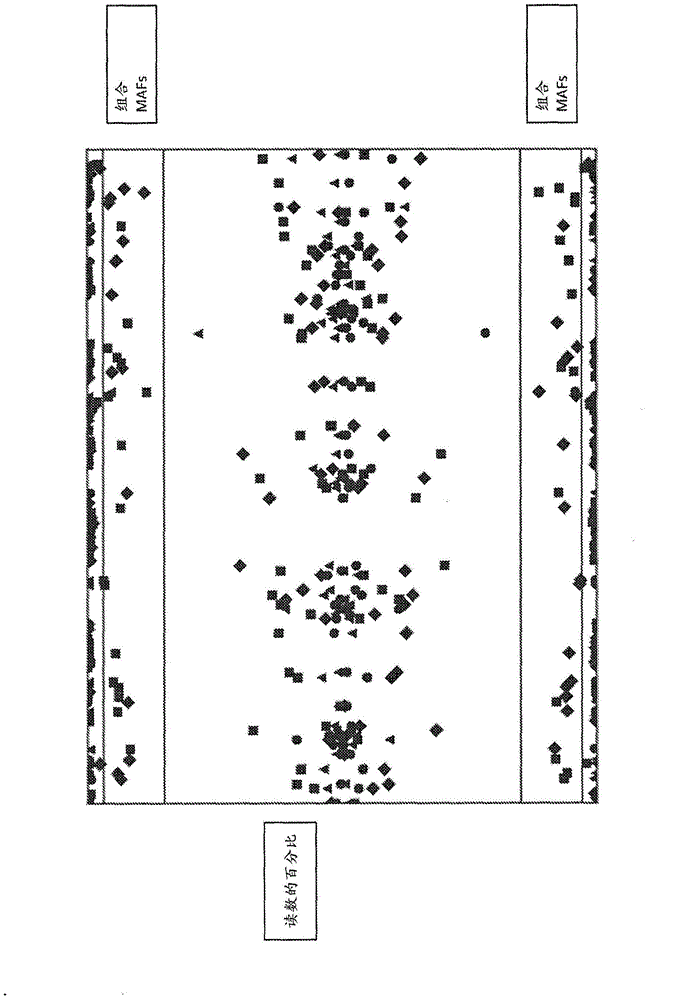
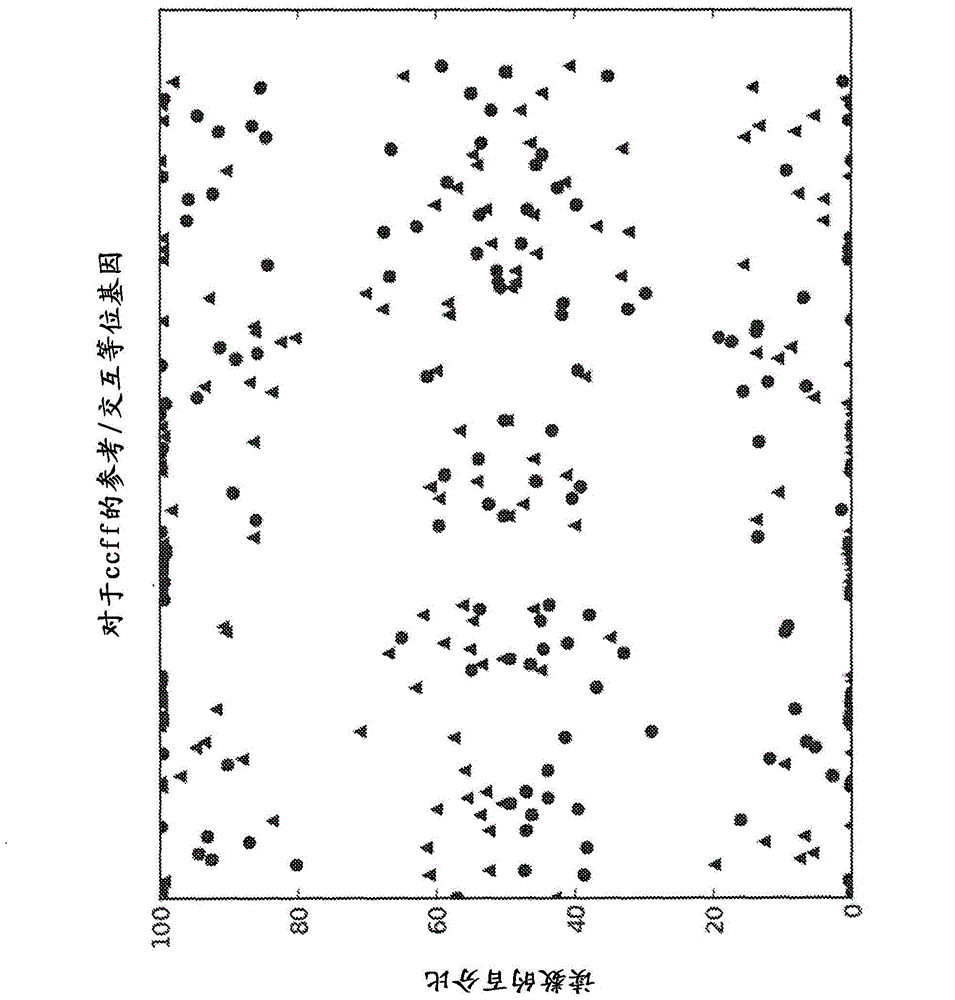
Methods of detecting diseases or conditions
A technology of pathological conditions and diseases, applied in the field of identifying markers of diseases or pathological conditions, can solve the problem of important information loss and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0405] Representative method for separating phagocytic cells with a DNA content of 2n from non-phagocytic cells and analyzing expression profiles 1
[0406] 1. Separate blood samples into plasma and buffy coat including WBC samples. Plates were coated with avidin to accept WBC samples.
[0407] 2. Add biotinylated antibody to non-phagocytic blood cells (such as T cells) in the wells, incubate at RT for 30 minutes, and wash the wells.
[0408] 3. Add magnetic beads.
[0409] 4. Add WBC blood sample.
[0410] 5. Incubate at 37°C (30 minutes - 1 hour).
[0411] 6. After the beads have been phagocytized by the phagocytes and the avidin-biotin-antibody has bound to the non-phagocytic cells, place the plate on a magnet and wash (phagocytes internalizing the magnetic beads and non-phagocytic cells bound to the antibody will be retained; all other cells will be washed away).
[0412] 7. Remove magnet and collect phagocytic cells and separate into phagocytic cells with DNA equal t...
Embodiment 2
[0414] Representative method for separating phagocytic cells from non-phagocytic cells II
[0415] 1. Separate blood samples into plasma and buffy coat including WBC samples.
[0416] 2. Cytospin WBC onto glass slides.
[0417] 3. Fix cells in acetone / methanol (-20°C for 5 minutes).
[0418] 4. Stain with hematoxylin and eosin and anti-T cell antibody.
[0419] 5. Isolation of T cells (non-phagocytic) and macrophages (phagocytic) using laser capture microscopy (LCM). Divide into phagocytic cells with DNA equal to 2n and DNA greater than 2n. Non-phagocytic and phagocytic cells with DNA equal to 2n are called cells with DNA equal to 2n.
Embodiment 3
[0421] Representative method for separating phagocytic cells from non-phagocytic cells III
[0422] 1. Separate plasma from whole blood.
[0423] 2. Isolation of non-phagocytic cells (such as T cells) and phagocytic cells (such as neutrophils and / or macrophages and / or monocytes) from whole blood using magnetic antibody-conjugated beads. Divide into phagocytic cells with DNA equal to 2n and DNA greater than 2n. Non-phagocytic and phagocytic cells with DNA equal to 2n are called cells with DNA equal to 2n.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com