Method for applying nitrogen to summer corn in different areas of Beijing area in consideration of area yields and environmental risks
An environmental risk and summer corn technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve problems such as increased errors, difficulty in calculating specific values, and outdated research methods, so as to prevent and control non-point source pollution, minimize high yield and environmental pollution, and promote coordinated development. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1. The method of dividing nitrogen application threshold for summer maize in Beijing area that takes into account regional yield and environmental risks:
[0028] 1) Divide the medium-low and medium-high yield areas according to the target yield, and design the nitrogen application plan
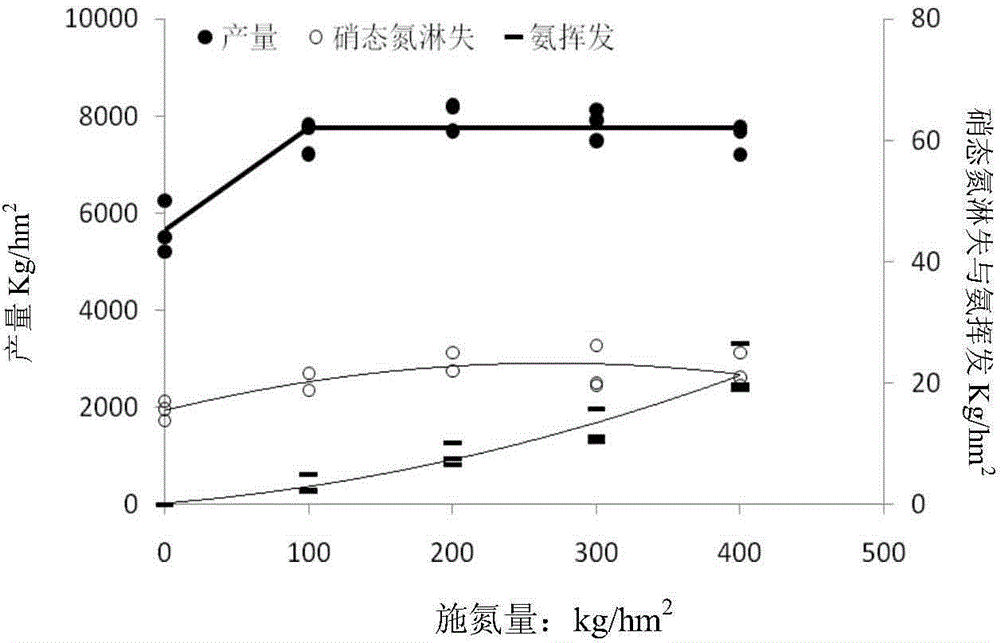
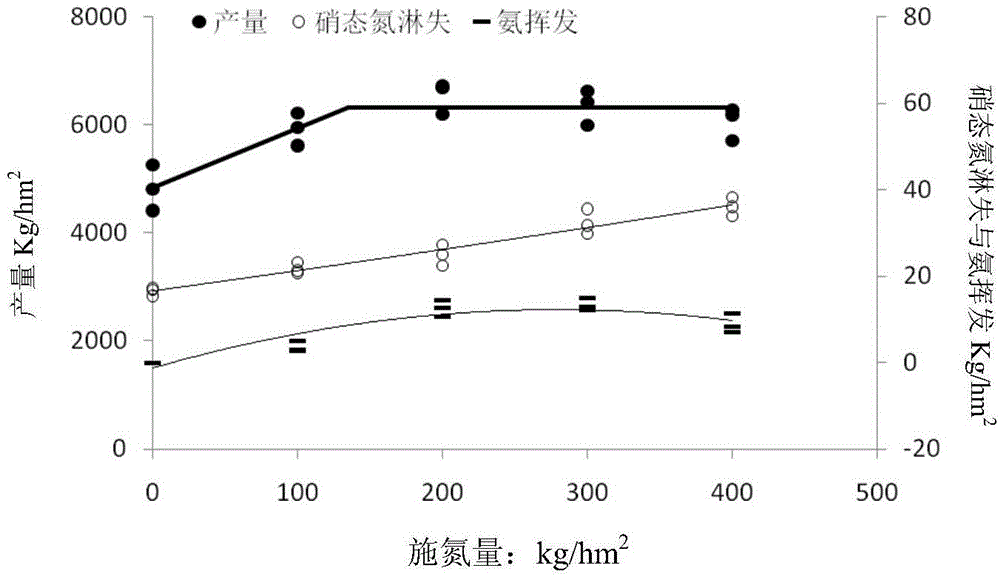
[0029] According to the different levels of output in different regions of Beijing area, it is divided into high-yield areas and low-medium-yield areas. According to the multi-year output data of Beijing area, summer corn ≥6800kg / hm 2 It is a medium and high production area, 2 It is a middle and low production area. Because the soil fertility is different in the middle-high-yield area and the middle-low-yield area, the characteristics of soil fertility are first analyzed.
[0030] It can be seen from Table 1 and Table 2 that the main nutrient index contents of the relevant soils in the middle-high and middle-low-yielding areas show a trend of higher and lower, and the soil is slightl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com