Entomopathogenic nematode HbSD and insecticide thereof, preparation method and application
A technology for entomopathogenic nematodes and insects, applied in the direction of insecticides, botanical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problem of high cost, achieve the effects of low cost, simplified preparation and use methods, and improved insecticidal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: the preparation method of entomopathogenic nematode HbSD suspension preparation
[0024] The first entomopathogenic nematode HbSD insecticide is a suspension preparation, and its preparation method comprises:
[0025] The preparation method of the entomopathogenic nematode HbSD suspension preparation: put a layer of filter paper at the bottom of the plastic box, select 100 of the last instar Tenebrio molitor larvae that grow healthy and place them on the filter paper, and use a pipette gun to absorb HbSD nematodes with a concentration of 1000 heads / ml Drop the suspension on the last instar Tenebrio molitor, cover it, and check the color change of the insect body after 4-5 days at room temperature: on the sixth day, the color of Tenebrio molitor normally infected with entomopathogenic nematodes turns reddish-brown, and discard the color. Normal Tenebrio molitors were continued to be cultured, and Tenebrio molitors infected with the entomopathogenic nematode...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Preparation of Entomopathogenic Nematode HbSD Entomicide
[0030] The second entomopathogenic nematode HbSD insecticide is an insecticide, and its preparation method comprises:
[0031] The preparation method of entomopathogenic nematode HbSD carcasses: on the first day, the harvested larvae of entomopathogenic nematode HbSD infection stage are used to infect the last instar Tenebrio molitor larvae. On the 6th day, select the Tenebrio molitor whose color has changed to reddish brown, and continue to cultivate. On the 9th day, the dead insects are harvested, placed in a 50-100mL centrifuge tube, and stored at 10-14°C for later use.
[0032] The survival rate of the entomopathogenic nematode HbSD is greater than 95%. The carcasses are the last instar Tenebrio molitor larvae infected by HbSD, and each carcass contains at least 5000 entomopathogenic nematode HbSD.
[0033] Two kinds of HbSD nematode insecticides of the present invention: nematode suspension prep...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: The insecticidal property experiment of entomopathogenic nematode HbSD
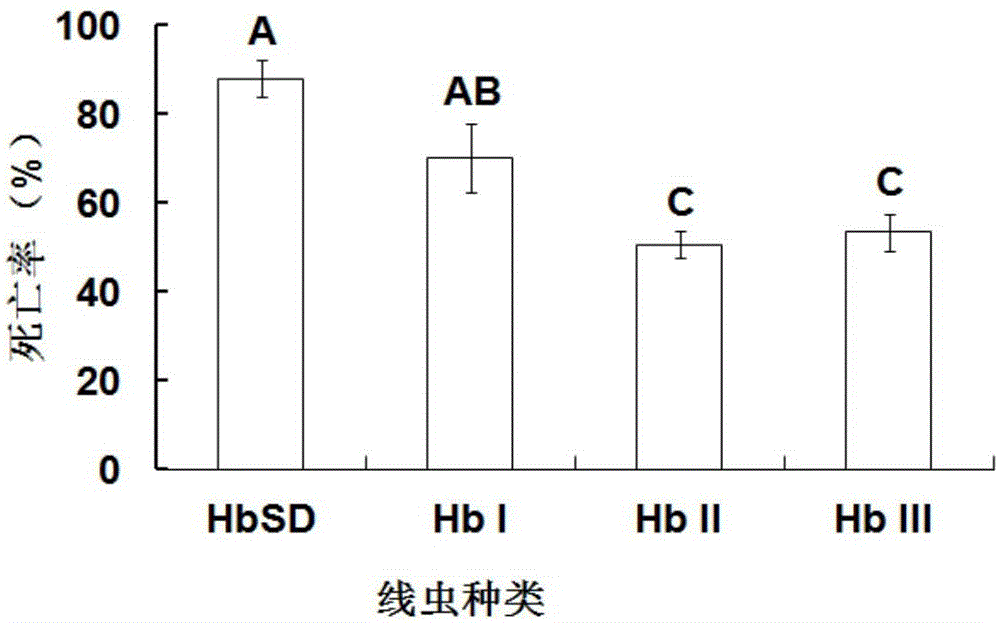
[0035] The tested nematode strains: 4 species of bacteriophage Heterobacterium nematodes HbSD, HbI, HbII and HbIII.
[0036] Insects tested: Larvae of the last instar wax moth
[0037] Test method: Indoor bioassay method, that is, to test the toxicity of the suspension of 4 kinds of Heterobacteria genus nematodes to the last instar wax moth larvae, and count the mortality after 6 days. The control group received no nematodes.
[0038] Result and analysis: the insecticidal activity of four species of Heterobacteria nematodes against last-instar wax moth larvae is as follows: figure 1 As shown, among the four tested nematode strains (HbSD, HbI, HbII, HbIII), the entomopathogenic nematode HbSD of the present invention has the highest insecticidal efficacy and strong reproductive ability. HbSD was chosen for further virulence assays.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com