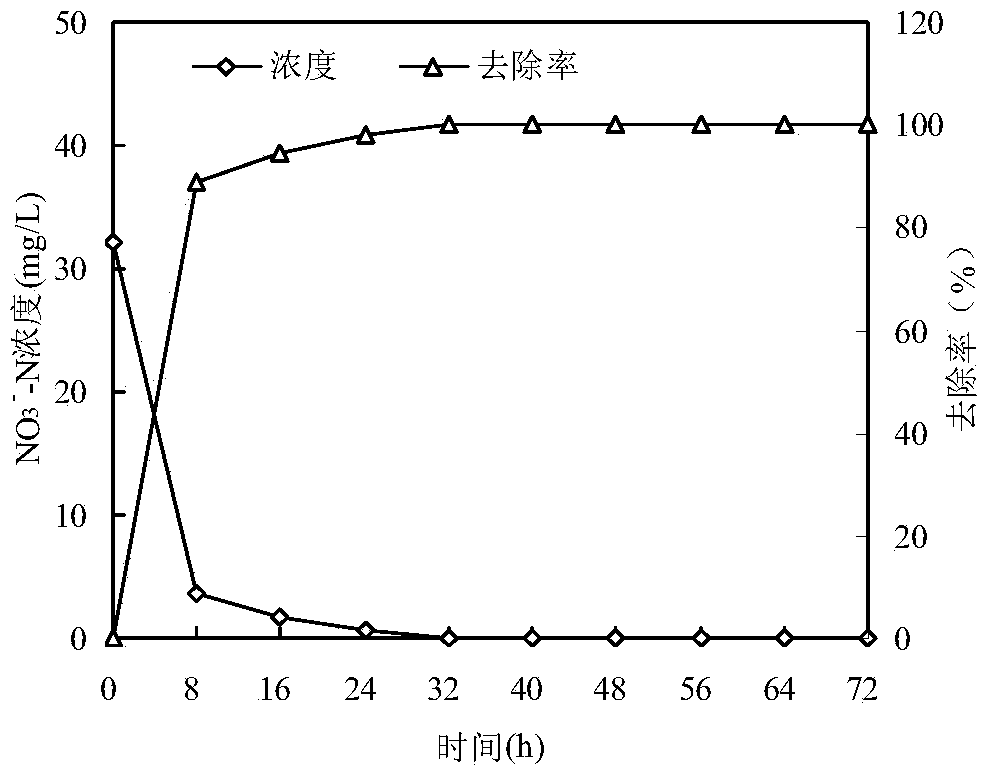
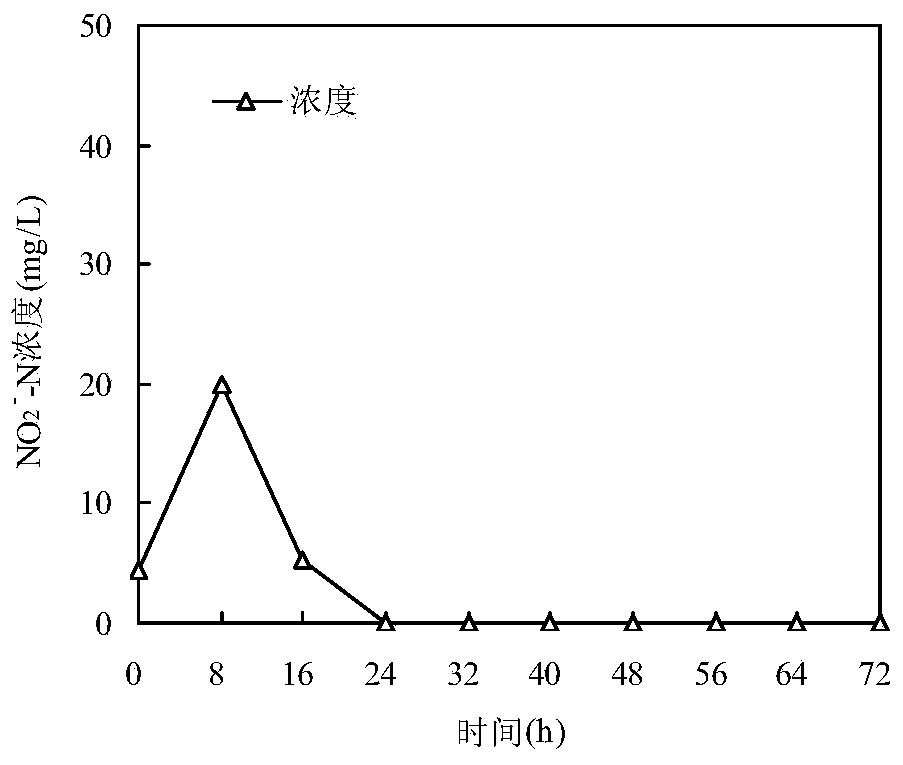
Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001 for removing ammoniacal nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and nitrous nitrogen in water body and application
The invention belongs to the technical filed of agricultural microorganisms, particularly relating to separate and screen Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001 for degrading ammoniacal nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and nitrous nitrogen in water body and application. The screened Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001 of the invention is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), with the preservation number being CCTCC NO:M 209107. The strain can effectively degrade ammoniacal nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and nitrous nitrogen in water body within the range of 20-37 DEG C, has no toxicity to chub, has good degradation function on ammoniacal nitrogen in water body at normal temperature, the microorganism of the invention is inoculated for 72 hours, the degrading ratios to ammoniacal nitrogen in domestic sewage and aquaculture wastewater are respectively up to 83.10% and 61.38%.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Pseudomonas stutzeri JSD-008 and its degradation function for organophosphorus pesticide
InactiveCN101096644APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChlorpyrifosMethyl parathion
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas stutzeri JSD-008 and degradation for organophosphorus pesticide, which is preserved in the 'Chinese germ management committee center (CGMCC)' with preservation number at CGMCC No.1738, wherein the strain is separated from the soil at pollution discharge pore of pesticide processing plant polluted by organophosphorus pesticide; the thallus and ferment liquid with the thallus can be degradation agent of organophosphorus pesticide to degrade the chlorpyrifos into trichlopyridinenol and methyl parathion into nitrophenol; fitting for rapid in-situ rehabilitation polluted by field soil pesticide.
Owner:谢明
Enzyme and microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101560488AImprove degradation rateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroides xylanisolvensFlavobacterium aquatile
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose and application thereof. The active component of the microbial inoculum consists of Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Clostridium xylanolyticum, Clostridium lentocellum, Flavobacterium aquatile, and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Experiments prove that the microbial inoculum has high degradation rate to the lignocellulose, and the degradation rate can reach between 60 and 70 percent. The microbial inoculum has low cost and simple preparation, breaks through the limitation that a purification bacterium and a clastic enzyme thereof cannot decompose the lignocellulose efficiently, provides a key technique for decomposing, saccharifying biomass containing cellulose and converting the biomass into an energy source, and has extensive application prospect in the field of decomposing the lignocellulose.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
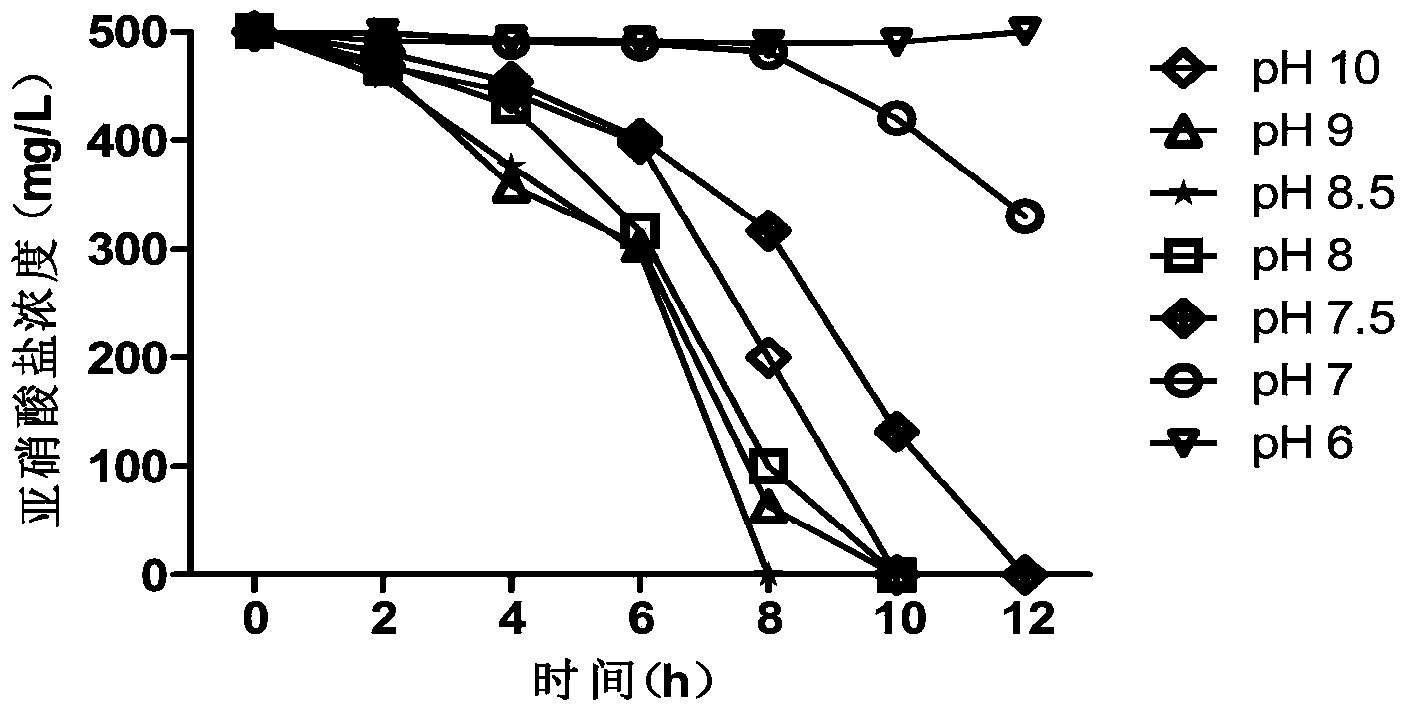
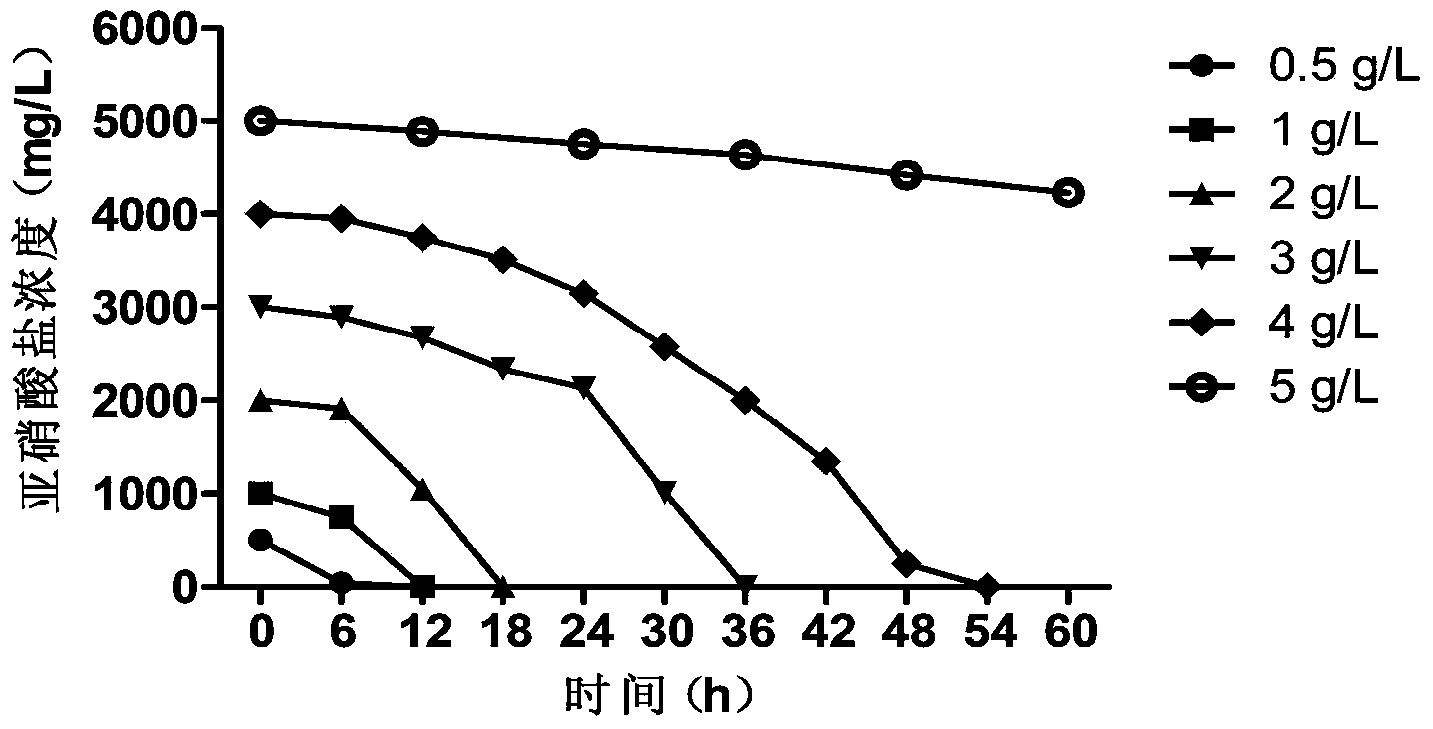
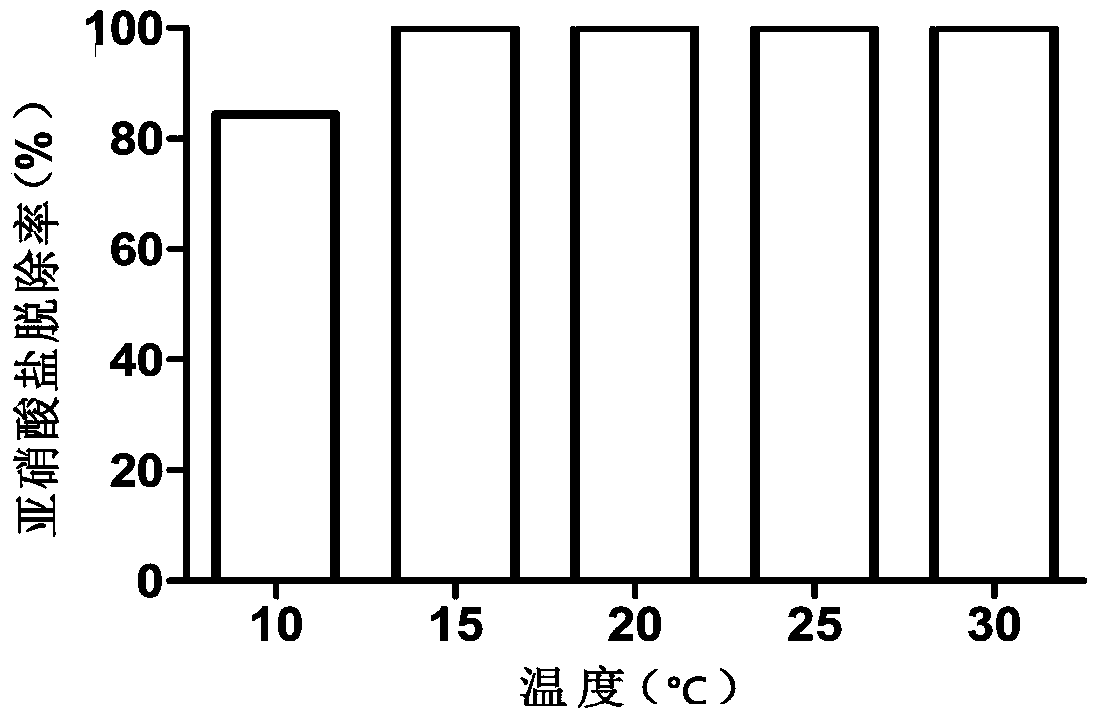
Salt-resistant pseudomonas stutzeri having low-temperature biological denitrification function
ActiveCN103773723AExcellent nitrite nitrogen removal abilityStrong nitrite nitrogen removal abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and in particular relates to a bacterium having low-temperature denitration biological activity. The bacterium is characterized by being pseudomonas stutzeri DN-3, and is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number CGMCC No.8291 on October 8, 2013. The invention further relates to method for culturing the bacterium, preparation of a biological denitration agent by taking the bacterium as a major component and an application of the bacterium to nitrogen degradation in a water body.
Owner:南京曜动节能环保科技有限公司
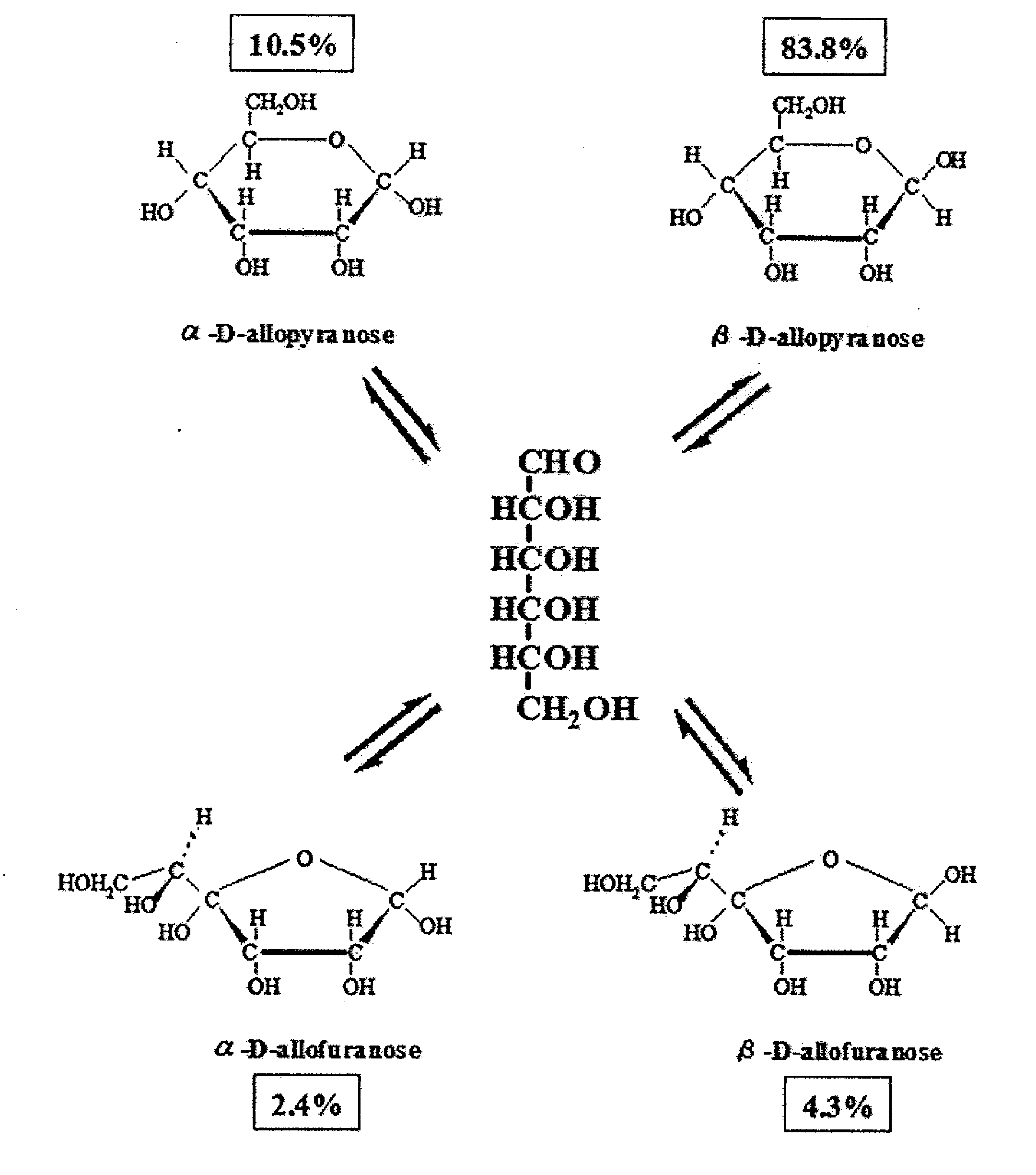
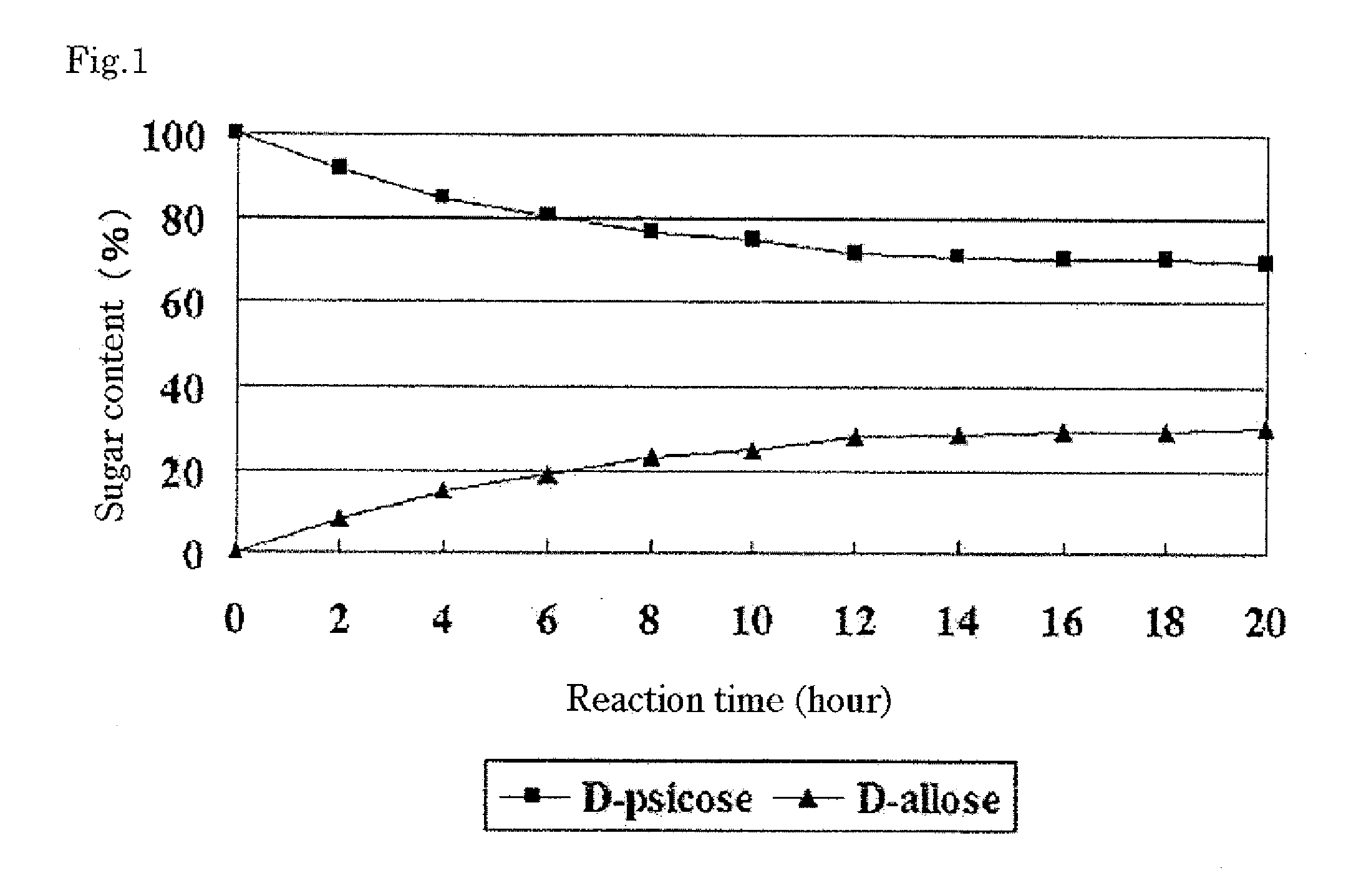
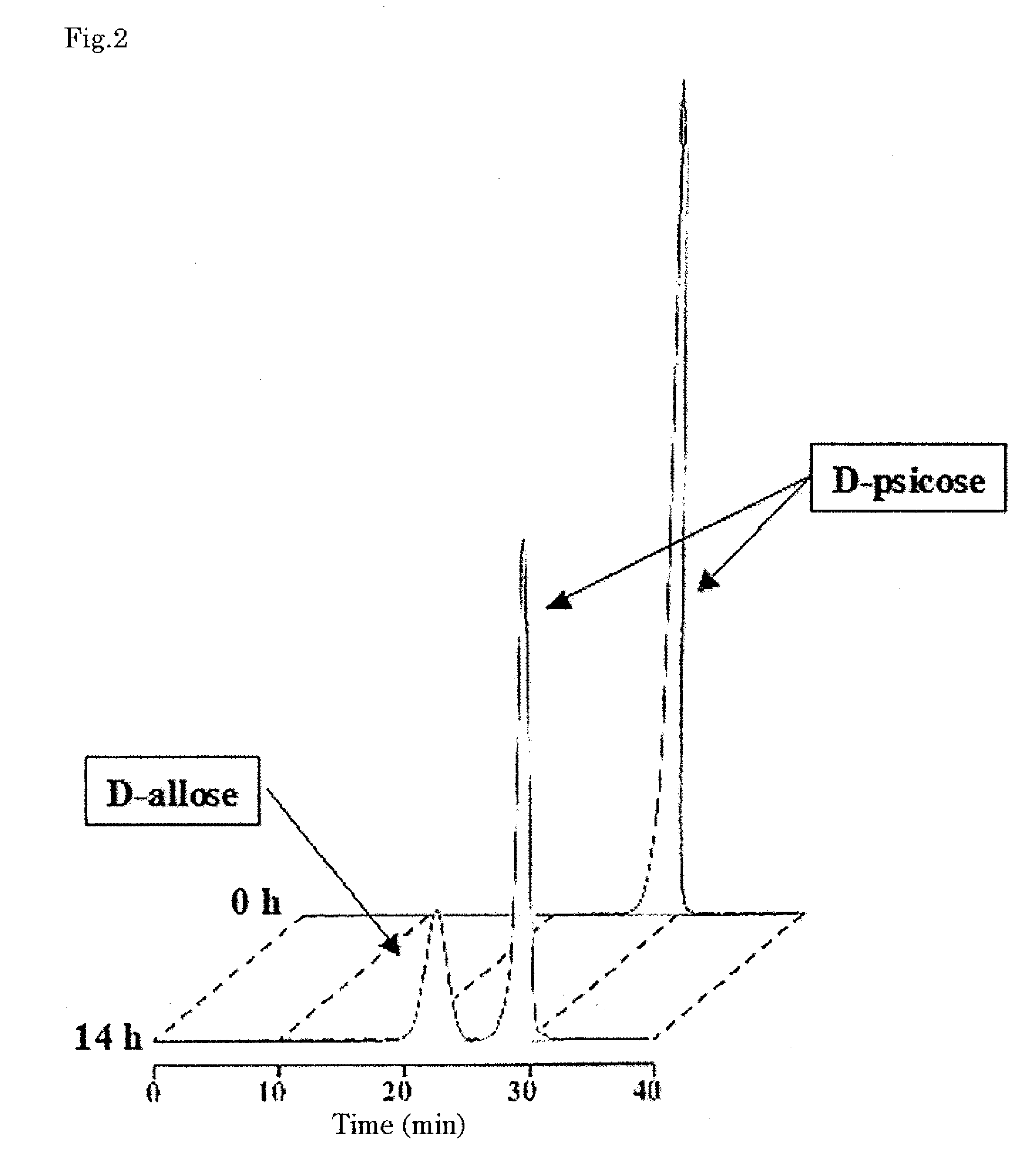
Complex crystalline sugar comprising d-psicose and d-allose and process for production of the same
ActiveUS20090068710A1Improve overall utilizationEfficient productionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAllosePsicose
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY +1
Aerobic denitrifying bacterium and application thereof in wastewater treatment
ActiveCN103667168AEasy to trainNo accumulationMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierDenitrifying bacteriaWastewater
The invention discloses an aerobic denitrifying bacterium and application thereof in wastewater treatment. The applicant selects an aerobic denitrifying bacterium through enrichment, Pseudomonas stutzeri JH-1, CCTCC NO: M2013488 from a wet land. The bacterium can be used for treating wastewater with high NO3<->, reaches the highest removing rate of 99.6%, avoids the accumulation of nitrite nitrogen, meanwhile can remove COD in organic wastewater with the highest removing rate of 60%-80%; compared with other reported aerobic denitrifying bacteria for wastewater treatment, the bacterial strain provided by the invention can efficiently treating wastewater, achieves the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen of 99.6% after 24 h and the denitriding rate of 22.6 mg. L<-1>.h<-1>, which is 1.51-4.57 times of that of the reported bacterial strains, can be independently used or solidified for wastewater treatment, and is widely applied.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Compound microbial agents, bacterial manure, preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of saline alkali soil
ActiveCN105838644AStrong decompositionStrong transformationBio-organic fraction processingFungiAlkali soilBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to compound microbial agents, bacterial manure, preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of saline alkali soil .In particular, the compound microbial agents comprises the bacillus megaterium microbial agent, the pseudomonas stutzeri microbial agent, the rhizobium radiobacter microbial agent, the candida tropicalis microbial agent and the lactobacillus delbrueckii microbial agent .The invention further comprises the bacterial manure containing the microbial agents, the preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of the saline alkali soil .By means of the compound microbial agents, the bacterial manure, the preparation methods thereof and application thereof to restoration of the saline alkali soil, raw materials which pollute the environment easily or need to be disposed such as straw, excrements of livestocks, household garbage and sludge can be utilized sufficiently, in addition, the compound microbial bacterial manure capable of restoring the saline alkali soil can be prepared, thus the immune function and stress resistance of plants can be improved, the land salinization degree can be improved, and the purpose of achieving second ploughing of salinized soil is achieved.
Owner:陈五岭
Preparation method and application of sea bdellovibrio bacteriovorus ecological preparation
InactiveCN101781627AGuaranteed lytic activityPromote lysisBiocideBacteriaNutrient brothCulture mediums
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a sea bdellovibrio bacteriovorus ecological preparation, and relates to a sea microbial ecological preparation and a preparation method of a bdellovibrio bacteriovorus preparation for mariculture. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a host bacteria suspension; separating and purifying bdellovibrio bacteriovorus; and propagating and culturing bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. The preparation method is characterized in that after pseudomonas stutzeri is connected with an incline and is activated, adding physiological saline in a test tube to prepare the bacterial suspension; then propagating and culturing with nutrient bouillon; adding a flocculating agent in the obtained bacterial suspension; standing and precipitating after uniformly shaking; adding the physiological saline to obtain 1012 cfu / mL of host bacteria suspension; separating and purifying the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus of collected sea and bottom sediment samples with a double agar plate method; pouring culture media containing the host bacteria suspension and the collected samples into sea agar in the lower layer for culture after uniformly mixing; and adding the host bacteria and the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus obtained by separation into sterilized natural sea, and culturing until the concentration of the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is 108 to 109 pfu / mL for future use.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Compound microbial agent for preventing and treating banana wilt disease and prevention and treatment method
ActiveCN105385643AControl Fusarium WiltReduce morbidityBiocideFungiBacillus thuringiensisTreatment effect
The invention relates to the field of banana cultivation, in particular to a compound microbial agent for preventing and treating a banana wilt disease and a prevention and treatment method. The compound microbial agent comprises paenibacillus polymyxa, bacillus subtilis, bacillus thuringiensis, pseudomonas stutzeri, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, cold-resistant brevibacteriaceae, trichoderma and metarrhizium anisopliae. By means of a reasonable proportion, all strains are mutually influenced and promoted, and the prevention and treatment effect on the banana wilt disease is greatly improved. The prevention and treatment method of the banana wilt disease can effectively adjust the composition of bacterial colonies in soil, promote growth and propagation of probiotics and antagonistic bacteria in the soil, rapidly restore and stabilize the balance of the bacterial colonies in the soil, prevent and treat occurrence and spread of the banana wilt disease, effectively decrease the occurrence rate of the banana wilt disease and maintain the stable and high yield of bananas.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Efficient biological desulfurization method for coal
InactiveCN103937576AEffectively retain active ingredientsEasy to operateSolid fuelsThiobacillus ferrooxidansThiobacillus
The invention discloses an efficient biological desulfurization method for coal, which is characterized in that coal is crushed through a crusher until the particle size is below 150 meshes; and three bacteria, namely Thiobacillus thioxidans, Thiobacillus caldus and Pseudomonas stutzeri, are adopted. The desulfurization process comprises the following sequential steps: removing organic sulfur in the coal through the Pseudomonas stutzeri; after the primary desulfurization is finished, preparing the Thiobacillus thioxidans and the Thiobacillus caldus into a desulfurization solution according to a certain total bacterial count ratio, and removing inorganic sulfur of the coal; and washing the desulfurized coal with water, filtering, and drying. The total sulfur removal ratio of the desulfurized coal is up to 57.8%; and the method is simple to operate, mild in treatment conditions and low in cost, and effectively retains effective components in the coal, thus being a desulfurization technology having very wide market prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Pseudomonas stutzeri and culture application thereof
ActiveCN106635857AGood COD removal performanceEasy to handleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalt resistanceMicroorganism
The invention relates to pseudomonas stutzeri and a culture application thereof. The strain is pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, collected at 'China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center' on June 1, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 10940. The strain can be applied to efficiently removing COD (chemical oxygen demand) in salty wastewater with salt content of 1.0wt%-10wt%, and can grow at the high temperature of 40 DEG C. The invention further provides COD removing salt-tolerant bacteria which comprise the pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5. The COD in the high-salt wastewater can be rapidly degraded by the pseudomonas stutzeri, and the pseudomonas stutzeri has the advantages of high salt resistance, good treatment effect and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
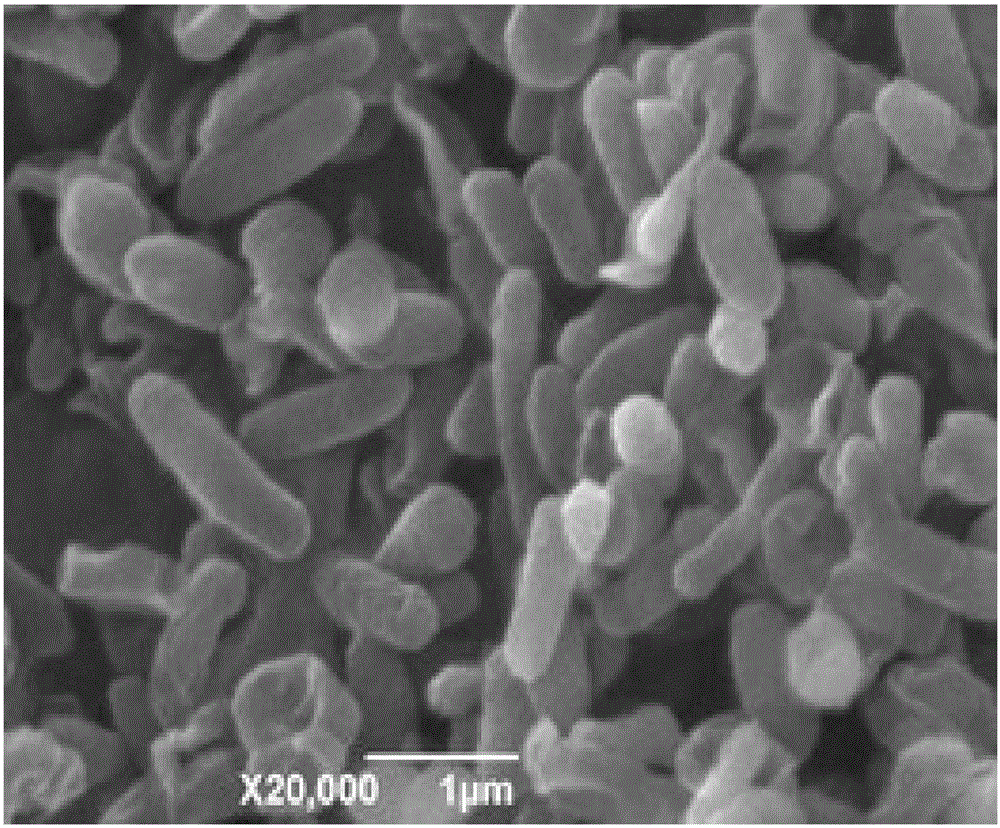
Pseudomonas stutzeri strain and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with high molecular weight
InactiveCN101603022APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSpore structure
The invention relates to a novel strain of bacteria and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with high molecular weight. The strain is identified and named as Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain which has bacteriological characteristic of Gram-negative, has cells in a straight or bent rod shape but not spiral shape and not in a chain, has the size of 0.60-0.8*1.4-2.0mu m, has polar flagellum, can move, does not form spore or have sheath or protrusion, has no poly beta hydroxybutyrate observed, has round bacterial colony, not irregular edge, rough surface and irregular bump shape, and is white and opaque. The Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain can be applied to degrading PAHs, BAP / BGP with high molecular weight. The Pseudomonas stutzeri MT-5 strain has the degradation efficiency of 65 percent on the BGP and 59.6 percent on the BAP in 168h, and has the degradation capacity higher than related bacteria for degrading the BAP / BGP reported at home and abroad.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Aerobic denitrifying fungicide, preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN103087918AImprove adaptabilityEnhanced degradation functionTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaBacillus licheniformisFungicide
The invention provides an aerobic denitrifying fungicide. The fungicide contains pseudomonas stutzeri and bacillus licheniformis. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method and applications of the aerobic denitrifying fungicide. According to the invention, the pseudomonas stutzeri is screened out from industrial wastewater produced by leather making, and finally identified as an original bacterium. In usual, people in the field believe that the pseudomonas stutzeri is an anaerobic denitrifying bacterium, the application confirms that the original bacterium also can be subjected to efficient denitrification under aerobic conditions, thereby widening the application scope of the pseudomonas stutzeri; and in addition, when the two kinds of denitrifying fungicides are conjunctively used, the denitrification efficiency under aerobic conditions can be greatly improved.
Owner:广州市微生物研究所集团股份有限公司
Pseudomonas stutzeri and application thereof
InactiveCN106754570AEfficient removalEasy to separateTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaHigh concentrationSludge
The invention discloses a pseudomonas stutzeri and application thereof. The name of pseudomonas stutzeri is pseudomonas stutzeri XL-2 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) on November 10, 2016; the preservation number is No. 13252. The strain is obtained by taking active sludge of Chongqing Jiguanshi Sewage Treatment Plant as the raw material and carrying out repeated domestication separation by using a high-concentration nitrate nitrogen NO3-N selective culture medium. The pseudomonas stutzeri is capable of carrying out aerobic denitrification by using high-concentration NO3-N under aerobic condition; after the pseudomonas stutzeri is cultured for 20 hours, the removal rate of NO3-N of the pseudomonas stutzeri reaches up to 95.5%; the removal rate of total nitrogen (TN) can reach 84.8%; the final removal rate of COD reaches 74.5%; and the accumulation of an intermediate product, namely nitrite nitrogen (NO2-N), is avoided. In addition, the pseudomonas stutzeri has the effect of automatically gathering and settling; rod-shaped cells are embedded with each other and are gathered at the bottom of the culture medium in bulks; sludge-water separation can be rapidly achieved; the pseudomonas stutzeri has a good application prospect in the field of treatment of high-concentration nitrogen-containing wastewater.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Facultatively anaerobic denitrifying bacteria and application thereof in biological denitrification of water body
InactiveCN102220264AEfficient denitrification activityPromote growth and reproductionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a strain of facultatively anaerobic denitrifying bacteria, and the strain is named as Pseudomonas stutzeri LZ-14 and belongs to the pseudomonas stutzeri of pseudomonas. The strain was collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 10th, 2011, wherein the collection number is CCTCC No.M2011119. The strain can be used for effectively removing ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen as well as a mixture thereof so as to reduce the total concentration of nitrogen, and can be used for removing CODCr (chemical oxygen demand) in organic wastewater at the same time, thereby being suitable for treating organic wastewater of relatively low concentration, nitrite of relatively high concentration or nitrate wastewater and having wider adaptability. In the denitrification process, nitrate accumulation is avoided, while a certain amount of nitrite accumulates but can be completely degraded in 24 hours later. By using the strain, the wastewater treatment process is simple and the denitrification effect is stable. If the bacteria is used for enhancing biological removal of pollutants in water, an LZ-14 bacteria liquid is added when the bacteria stays for 8 days so as to enhance the biological removal effect, so that the CODCr in the polluted river water is reduced from 33.9 mg / L to 15.9 mg / L at a removal rate of 53.1%; and TN is reduced from 4.07 mg / L to 0.98 mg / L at a removal rate of 75.9%.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for strengthening biochemical water treatment effects by microbial preparation
ActiveCN105907673AEasy to handlePromote degradationFungiBacteriaChemical oxygen demandTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a microbial preparation which comprises pseudomonas stutzeri, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus, alcaligenes faecalis and aspergillus niger. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the microbial preparation and a method of strengthening the biochemical water treatment effects by the microbial preparation. The pseudomonas stutzeri, the bacillus subtilis, the lactobacillus, the alcaligenes faecalis and the aspergillus niger in the microbial preparation can form dominant bacterial communities in a sewage treatment system, strengthen the treatment effects of COD (chemical oxygen demand) and the like in sewage, and particularly can form advantages in a printing and dyeing sewage treatment system after matching with aniline-degrading bacteria and aerobic denitrifying bacteria, so that printing and dyeing sewage COD, aniline, chroma and total nitrogen are rapidly degraded in a targeted manner, and the printing and dyeing sewage treatment effects are strengthened.
Owner:广州市佳境水处理技术工程有限公司
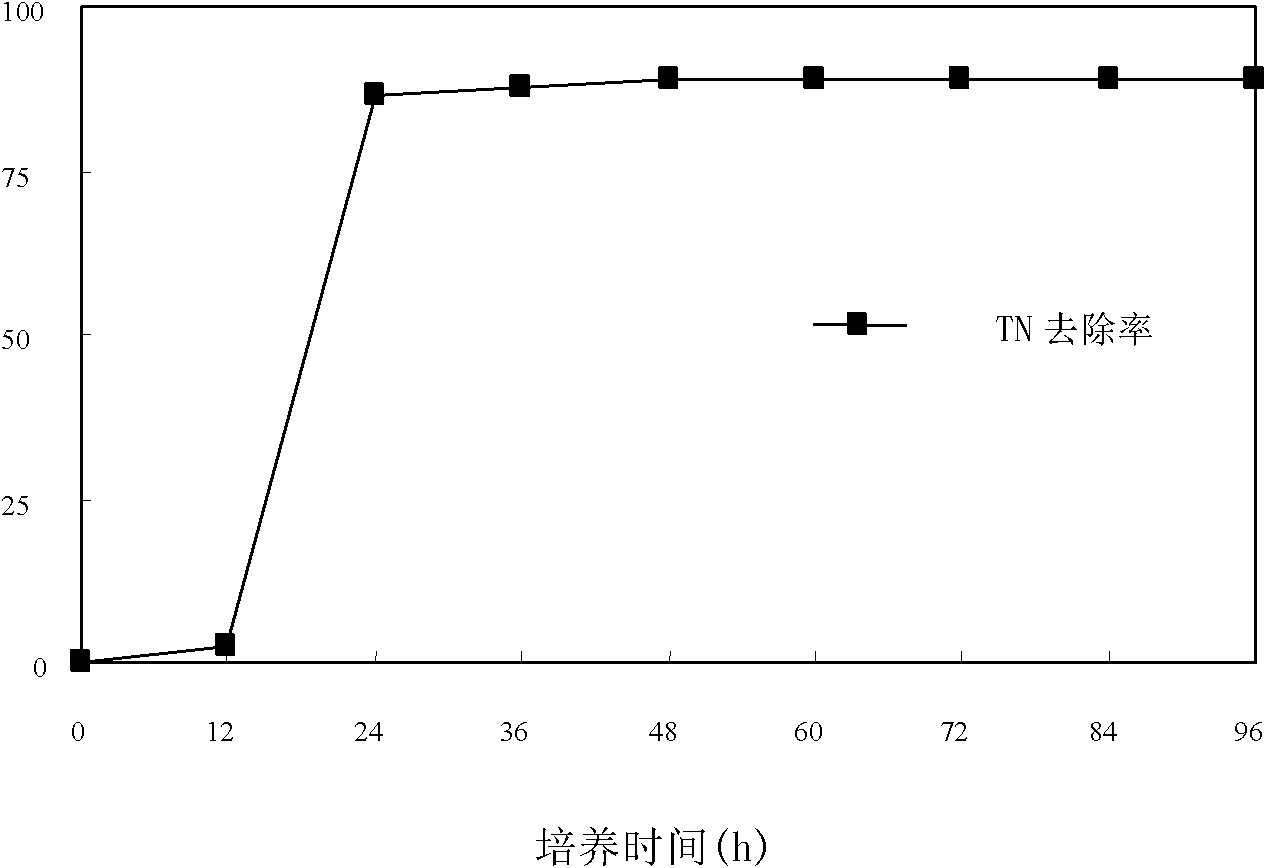
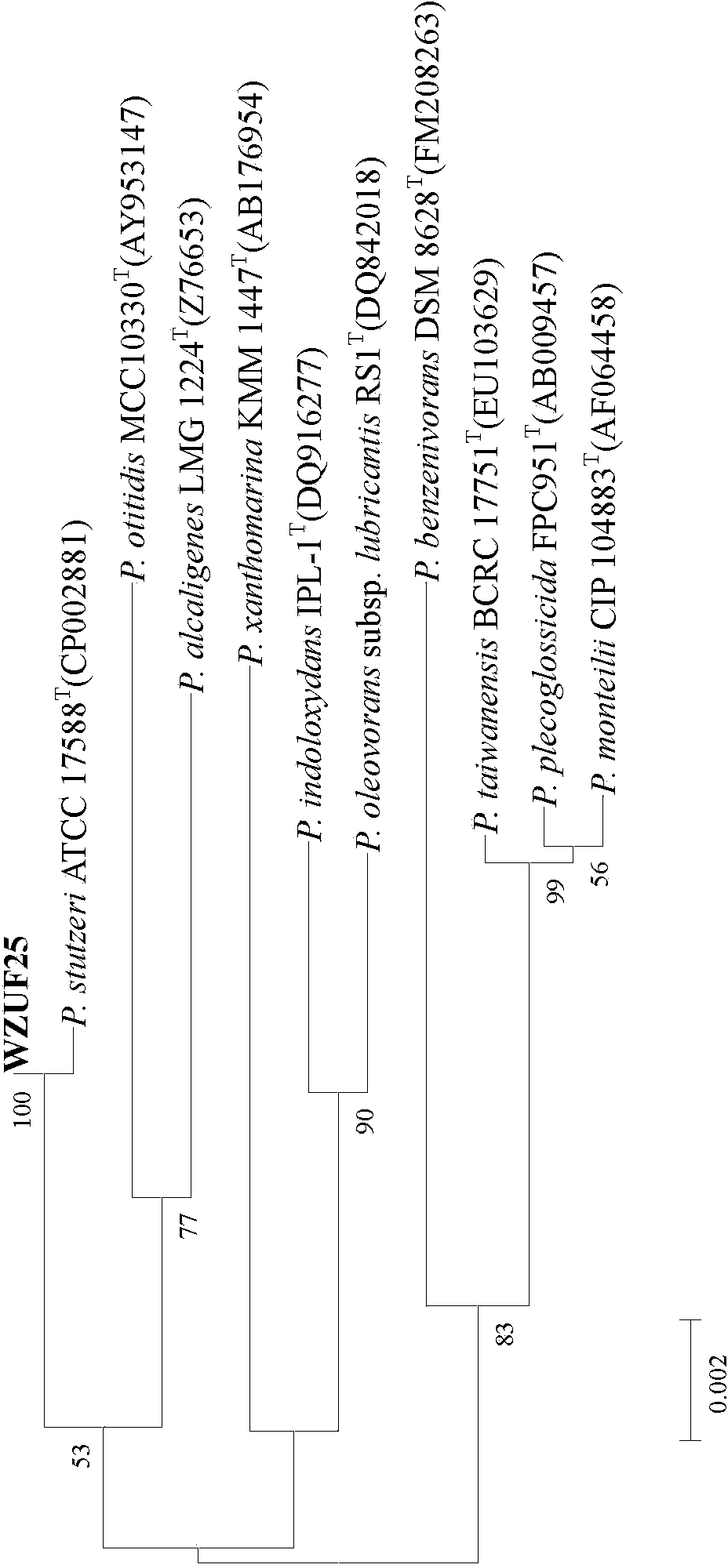
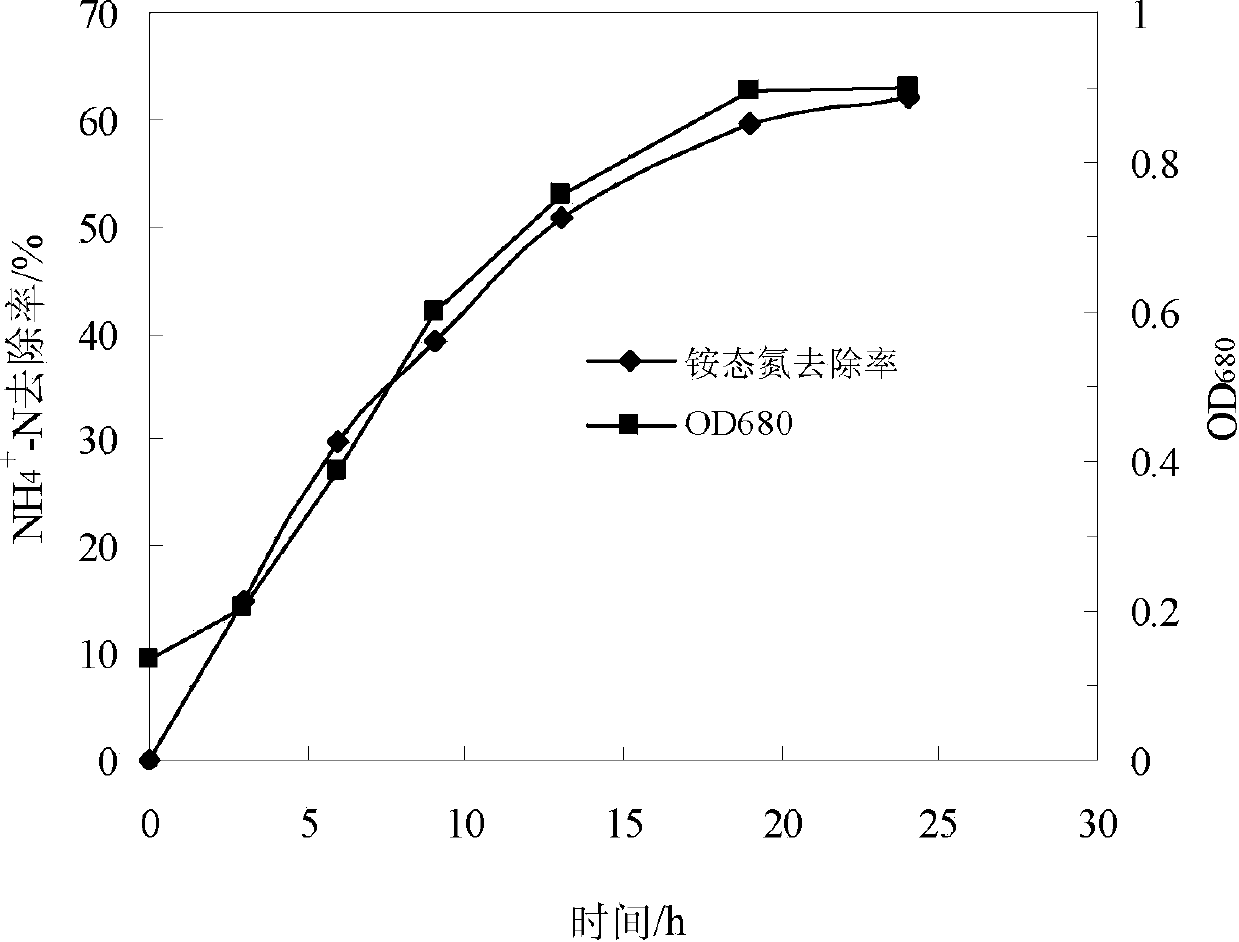
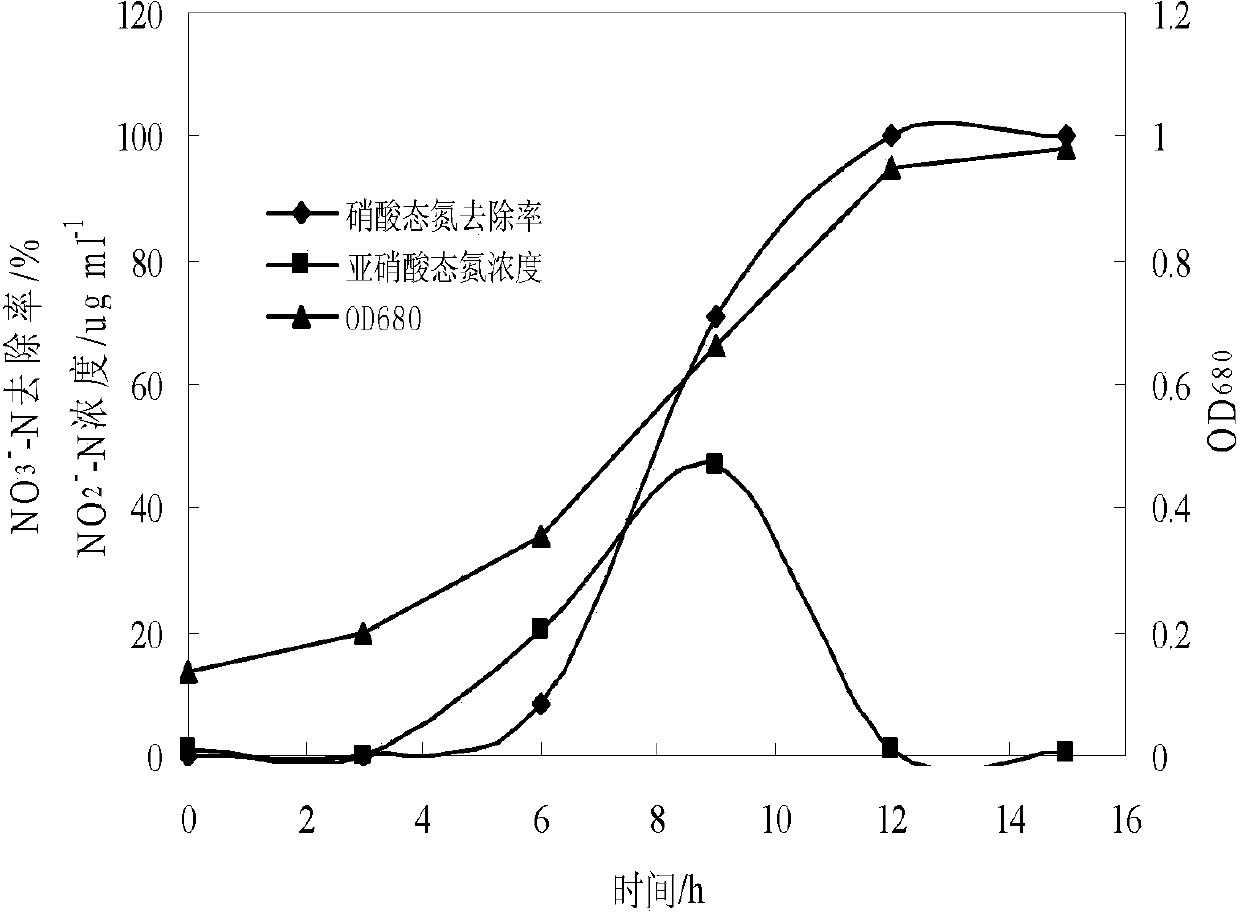
Pseudomonas stutzeri and its culture, immobilization and use
InactiveCN103497908AHigh removal rateWide pH rangeBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobiological cultureDenitrification
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
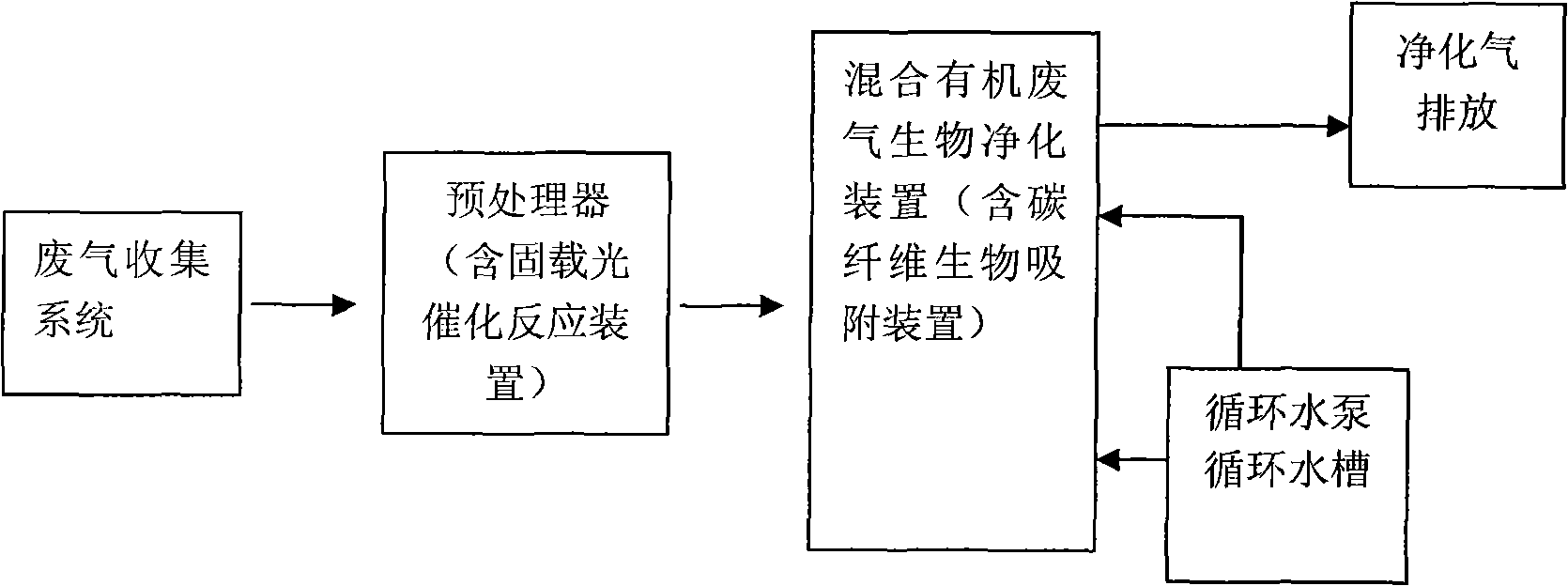
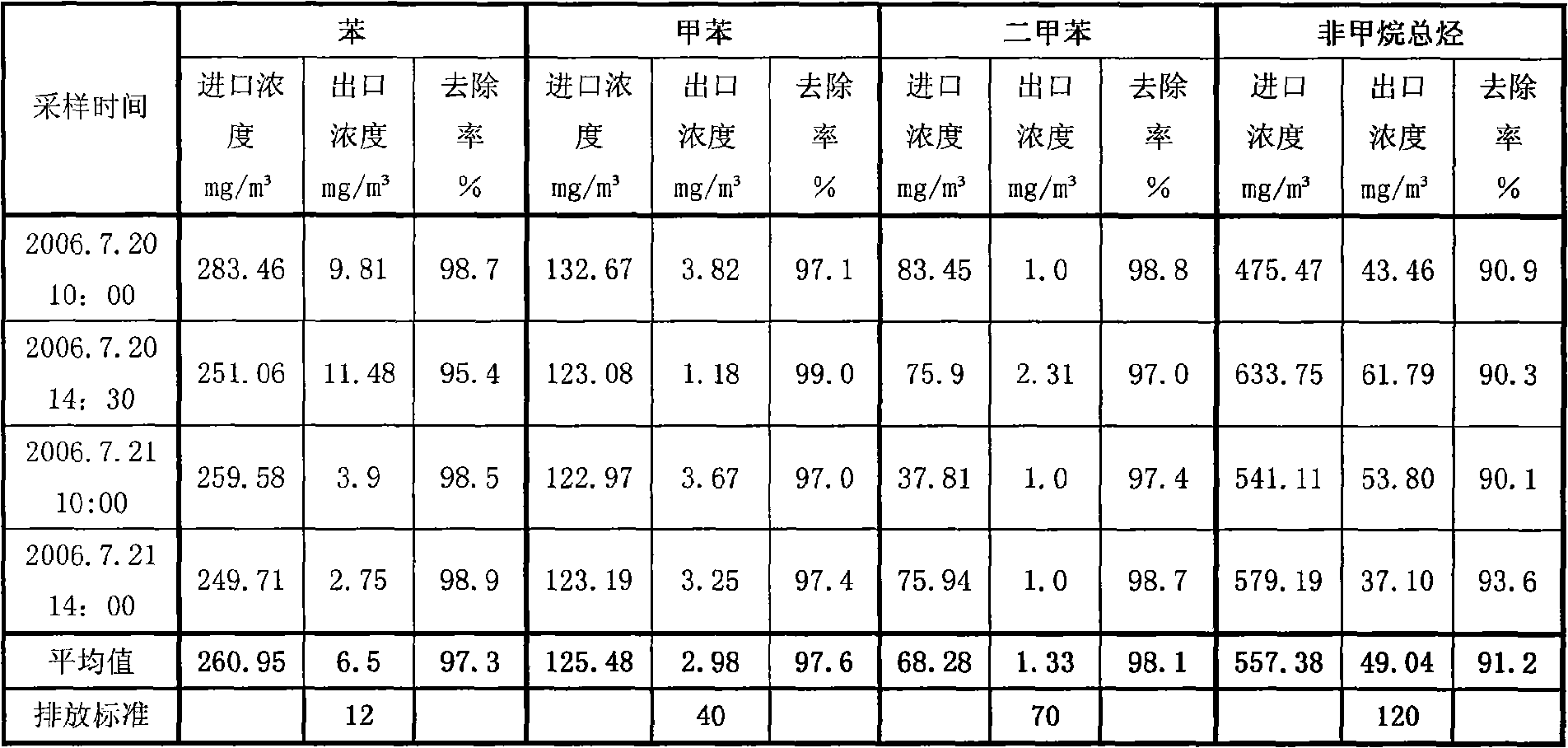
Culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas
The invention relates to a culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas. The method comprises the following steps: a), culturing a first strain; b), carrying out the combined inoculation of the first strain and a second strain and using tap water to prepare the sludge concentration of the mixed strains; and c), using mixed organic matter in the waste gas as a substrate to be cast into an insition culture medium so as to culture and train insitions. The first strain is prepared by culturing and training from activated mud taken from a printing and dyeing sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain of flavobacterium and Bacillus cereus, and the second strain is prepared by collecting activated mud collected from a secondary sedimentation tank of a petrochemical sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain comprising the flavobacterium, the Bacillus cereus, xylose oxidase Achromobacter and Pseudomonas stutzeri. The method facilitates the balanced growth of various cultured microorganisms and can simultaneously decompound various target configuration compounds at high efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUANFA ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD
Pseudomonas stutzeri with aerobic denitrification function and use thereof
ActiveCN109943497AHigh activitySmall impact of speciesTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemistryDegradation process
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a strain of pseudomonas stutzeri ZH-14 with an aerobic denitrification function. The preservation number of the pseudomonas stutzeriZH-14 is CCTCC NO:M2018730. The pseudomonas stutzeri can be applied to degrading ammonia nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen or nitrite nitrogen or COD in nitrogen-containing sewage. The pseudomonas stutzeri ZH-14 has the advantages that the pseudomonas stutzeri ZH-14 has the aerobic denitrification function and a heterotrophic nitrification function, and the accumulation of the nitrite nitrogen with the extremely low content is involved in the degradation process; nitrite can be directly utilized for growth metabolism, the activity of nitrate reductase of the pseudomonas stutzeri ZH-14 is still high in an environment with a low carbon-nitrogen ratio, the aerobic expression is less influenced by the types of adopted carbon sources, and the carbon source problem in the process of utilizing aerobic denitrification bacteria for treating nitrogen-containing wastewater is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Pseudomonas stutzeri for efficiently processing nitrogen-containing sewage and application thereof
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Degradation strain JN4 for petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge and application thereof
ActiveCN108048374APromote degradationOptimize the microbial systemBacteriaWater contaminantsSludgeGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
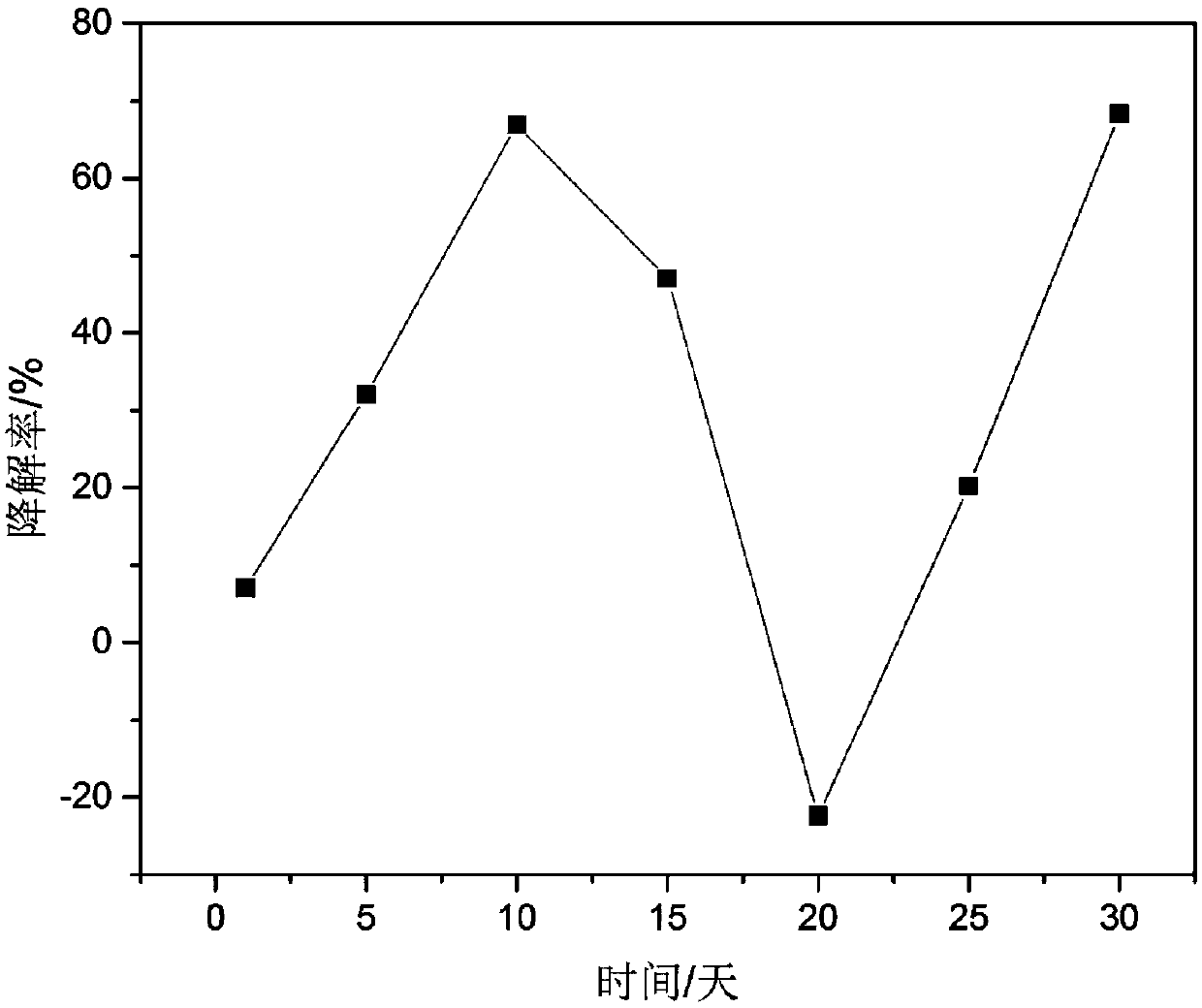
The invention discloses a highly effective degradation strain JN4 for petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of bioremediation. The degradation strain JN4 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC NO.14975, and the classification number is Pseudomonas stutzeri. The strainJN4 with a petroleum hydrocarbon degradation function which is disclosed by the invention is applied to treatment of oily sludge by degrading petroleum hydrocarbons. The degradation rate of the bacteria on total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in oily sludge is 71.05 percent within 30 days. The single strain provided by the invention has obvious degradation capability on n-C10 to n-C30, and GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) analysis indicates that the strain has strong degradation capability on cycloalkane naphthane, indane and d-homoandrostane. The optimum degradation conditions of the bacteria on petroleum pollutants are 25 DEGC to 40 DEG C and the pH value of 5 to 11. The biological method is used in oily sludge remediation technology, and has the advantages of high effectiveness, low cost, environment-friendliness and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Lincomycin production wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN106746155AEfficient and stable removalImprove processing efficiencyTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWastewaterPseudomonas stutzeri
The invention relates to a lincomycin production wastewater treatment method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out pretreatment on lincomycin production wastewater by an advanced oxidation technology; (2) carrying out coagulating sedimentation on an oxidation effluent, filtering to remove generated precipitates; (3) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on the filtered effluent; and (4) carrying out biological contact oxidation process on an anaerobic effluent while pouring salt-tolerant COD-removal strain. The salt-tolerant COD-removal strain is Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and / or Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and was collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015. The collection number is CGMCC No. 10938 and CGMCC No. 10940. By the technology of advanced oxidation-coagulating sedimentation-anaeronic biochemical treatment and by pouring specific salt-tolerant COD-removal strain into a contact oxidation unit, antibiotic in wastewater can be resisted, and efficient stable removal of COD in wastewater is realized. The method of the invention has characteristics of simple process, high treatment efficiency, low treatment cost and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Composite microbial agent for treating domestic garbage and method for treating domestic garbage by using composite microbial agent
InactiveCN106978370AIncrease functional diversityImprove applicabilityFungiBacteriaPseudomonas putidaMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent for treating domestic garbage and a method for treating the domestic garbage by using the composite microbial agent. The composite microbial agent for treating the domestic garbage is prepared from the following components: brevendimonas diminuta, pseudomonas stutzeri, pseudomonas maltophilia, pseudomonas fluorescens, pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, candida lipolytica, schizosaccharomyces pombe, schizosaccharomyces octosporus, bacillus megatherium, bacillus subtilis, bacillus cereus, alcaligenes faecalis, clostridium beijerinckii, achromobacter denitrificans, nocardia coralline, and the like, wherein the parts by weight of the brevendimonas diminuta are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas stutzeri are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas maltophilia are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas fluorescens are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas putida are 1-5, the parts by weight of the candida utilis are 1-5, and the parts by weight of the candida lipolytica are 1-5.
Owner:哈尔滨明慧生物技术开发有限公司
Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102212124ABroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsShigella flexneriScylla paramamosain
The invention relates to genetic engineering of Scylla paramamosain, and provides a Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: building a recombinant expression vector for the Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor; introducing the recombinant expression vector into host cells, and carrying out induced expression on the host cells to obtain an expression product; and separating and purifying the expression product to obtain a recombinant protein, namely the Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. The Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor has obvious growth inhibition and sterilization effects on Gram-negative bacteria such as Shigella flexneri, Vibrio alginolyiicus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Pseudomonas stutzeri and Pseudomonas fluorescens and Gram-positive bacteria such as Corynebacterium glutamicum, and has a potential application value in the preparation of antibacterial medicaments and antimicrobial additives for animal feed.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Process for producing agricultural wastes converted biological feedstuff
InactiveCN101171953AEliminate polluted environmentTake advantage ofFood processingAnimal feeding stuffGenus RathayibacterMicrobial transformation
The invention discloses a preparation method for transforming the agricultural waste into biological feed through microorganism. The expanded and cultured bacteria including one plant of Pseudomonas stutzeri, two plants of Bacillus subtilis, and one plant of Lactobacillus are inoculated into the agricultural waste (dried chicken manure which occupies 40 to 65 percent, crushed corn stalk or rice straw occupies 10 to 25 percent, and pineapple slug occupies 15 to 35 percent) with water content of 25 to 40 percent according to the inoculum size of 1 to 5 percent, evenly mixed, and packaged into a closed vessel, the agricultural waste is compressed, without air inside, sealed, and fermented for 48 to 72 hours under the temperature of 20 to 38 DEG C, the culture is stopped, and then the agricultural waste is positioned at a shady and dry position at the room temperature; the pH value of the fermented agricultural waste is lower than or equal to 3.5, the color of the finished product is grey, and has a slight golden yellow, the smell is fragrant, and the agricultural waste has lactic acid taste. The finished product fermented in a closed vessel can be stored for 3 to 6 months at the room temperature, and the finished product can only be taken out of the closed vessel when being required to use. The fermented agricultural waste can be used as the feed for cows, pigs and java tilapias, etc.
Owner:AGRI BIO TECH INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microbial preparation for water deodorization and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105174491ASolve efficiency problemsSolving activityBiological water/sewage treatmentBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention provides a microbial preparation for water deodorization. The active ingredients of the microbial preparation are prepared from, by weight, 25-35 parts of thiobacillus denitrificans, 15-25 parts of bacillus pumilus, 15-25 parts of candida utilis, 10-20 parts of lactobacillus acidophilus and 10-20 parts of pseudomonas stutzeri. After the microbial preparation is prepared, black and odorous sewage can be cleaned through the steps of sewage pretreatment, sewage re-treatment and microbial oxidation. The microbial preparation has the advantages that activity is high, reproduction is quick, environment friendliness is achieved, pollution is avoided, cost is low, and strains are reasonable in compatibility, symbiotic, coordinated and not antagonistic. The water deodorization efficiency is high, and especially the good removal effect is achieved for hydrogen sulfide and ammonia gas.
Owner:南京润中生物科技有限公司
Efficient sewage treatment microbial agent
InactiveCN105462903APromote degradationPromote decompositionFungiBacteriaSynechococcusMicrobial agent
The invention discloses an efficient sewage treatment microbial agent. The efficient sewage treatment microbial agent is prepared from, by weight, 2-4 parts of nitrosobacteria, 10-20 parts of bacillus subtilis, 8-15 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 5-10 parts of bacillus megatherium, 2-8 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa, 2-10 parts of candida lipolytica, 2-8 parts of deoxidized paracoccus, 2-6 parts of pseudomonas stutzeri, 2-10 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae, 1-4 parts of aspergillus niger, 0.1-0.6 part of yeast extract, 2-6 parts of peptone, 0.1-0.5 part of glucose, 8-15 parts of kaolin, 2-5 parts of aluminum polychlorid, 0.1-0.5 part of FMEE and a proper amount of water. The efficient sewage treatment microbial agent is suitable for treating industrial waste water, breeding waste water and the like, all strains are in cooperation, symbiotic coordination is achieved, high activity is achieved, and reproduction is fast. The efficient sewage treatment microbial agent is put in the waste water to be treated, the degradation effect can be effectively accelerated, the treatment water quality can be greatly improved, operating cost can be reduced, the treated water reaches the standard to be drained, and damage to environment is reduced.
Owner:南京国龙生物科技有限公司
Nitrobacter winogradsky and nitrobacteria-denitrifying bacteria complex microbial inoculants, production method and application
ActiveCN105274029AShorten fermentation timeReduce incubation timeBacteriaWater contaminantsNitrifying bacteriaNitrobacter
The invention discloses nitrobacter winogradsky and nitrobacteria-denitrifying bacteria complex microbial inoculants, a production method and application. Nitrobacter winogradsky is deposited at the China Center for Type Culture Collection with the accession number of ((i) Nitrobacter Winogradsky i ( / i)) Y3-2, CCTCC NO: M2014203. The nitrobacter winogradsky has a function of effectively treating nitrite, and is mixed with nitrosomonas europaea and pseudomonas stutzeri to obtain the complex microbial inoculants, and the complex microbial inoculants can efficiently remove nitrogen in water, and can be used for treating aquaculture water, livestock breeding sewage or industrial sewage.
Owner:WUHAN SHUIZHIGUO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Pseudomonas stutzeri and application thereof to water body dephosphorization
InactiveCN102061275AAbundant resourcesAdaptableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSocial benefitsEutrophication
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas stutzeri and application thereof to water body dephosphorization. The Pseudomonas stutzeri YG-26 provided by the invention has a preservation number of CGMCC No.4093. An immobilized bacterium can be obtained by using the YG-26 embedded by sodium alginate and polyvinyl alcohol. The strain YG-26 and the immobilized bacterium thereof can be used for maximumly removing phosphorus in sewage so as to effectively prevent and control the occurrence of water body nutrition enrichment. By using the strain or the immobilized bacterium provided by the invention to perform water body treatment, the removal ratio is high, the method is simple in operation, and the cost is low along with economical efficiency and environmental protection, so the strain or the immobilized bacterium can be widely applied to further treatment of the sewage, and have significant economic, environmental and social benefits.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pseudomonas stutzeri with both hexavalent chromium removal and aerobic denitrification performances and application of pseudomonas stutzeri
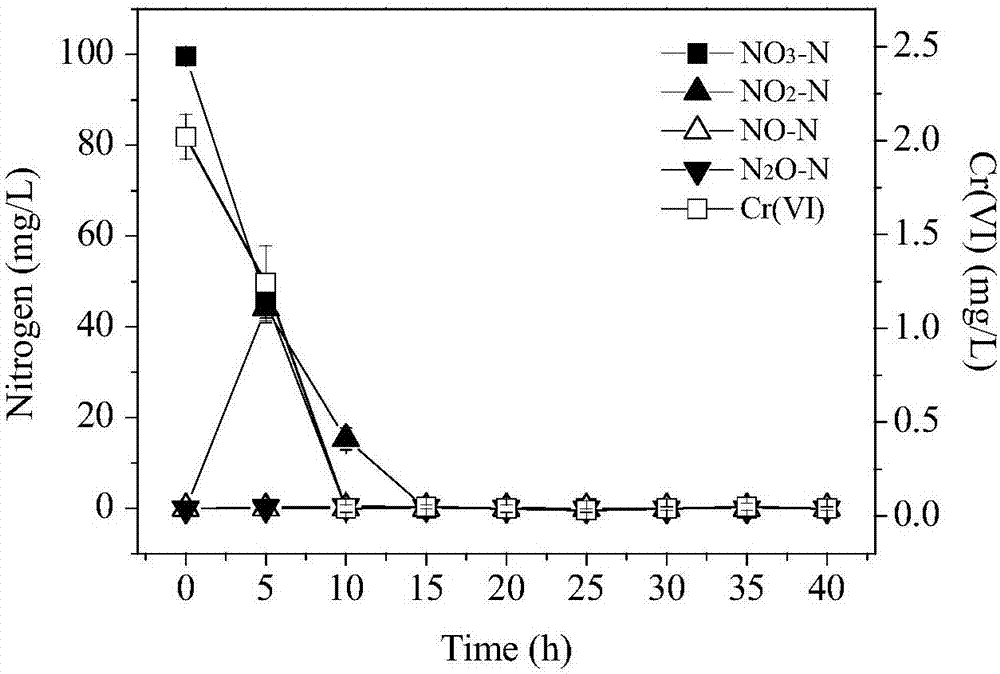
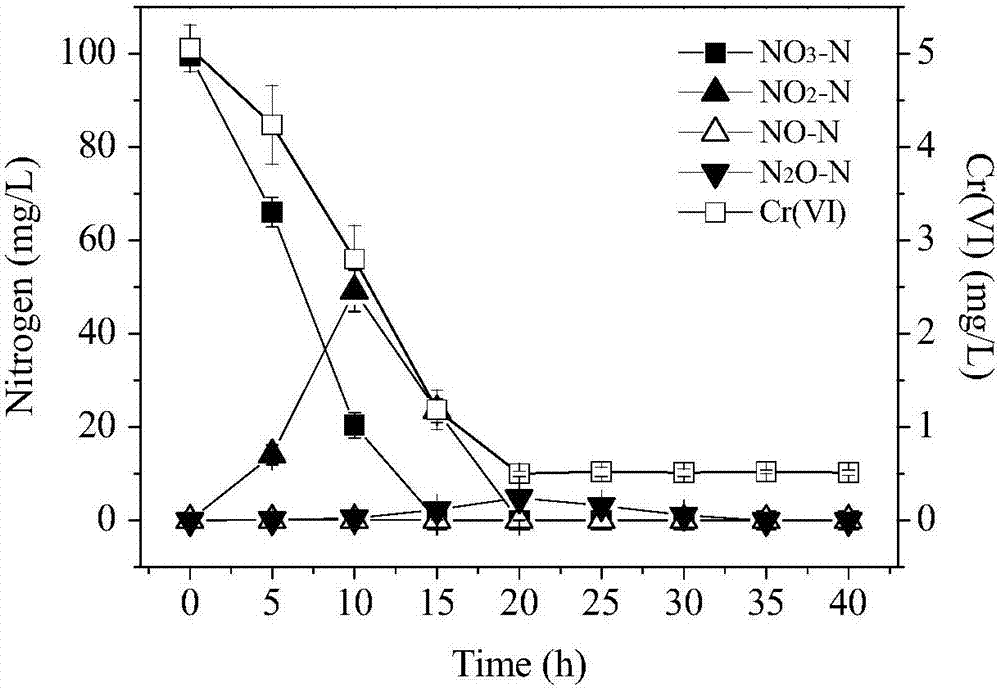
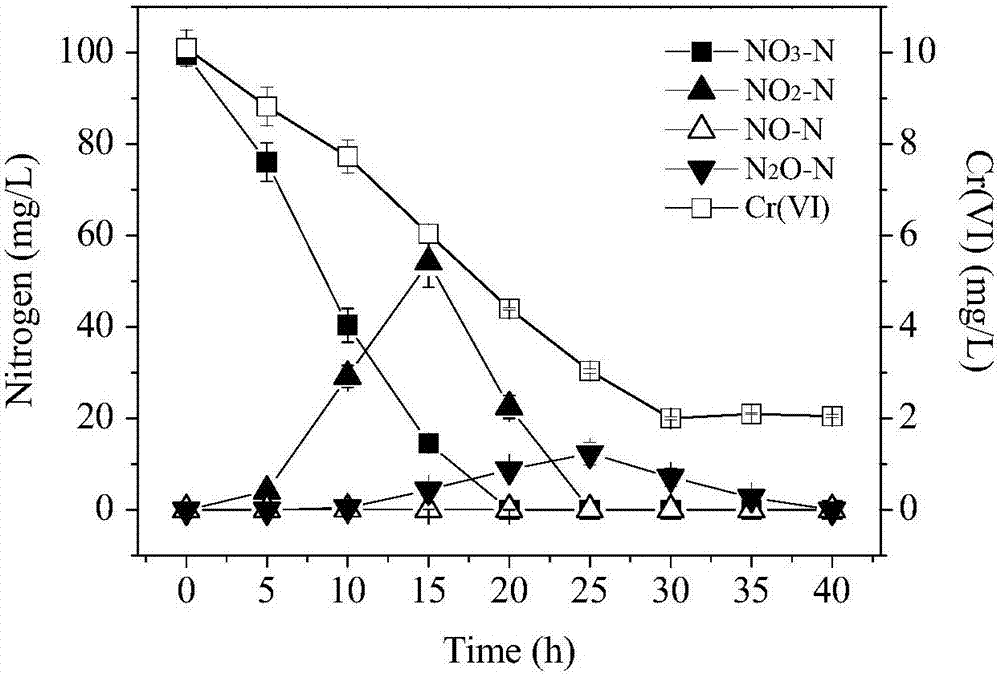
ActiveCN107236687AAnoxic denitrification is needed to solve biological denitrificationSolve processingBacteriaWater contaminantsOxygenMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to pseudomonas stutzeri with both hexavalent chromium removal and aerobic denitrification performances and an application of the pseudomonas stutzeri in sewage treatment. The preservation number of the pseudomonas stutzeri is CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) No. 14062, and the pseudomonas stutzeri has both capabilities of hexavalent chromium removal and denitrification in the aerobic condition. When hexavalent in sewage is within 0-10mg / L in concentration, a strain can take nitrate nitrogen as the sole nitrogen source, the removal rate of the nitrate nitrogen can reach 100% in the aerobic condition, and the removal rate of the hexavalent can reach 80% or even 90% above. The pseudomonas stutzeri and the application thereof have the advantages of convenience in operation, high denitrification efficiency and the like, and great significance is achieved in optimizing a sewage treatment system and weakening the effect of the hexavalent chromium on the sewage denitrification system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com