Process to thicken a liquid detergent composition
A technology of liquid detergent and composition, applied in the preparation of detergent composition, soap detergent composition, detergent mixture composition, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
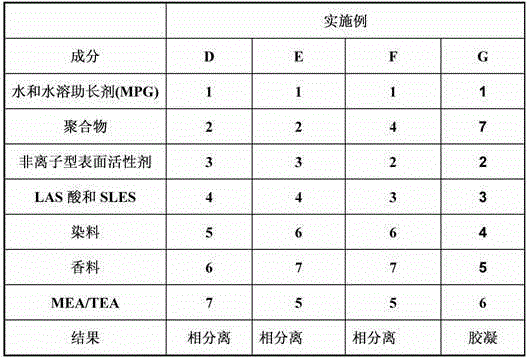
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] We make a separate premix consisting of a blend of nonionic surfactant, MPG, thickening polymer and water. Surprisingly, by using this method we produced stable compositions without the need for high energy mixing and without a significant increase in processing time. The method of using such a premix to provide a stable 1 wt % polymer thickened liquid composition is given in Table 2 below.
[0131] Table 2
[0132] join order Element as 100%(%) 1 softened water 27.81 2 MEAs 6.20 3 TEA 4.00 4a NI 7EO 8.40 4b MPG 8.00 4c thickening polymer 1.00 4d softened water 10.00 5 citric acid 2.50 6 fluorescent agent 0.25 7 LAS acid 11.20 8 Dequest 2010 1.50 9 Prifac 5908 3.50 10 Sulfite 0.25 11 SLES 3EO 8.40 12 EPEI 3.00 13 Enzymes and Fragrances to 100
[0133] The ingredients added in order 4a, 4b, 4c and 4d were formulated in this order as a prem...
Embodiment 2
[0149] The premixing method used in Example 1 required a separate mixing vessel for polymer premixing. Example 2 is a modification of Example 1, using a "one pot" process to make the same composition. The amine addition was split into two separate additions, TEA was added to the polymer mixture before the LAS acid and MEA was added after it. However, if the amount of polymer to be added is not too high, it has been found that all of the base can be added to the polymer prior to the introduction of the LAS acid and the order of addition of TEA and MEA is not critical. We have found that adding base to the polymer avoids viscosity peaks that are too high, since mixing can be controlled to ensure that localized high pHs are avoided, and thus localized formation of high viscosity "gels".
Embodiment 3
[0151] The order of addition (OOA) for the one-pot process using Viscolam® CK57 polymer and separate addition of amine base is shown in Table 3. The polymer is readily dispersed in a mixture of water, MPG and nonionic surfactant. The addition of MEA thickened the mixture to the highest viscosity seen during the process. The viscosity drops again when LAS acid is added and rises after adding TEA, but not to as high a level as before. This method choice is particularly useful for more viscous compositions.
[0152] table 3
[0153] OOA Element as 100%(%) 1 softened water 37.71 2 fluorescent agent 0.25 3 MPG 8.00 4 NI 7EO 8.40 5 Viscolam CK57 1.00 6 MEAs 6.20 7 LAS acid 11.20 8 TEA 4.00 9 citric acid 2.50 10 Prifac 5908 3.50 11 Dequest 2010 1.50 12 Sulfite 0.25 13 SLES 3EO 8.40 14 EPEI 3.00 15 Enzymes, oil-free fragrances, colorants and sunscreens to 100 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com