Identification method for adaptability of plant to low-phosphorus environment
An identification method and an adaptive technology, applied in the field of ecological governance, can solve the problems of restricting plant growth and development in karst areas, the limitation of inorganic phosphorus supply, etc., and achieve the effect of fewer steps, reliable data and simple calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0040] Example of the present invention: it comprises the following steps:
[0041] First, hydroponically culture the investigated plants to a suitable size, select seedlings of the same size, and starve them for 48 hours in a culture solution without adding inorganic phosphorus with a certain number of seedlings as a unit;
[0042] Second, the plant seedlings under investigation after starvation culture were placed in an additional 0.2 mmol / L CaSO 4 Dihydrogen phosphate ion absorption experiments were carried out in the absorption solution containing dihydrogen phosphate ions.
[0043] Third, according to the above-mentioned ion absorption experiments, the Michaelis constants of the dihydrogen phosphate ion absorption of the investigated plants were respectively obtained K m and the minimum concentration, that is, the external nutrient concentration when the net absorption rate of dihydrogen phosphate ion by plant roots is equal to zero C min .
[0044] Fourth, measure t...
Embodiment 1
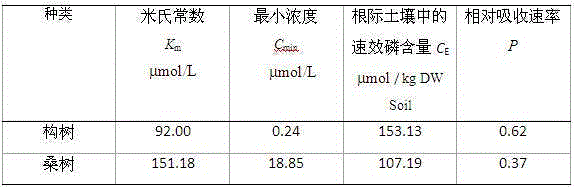
[0053] Example 1 Adaptability of mulberry and mulberry to the low phosphorus environment of lime soil in karst area
[0054] The following is an example of measuring the adaptability of mulberry and mulberry to the low-phosphorus environment of lime soil in the karst area to show its specific implementation steps and implementation effects.
[0055] The mulberry tree and mulberry tree were used as experimental materials. Take mature mulberry and mulberry seeds, sow part of them in the low-phosphorus environment to be tested (lime soil in karst area) and let them grow for 4 months, then take the rhizosphere soil of mulberry and mulberry trees to analyze the available phosphorus content in the soil. Part of the experiments were carried out on the absorption of dihydrogen phosphate ions.
[0056] The dihydrogen phosphate ion absorption experiment is:
[0057] Seeds were sown in the soil of the greenhouse to grow seedlings. After two true leaves grew, they were transplanted ...
Embodiment 2
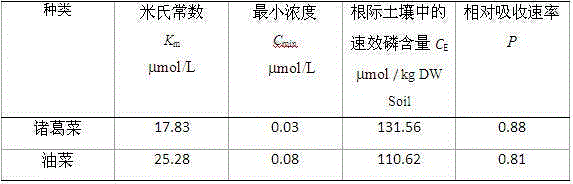
[0064] Example 2 The adaptability of Zhuge vegetable and rapeseed to the low phosphorus environment of lime soil in karst area to be tested
[0065] Using the method of the present invention to obtain the Michaelis constant absorbed by the dihydrogen phosphate ion of Zhuge Cai and Rapeseed K m , minimum concentration C min and available phosphorus content in the rhizosphere environment C E ,. Table 2 shows the relative absorption rate of inorganic phosphorus in the tested karst lime soil of Zhuge vegetable and rapeseed.
[0066] Table 2 The relative absorption rate of inorganic phosphorus absorption in karst lime soil of Zhuge vegetable and rapeseed
[0067]
[0068] It can be seen from Table 2 that both Zhugecai and rape have strong adaptability to the low phosphorus environment of the karst lime soil under investigation. The rapeseed used here is Brassica napus. Zhuge Cai is a plant suitable for karst growth, and its strong adaptability to low phosphorus may be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com