Time source selecting and switching method capable of improving time service output reliability
A reliable, time-sourced technology, applied in time-division multiplexing systems, electrical components, multiplexing communications, etc. The effect of reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the time source selection and switching method for improving the timing output reliability of the present invention includes a clock synchronization device, the clock synchronization device is provided with a plurality of input time sources, the clock synchronization device is provided with a time source processing unit, and the time source processing unit Select the best time source according to the synchronization situation, phase difference and priority of each time source, switch the best time source to the timing source when the status of each time source changes, and use smooth tracking when switching time sources switch.
Embodiment 2
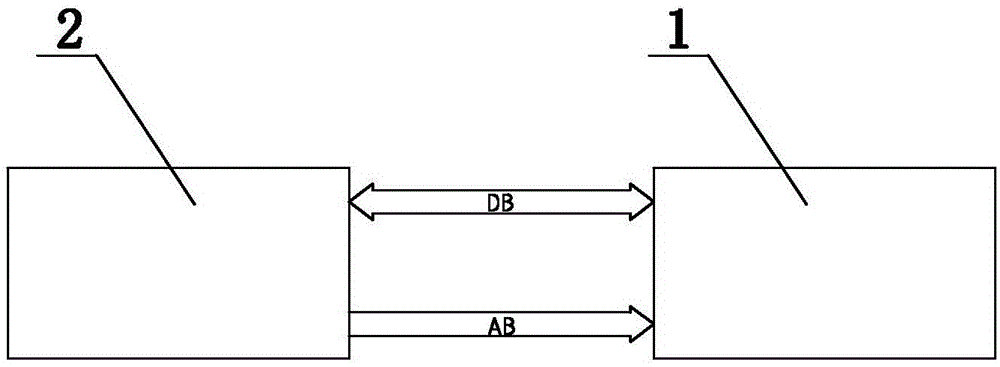
[0026] Embodiment 2: On the basis of the structure described in embodiment 1, the time source processing unit comprises FPGA1 and 32 processors 2, FPGA1 and 32 processors 2 communicate by data bus and address bus, and 32 processors 2 select at first Synchronized time sources, and then select two time sources whose phase difference is within the standard difference time among the synchronized time sources, and finally sort the selected time sources according to the priority set by the customer, select the first time source, time source Including external time source and local time source, the standard difference time is recorded as P_th, which is 3μs-7μs, and the specific selection logic is: the subscript "0" represents the local time source, the subscript "1-5" represents the external time source, the following The marks "x" and "y" represent arbitrary and different external time sources, for example "|ΔTS 01 |" is the phase difference between the local time source and the fir...
Embodiment 3
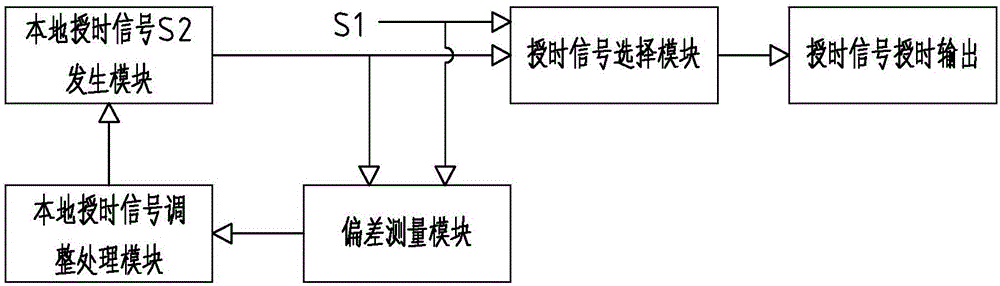
[0031] Embodiment 3: on the basis of the structure described in embodiment 2, as figure 2 As shown, the smooth tracking switch includes deviation time, deviation standard time and tracking time. FPGA1 continuously measures the deviation time between the time source to be changed and the original time source, and triggers the 32-bit processor 2 to perform circular tracking when the time source is switched. 32 Bit processor 2 increases the tracking time once in each cycle until the deviation time is less than the deviation standard time, the cycle tracking stops, FPGA1 directly outputs the time of the time source to be changed, the deviation standard time is 0.1μs-1μs, and the tracking time is 0.1μs -0.5μs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com