Voltage conversion circuit
A circuit and charge pump technology, applied in the field of circuits, can solve problems such as reducing charge pump and power consumption waste, and achieve the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
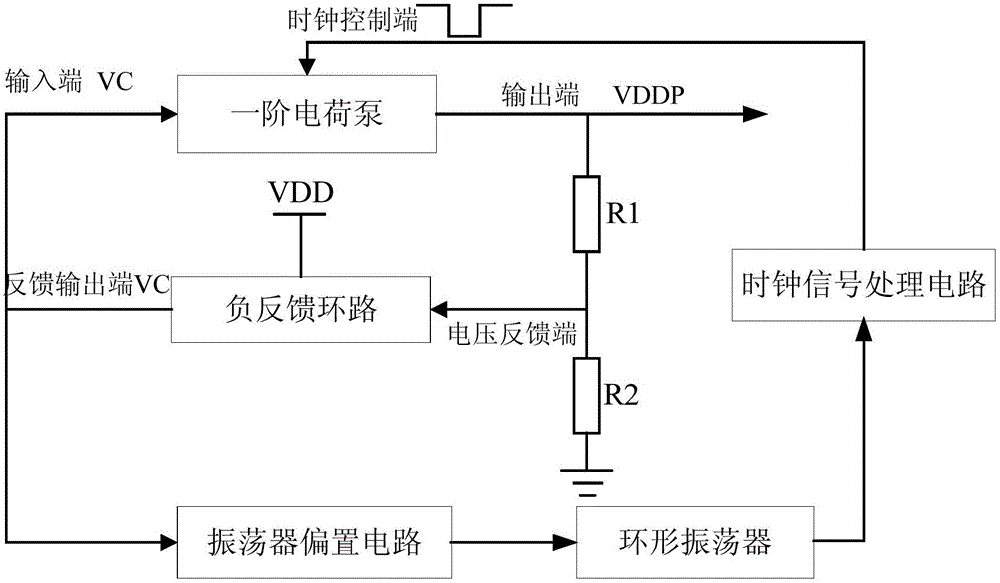
[0018] figure 1 The block diagram of a voltage conversion circuit provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention is applicable to the case where the load requires a supply voltage with a narrow variation range. A block diagram of a voltage conversion circuit provided in this embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including: a first-order charge pump, a negative feedback loop, an oscillator bias circuit, and a ring oscillator.
[0019] The first-order charge pump includes an input terminal, an output terminal, a forward clock control terminal (CLKB) and a reverse clock control terminal (CLK). Under the control of the clock signal, an output voltage is formed and output from the output terminal to provide voltage for the load.
[0020] The negative feedback loop includes a power supply terminal, a voltage feedback terminal and a feedback output terminal, the voltage feedback terminal is connected to the output terminal of the first-order charge pump, and is used to adjust the ...
Embodiment 2
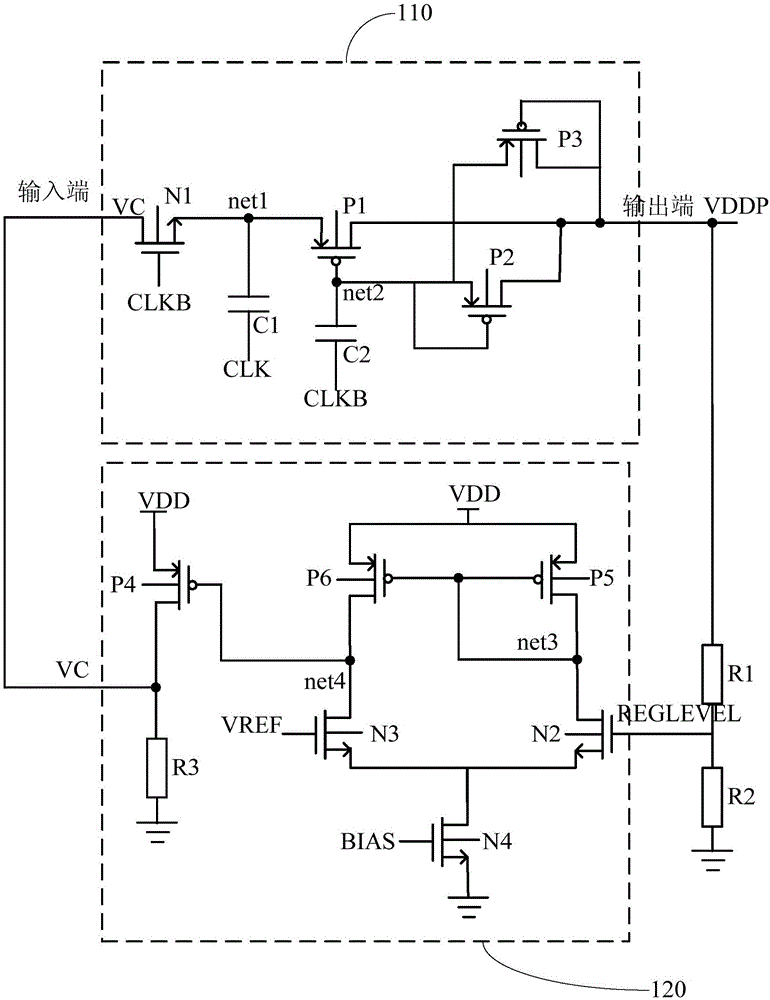
[0026] On the basis of the above embodiments, in order to more clearly describe the working principle of the first-order charge pump and the negative feedback loop, as a preferred embodiment, figure 2 The specific circuit diagram of the first-order charge pump and negative feedback loop is given, as figure 2 As shown: the first-stage charge pump 110 includes: a first N-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (NMOS) N1, a first P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (PMOS) P1, a second PMOS transistor P2, third PMOS transistor P3, first capacitor C1 and second capacitor C2;
[0027] Wherein, the drain of the first NMOS transistor is the input terminal of the first-order charge pump, the gate is the positive clock control terminal, the source is connected to the reverse clock control terminal through the first capacitor, and is connected to the first PMOS The source of the tube is connected; the gate of the first PMOS tube is connected t...
Embodiment 3
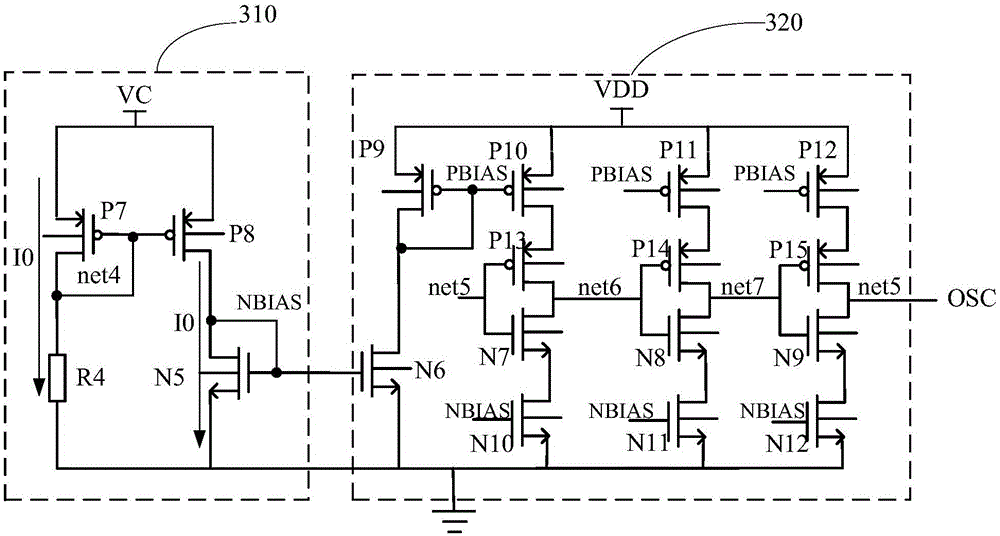
[0034] In order to realize that when the load current is small, the ability of the first-order charge pump can be reduced by the feedback voltage VC while the operating frequency of the first-order charge pump can be reduced, thereby reducing the power consumption of the first-order charge pump. This embodiment is used as a preferred embodiment. On the basis of the second embodiment, an oscillator bias circuit 310 and a ring oscillator 320 are added such as image 3 shown. The oscillator bias circuit 310 includes a seventh PMOS transistor P7, an eighth PMOS transistor P8, a fifth NMOS transistor N5 and a fourth resistor R4;
[0035] Wherein, the source of the seventh PMOS transistor is connected to the feedback voltage terminal of the negative feedback loop, the drain is grounded through the fourth resistor, and the gate is connected to the gate of the eighth PMOS transistor; The PMOS transistor is mirror-connected to the seventh PMOS transistor, and the drain is connected to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com