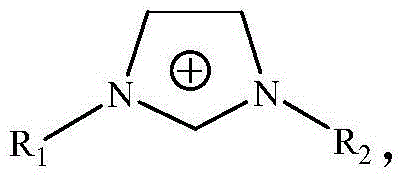
Method for efficiently dissolving full components of plant fiber
A plant fiber, full-component technology, applied in the field of plant fiber treatment, can solve the problem of inability to efficiently dissolve cellulose and lignin, and achieve the effect of reducing use and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Add 2.0g of eucalyptus powder into a 100mL clean and dry reaction vessel, add 50g of different types of ionic liquid aqueous solutions with a mass fraction of 90%, and stir magnetically in a microwave instrument with a power of 500W, the stirring speed is 200rpm, and the temperature is controlled. After reacting at 170°C for 20 minutes, cool down to room temperature and centrifuge to obtain plant fiber solution and undissolved solid matter. The solid matter is washed and dried to obtain a dissolved residue, and the dissolution rate is calculated.
[0026] Under the conditions of different kinds of ionic liquid aqueous solutions, the dissolution rates of plant fibers are shown in Table 1:
[0027] Table 1 Dissolution rate of plant fiber under the condition of different kinds of ionic liquid aqueous solution
[0028] Types of Ionic Liquids
[Mmim] DMP
[Amim] Cl
[Bmim] Cl
[Emim] Ac
Plant fiber dissolution rate (%)
92.9
58.4
47.6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 2.0g of eucalyptus powder was added to a 100mL clean and dry reaction vessel, and 50g of [Mmim]DMP ionic liquid aqueous solution of different concentrations (mass fractions) were added, and magnetically stirred in a microwave instrument with a power of 500W, and the stirring speed was 200rpm. Control the temperature at 170°C, react for 20 minutes, cool down to room temperature, and centrifuge to obtain a plant fiber solution and undissolved solid matter. The solid matter is washed and dried to obtain a dissolved residue, and the dissolution rate is calculated.
[0036] Under the conditions of different concentrations of ionic liquid aqueous solution, the dissolution rate of plant fiber is shown in Table 2:
[0037] Table 2 Dissolution rate of plant fibers under different concentrations of ionic liquid aqueous solution
[0038] Ionic liquid concentration (%)
[0039] As can be seen from the results in Table 2, when the concentration of the ionic liquid aqueous ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 2.0g of eucalyptus powder was added to 100mL of clean and dry reaction vessel, and 50g of [Mmim]DMP ionic liquid aqueous solution was added with a concentration (mass fraction) of 90%, and magnetically stirred in a microwave instrument with a power of 500W, and the stirring speed was 280rpm , control the temperature at 170°C, 150°C, 130°C, 110°C and 90°C respectively, react for 20 minutes, cool down to room temperature, and centrifuge to obtain plant fiber solution and undissolved solid matter. The solid matter is washed and dried to obtain Dissolve the residue and calculate the dissolution rate.
[0042] Under different dissolution reaction temperatures, the dissolution rates of plant fibers are shown in Table 3:
[0043] The dissolution rate of plant fiber under different dissolution reaction temperatures in table 3
[0044] Reaction temperature (°C)
[0045] It can be seen from the results in Table 3 that when the dissolution reaction temperature is higher...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com