The method of indoor rearing of predatory dirty fly larvae
A technology for larvae and filth flies, which is applied in the field of culture substrates for indoor breeding of predatory larvae of filth flies, can solve the problems of unreported prey density, and achieve the effects of facilitating adult eclosion, shortening the total development period, and low production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
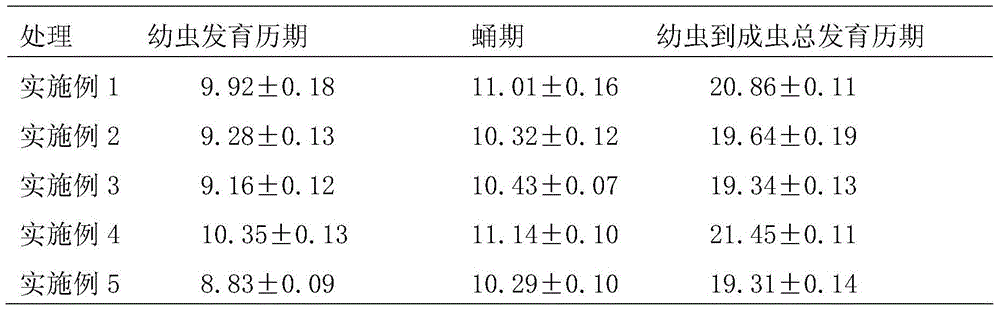
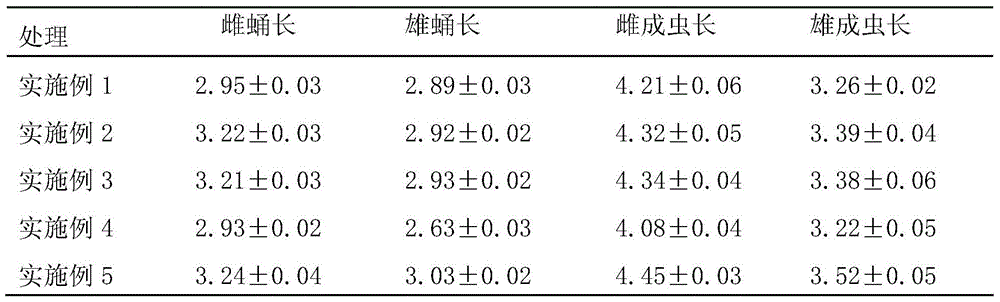
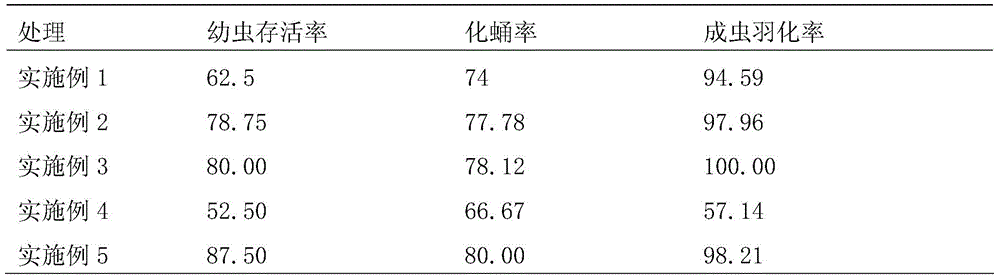
[0030] In the feeding method of the present embodiment, the culture substrate is made of the following raw materials in the ratio of parts by volume: 2 parts of coconut bran; 1 part of peat. Add water to the culture substrate and stir evenly, it is only necessary to be moist without outflowing water. The larvae of the emaciated dirty fly and its prey, the larvae of the fungus gnat, live in the culture medium. The culture medium that each emaciated dirty fly larva occupies is 0.5 cubic centimeter. 1-3 day-old thin and weak fly larvae, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 3 3rd-instar fungus mosquito larvae; from 4-day-old to pupal stage, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 5 4th-instar fungus mosquito larvae every day .
Embodiment 2
[0032] In the breeding method of this embodiment, the culture substrate is made of the following raw materials in the ratio of parts by volume: 1 part of peat; 3 parts of mushroom dregs; 2 parts of sawdust. Add water to the culture substrate and stir evenly, it is only necessary to be moist without outflowing water. The larvae of the emaciated dirty fly and its prey, the larvae of the fungus gnat, live in the culture medium. The culture medium that each emaciated dirty fly larva occupies is 2 cubic centimeters. 1-3 day-old thin and weak fly larvae, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 5 2nd-instar fungus mosquito larvae; from 4-day-old to pupal stage, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 7 third-instar fungus mosquito larvae every day .
Embodiment 3
[0034] In the breeding method of the present embodiment, the culture substrate is made of the following raw materials in the ratio of parts by volume: 1 part of peat; 7 parts of vermiculite; 5 parts of mushroom dregs; 3 parts of sawdust. Add water to the culture substrate and stir evenly, it is only necessary to be moist without outflowing water. The larvae of the emaciated dirty fly and its prey, the larvae of the fungus gnat, live in the culture medium. The culture medium that each emaciated dirty fly larva occupies is 1.5 cubic centimeters. 1-3 day-old thin and weak fly larvae, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 7 3rd-instar fungus larvae; from 4-day-old to pupal stage, each thin and weak fly larva was fed with 9 second-instar fungus larvae per day .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com