Method for artificially breeding great amounts of pea aphids
A pea aphid and a large number of technologies are applied in the field of artificial mass propagation of pea aphid, and can solve the problems of reducing the propagation speed of pea aphid, broad bean wilting, soil acidification and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
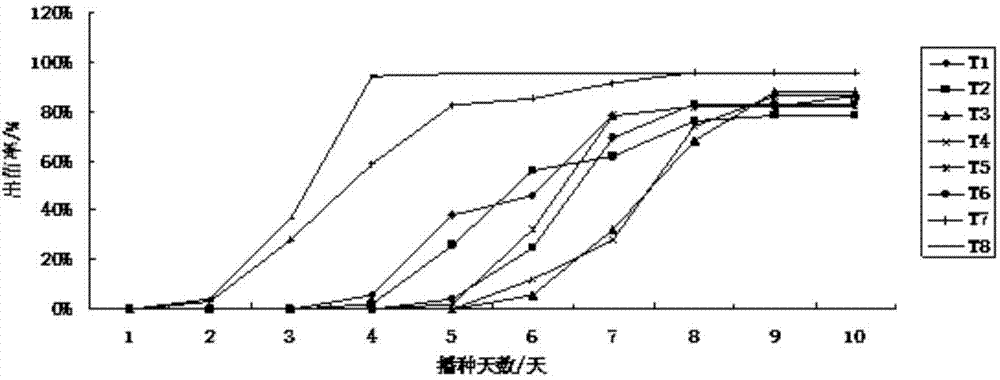
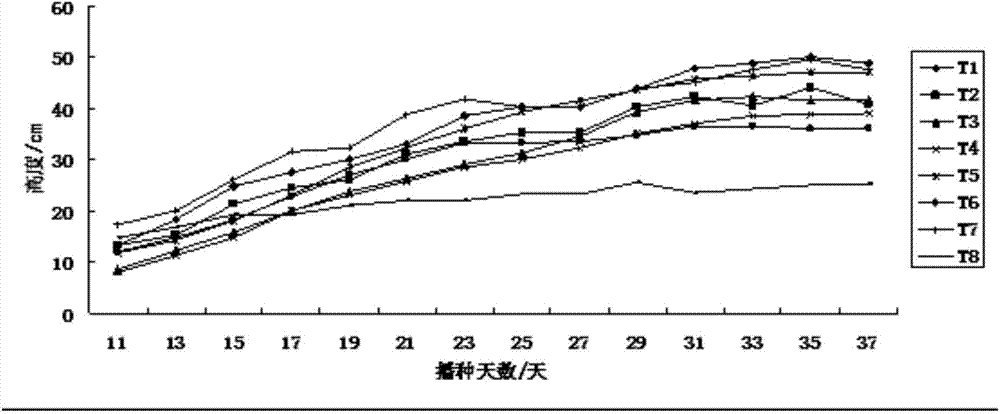
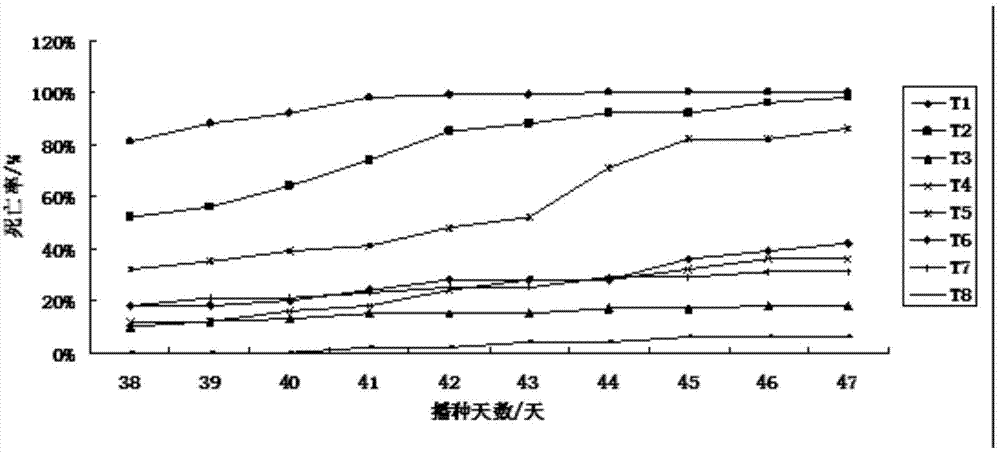
[0062] Embodiment 1: the method for artificially multiplying pea aphids in large quantities of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0063] a. Seed treatment: soak the broad bean seeds in water for 24 hours, and air-dry them for 12 hours to prepare for sowing;
[0064] b. Filling the substrate and sowing: Fill the seedling raising floating tray with moist tobacco seedling raising substrate that is kneaded into a mass and then loosened until the substrate plane is consistent with the floating tray plane; select broad bean granules with full grains, and insert one seed into each seedling raising hole ;
[0065] c. Floating dish enters water: in black water dish, fill water 50cm deep, add the tobacco compound fertilizer of 20g active ingredient N:P:K=10%:10%:20% in water dish; Put the pan into a black water pan with sufficient water and fertilizer;
[0066] d. Emergence inoculation: 3 days after sowing, the broad beans basically emerged, and a small number of u...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: In May, when field aphids begin to occur, predatory natural enemies need to be multiplied in large quantities, which belongs to the expansion breeding mode. The natural enemy insects reproduce in large numbers, and the number increases sharply. Each time the seedlings are raised, a floating tray is added until the seedling space is full, and then enters the stable multiplication mode. In the expansion breeding mode, the food demand continued to increase, and 6 batches of seedlings were maintained, with a 30-day cycle. Each batch of seedlings provides food for 5 days, that is, the broad bean seedlings are divided into 5 parts, and one part is cut every day (only the stem tips covered with pea aphids are cut), and put into the natural enemy insect insect breeding box. If pea aphids are not enough to use, natural enemy insects will ensure the full utilization of limited food through natural selection by survival of the fittest.
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: In August, a large number of aphids occurred in the field, and the natural enemy insects produced at full capacity, which belonged to the stable multiplication mode. During this period, the seedling space was operating at full capacity, the amount of seedlings remained basically unchanged, and the production of pea aphids also remained basically unchanged. Still maintain 6 batches of seedling cultivation, a cycle of 30 days, and each batch of seedlings provides food for 5 days. When the pea aphid cannot provide enough food, the excess natural enemy insects are released in the field to ensure the expansion of the production of the remaining insects.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com