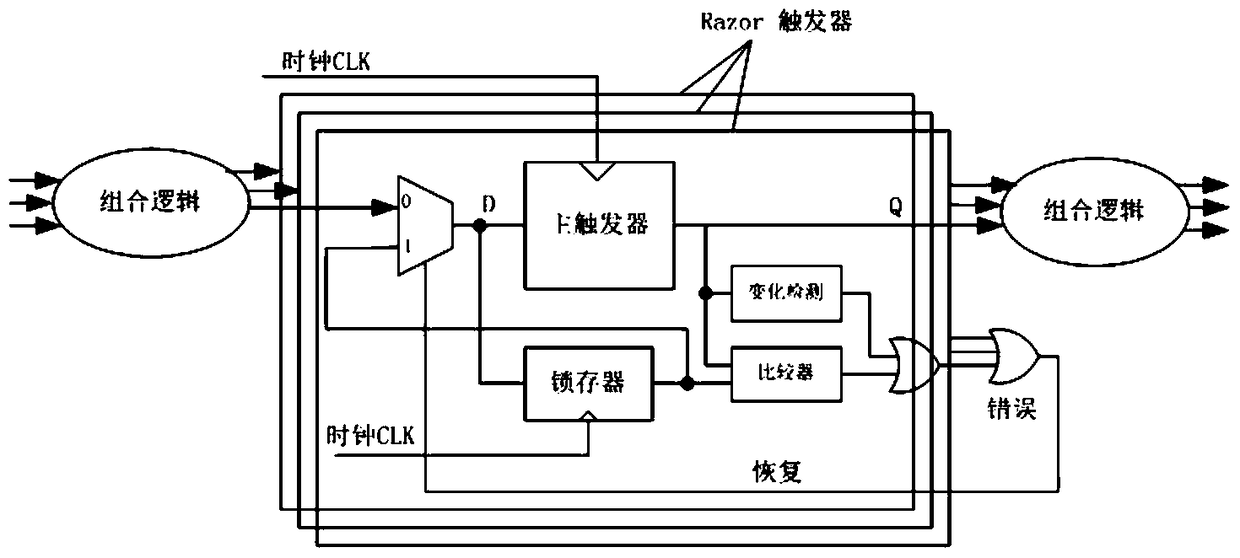
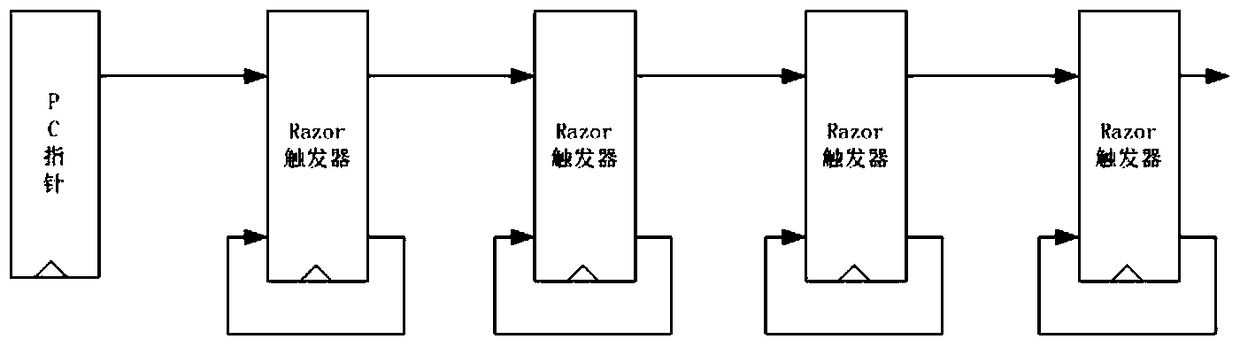
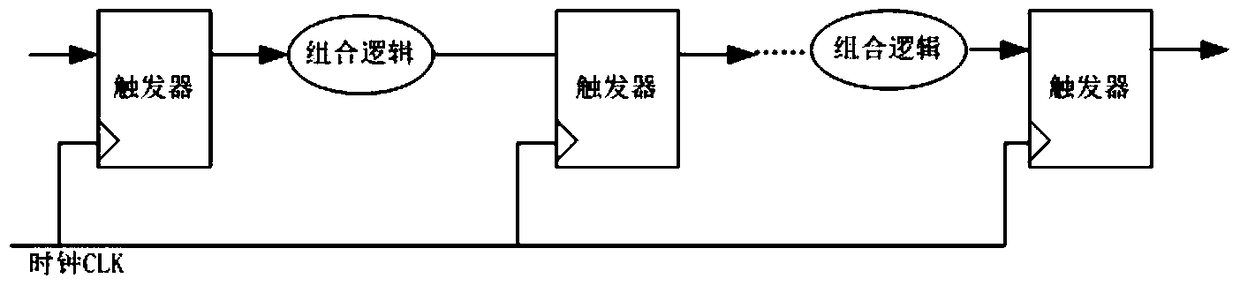
Locating System-on-Chip Sequential Logic Errors, Error Rate Calculation and Application Method
A sequential logic and system-on-chip technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, measuring electronics, etc., can solve the problem of adding logic, etc., and achieve the effect of saving cost, increasing chip area and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] DVFS technology is a method to optimize processor energy consumption, but changes in voltage and frequency will inevitably cause internal timing logic errors. User acceptable error rate means that under a specific condition (voltage V, frequency F, temperature T, etc.), the processor can avoid erroneous instructions and / or data when running the specific application program of the specific user; or It is said that under a specific condition (voltage V, frequency F, temperature T, etc.), the probability that some instructions and / or data will be wrong during all tests is not 100%. Once these instructions and / or data are wrong, the chip will The system where it resides can resume normal work under a specific recovery mechanism, and the recovery process caused by erroneous instructions and / or data does not affect the user's experience.
[0045] For example, a recovery mechanism using a watchdog circuit is as follows: enable and disable the watchdog before and after the prog...
Embodiment 2
[0061] According to the method for locating the sequential logic error of the system on chip proposed in the first embodiment, the present invention proposes a method for reducing the error rate of the sequential logic of the system on chip.
[0062] Instructions and / or data that have errors can be divided into two situations: one is 100% error occurrence rate, that is, all test results of the instruction and / or data under a certain test condition show that logic or timing has occurred Error; one is a non-100% error rate, that is, the instruction and / or data under a certain test condition, some test results show that no error occurs, and some do not occur error. Through the above grouping, users can choose those grouping chip products that are suitable for the working conditions of the customer's application environment and the appropriate power consumption budget. If user A wants the chip to meet the power consumption budget PBx (1≤x≤N), then it can work under the condition o...
Embodiment 3
[0067] According to the method for locating the SOC sequential logic error and the method for reducing the SOC sequential logic error rate proposed in the above embodiments, this embodiment further describes the specific application of the method for locating the SOC sequential logic error.
[0068] Assuming that the system chip on a chip is under the test conditions V1, T1, and F1, after adopting the test method of the multiplexed scan chain technology of the present invention, all instructions and / or data pass without error, as shown in the attached Figure 7 As shown, its power budget is PB1. Then the chip can be provided to some customer applications whose power consumption budget is above PB1. If the system-on-chip is under test conditions V2, T1, and F1 (V2<V1), the power consumption is reduced to PB2 (PB2<PB1), but through the verification of the test method of the multiplexing scan chain technology of the present invention, only instructions and / Or a logic error will...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com