A method for rapidly promoting deformation-induced martensitic transformation
A technology of martensitic transformation and deformation induction, applied in the field of metal material processing, can solve the problems of slow fine-grain strengthening efficiency, low strength and hardness, reduced product quality and service life, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
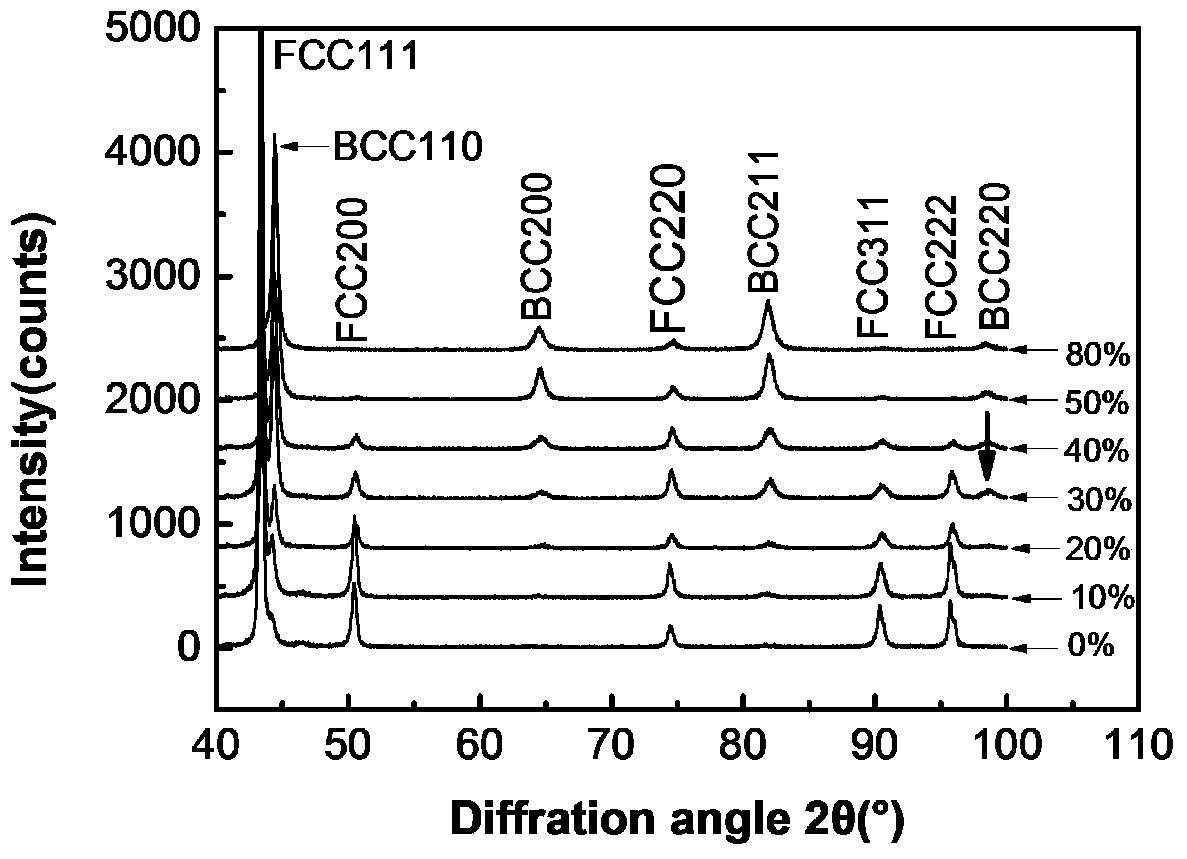
[0026] The commercial 304 stainless steel hot-rolled plate is milled into a size of 10*30*100 (mm), and the upper and lower surfaces are smooth. The plate was kept in vacuum at 1100°C for 1 hour, and quickly quenched in water after being out of the furnace. The quenched 304 stainless steel plate is subjected to cold rolling deformation at room temperature, and the deformation amount of each pass is 10%, and the interval between each pass is 15-20 minutes or continuous cold rolling, respectively to obtain 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, Rolled plate with 80% deformation. Use XRD diffraction pattern for phase analysis, use TEM for microstructure morphology analysis, the example pictures are respectively figure 1 with Figure 4 . figure 1 It is the X-ray diffraction pattern of 304 stainless steel rolled at room temperature. It can be seen from the figure that the intensity of the martensite diffraction peak increases with the increase of deformation during the rolling process, and th...
Embodiment 2
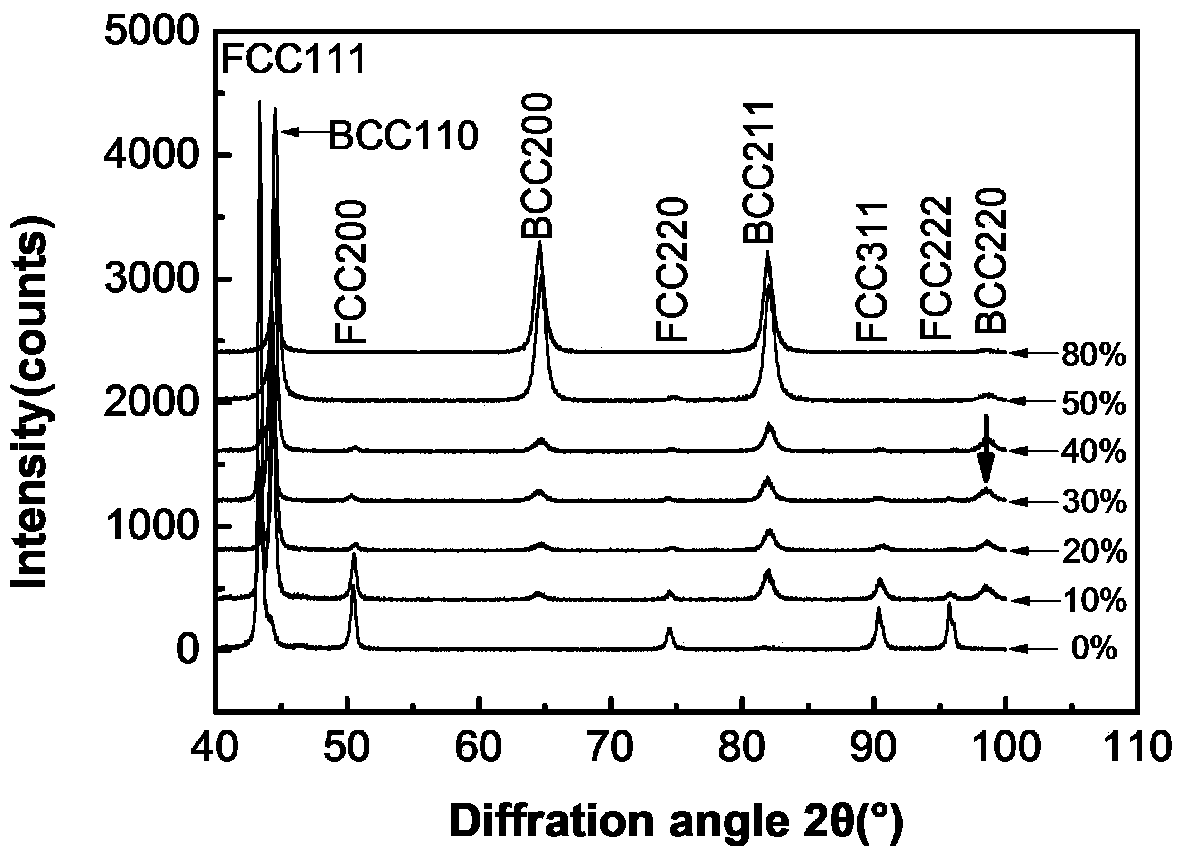
[0028] The commercial 304 stainless steel hot-rolled plate is used as the rolling raw material, and the initial material is surface milled to make a 10*30*100 (mm) plate to ensure smooth upper and lower surfaces. The plates were vacuum treated at 1100°C for 1 hour and then water quenched. The heat-treated stainless steel plate is immersed in liquid nitrogen to cool for more than 2 hours, and then rolled with 10% pass deformation. The stainless steel plates were immersed in liquid nitrogen for cooling for 15-20 minutes between each pass, and the total deformations were respectively obtained by 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, and 80%. Use XRD diffraction pattern for phase analysis, use TEM for microstructure analysis, the example pictures are respectively figure 2 , Figure 5 (a) and Figure 5 (b). The XRD diffraction spectrum of comparative example 1, just can make four diffraction peaks of martensite all appear ( figure 2 ), while embodiment 1 needs to reach 30% rolling deform...
Embodiment 3
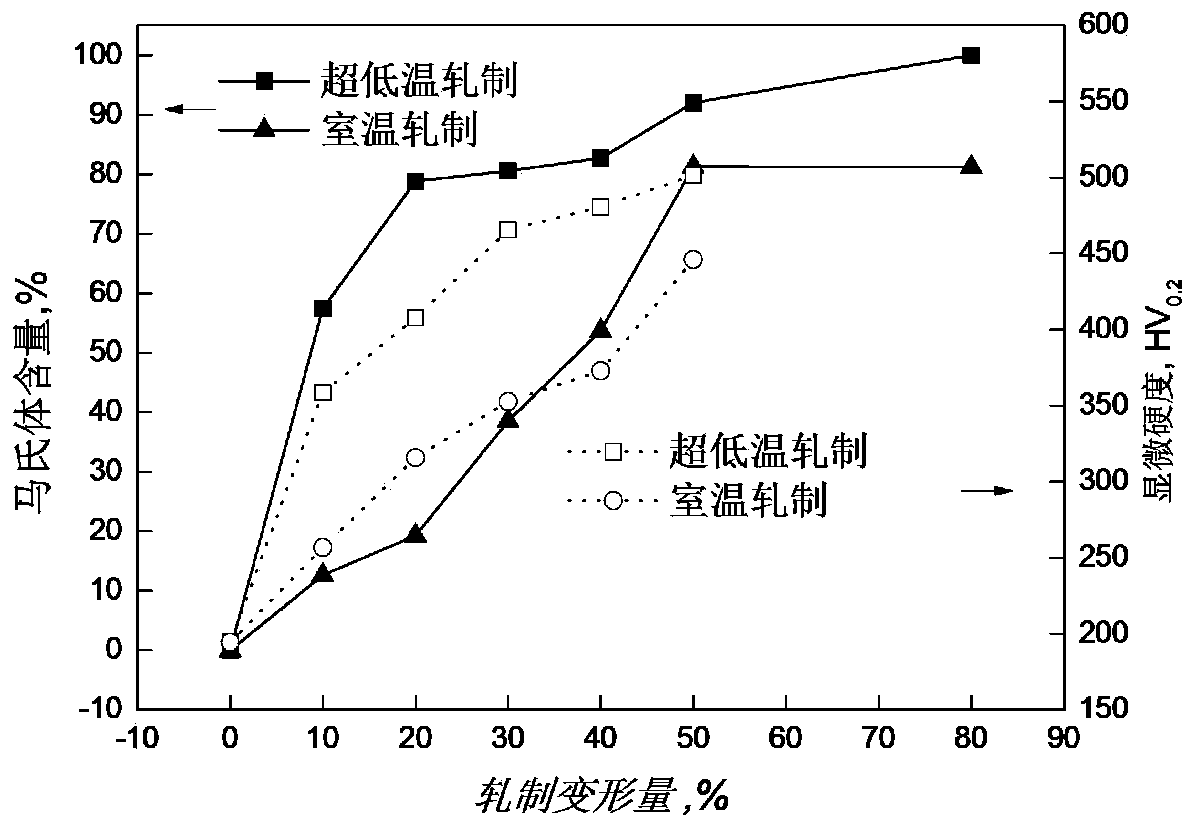
[0031]The commercial 304 stainless steel hot-rolled plate is used as the rolling raw material, and the initial material is milled into 10*30*100 (mm) specifications to ensure smooth upper and lower surfaces. The plates were vacuum treated at 1100°C for 1 hour and then water quenched, and the quenched plates were divided into two groups, A and B. The stainless steel plates of Group A were immersed in liquid nitrogen to cool for more than 2 hours, and then rolled with 10% pass deformation, while the plates of Group B were directly rolled and deformed at room temperature. The deformation amount is 20% and 40% rolling deformation. Among them, the plates of group A need to be immersed in liquid nitrogen for cooling for 15-20 minutes between rolling passes, and the plates of group B are directly cooled in the air. Subsequently, the martensitic phases of the surface layer, 1 / 4 thickness layer and 1 / 2 thickness layer of the A and B group plates were analyzed.
[0032] Table 1 shows ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com