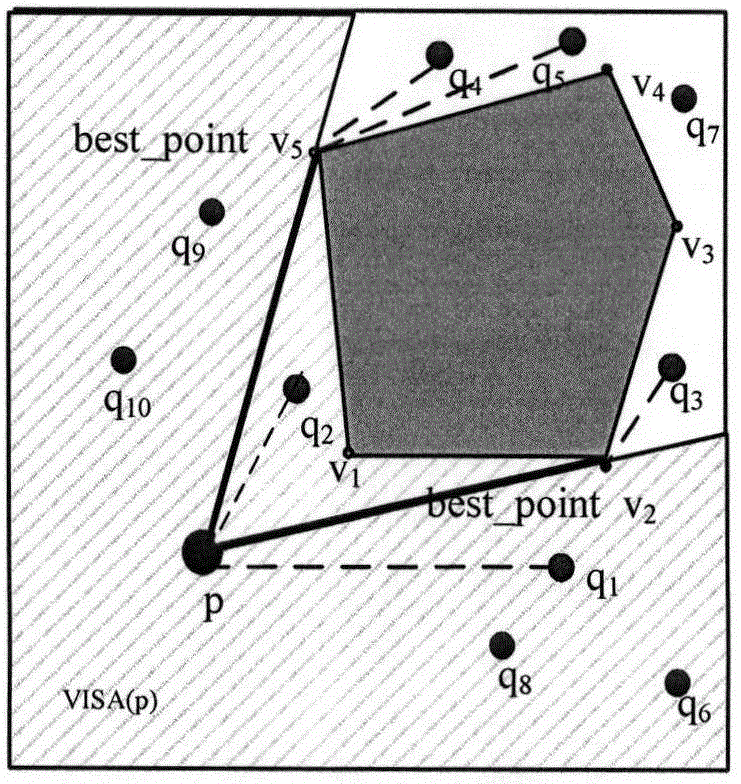
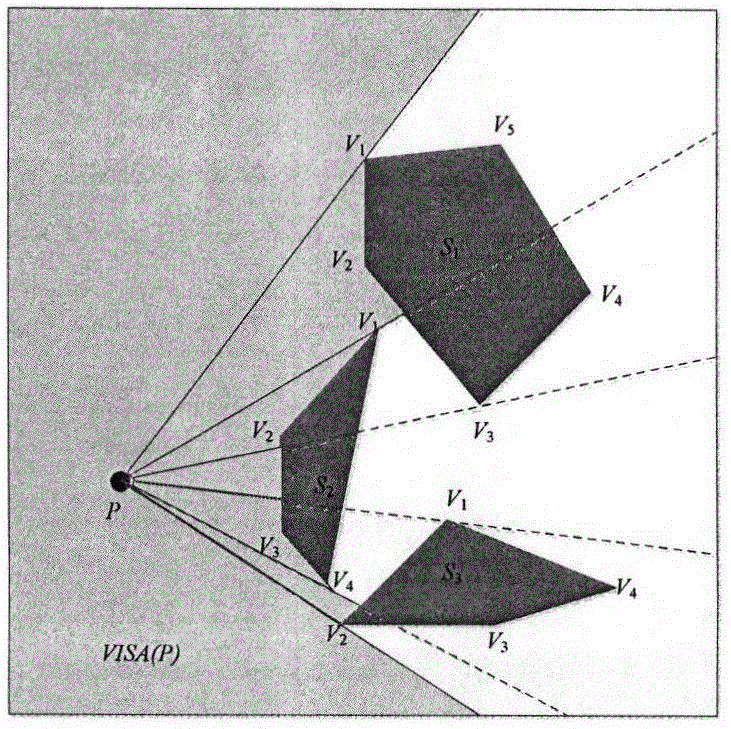
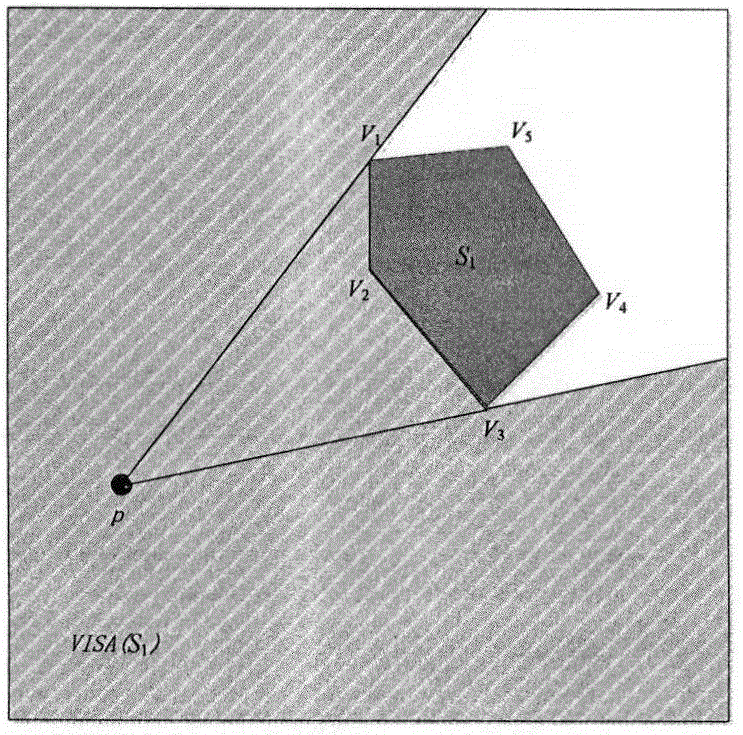
Minimum distance calculating method of moving object in restricted space
A technology with the shortest distance and moving objects, applied in computing, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as distance calculation of moving objects, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment two of the present invention is as Figure 8 As shown in , it shows that when the query point of the moving object is above or below the convex polygon, the specific steps to directly calculate the angle difference between the two are as follows:
[0053] A. Randomly take the two vertices of the convex polygon corresponding to the restricted space and mark them as a and b;
[0054] B. Construct a straight line between the moving object p and the vertex a, and find the angle formed between the straight line and the x-axis;
[0055] C. Construct a straight line between the moving object p and the vertex b, and find the angle formed between the straight line and the x-axis;
[0056] D. Find the difference between the two included angles and denote it as θ;
[0057] E. Save the angle difference between the mobile query point p and the vertex.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment three of the present invention is as Figure 9 As shown in , it shows that when the query point of the moving object is not above or below the convex polygon, the specific steps to adjust the angle difference between the two are as follows:
[0060] A. Randomly take the two vertices of the convex polygon corresponding to the restricted space and mark them as a and b;
[0061] B. Construct a straight line between the moving object p and the vertex a, and find the angle formed between the straight line and the x-axis;
[0062] C. Construct a straight line between the moving object p and the vertex b, and find the angle formed between the straight line and the x-axis;
[0063] D. Find the difference between the two included angles and denote it as θ;
[0064] E. Subtract θ from 180° to get the latest angle difference;
[0065] F. Save the angle difference between the moving query point p and the vertex.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com