Colorful low-melting-point metal wire for 3D printing and preparation method thereof
A low-melting-point metal and 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve problems such as single color, achieve the effects of reducing the yield of finished products, inhibiting dynamic recovery or recrystallization, and reducing the ability of atomic diffusion and migration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
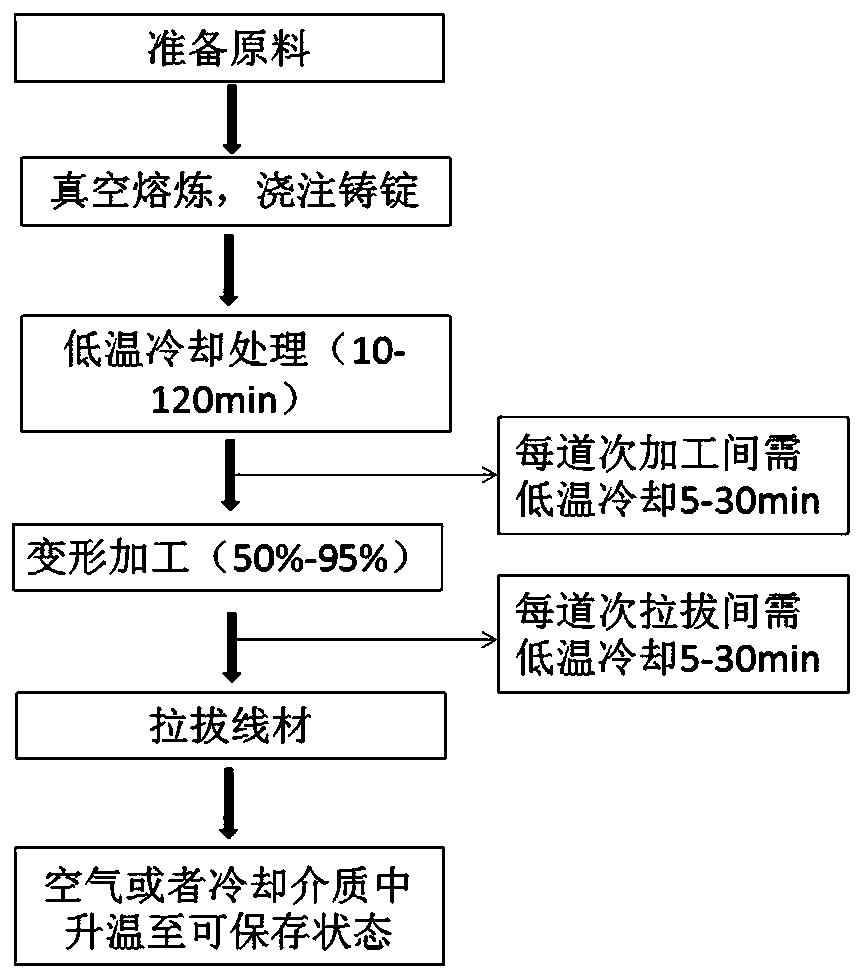
[0033] This embodiment relates to a preparation method of a liquid metal wire, including the following steps, the specific process see figure 1 :
[0034] 1) Pure bismuth, indium, tin and zinc metals are formulated in a mass ratio of 35:48.6:15.9:0.4 to make 1kg of raw materials with an alloy melting point of about 58°C. In addition, 100g of cinnabar with a diameter of 400nm and 25g of titanium with a diameter of 600nm Put them together in a vacuum melting furnace and heat them to 200°C for melting, and stir the solution from time to time to make them fully mixed. Keep argon flowing during the entire stirring process to avoid oxidation of the melt; after melting, cast the alloy into a round rod with a diameter of 20mm, and place the round rod in liquid nitrogen to cool until the temperature is -10°C;
[0035] 2) After the cooling treatment, the round bar is passed through a rolling mill to roll the alloy into a bar with a diameter of 6mm, and the rolling deformation of each p...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This embodiment relates to a method for preparing a liquid metal wire, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Prepare pure bismuth, indium and tin metals with a mass ratio of 53.6:30.3:16.1 to make 1 kg of raw materials with an alloy melting point of about 83°C. In addition, 100g of cinnabar with a diameter of 400nm and 25g of titanium with a diameter of 600nm are placed in vacuum melting Melt in a furnace heated to 300°C and stir the solution from time to time to mix thoroughly. Keep argon flowing throughout the stirring process to avoid oxidation of the melt. After the smelting is completed, the alloy is cast into a round rod with a diameter of 20mm, and the round rod is cooled in liquid nitrogen until the temperature is -20°C;
[0040] 2) The processed round bar is passed through a rolling mill to roll the alloy into a bar with a diameter of 4 mm, and the rolling deformation in each pass is 10%, and the bar should be put back into liquid nitrogen for low-temper...
Embodiment 3
[0043] This embodiment relates to a method for preparing a liquid metal wire, comprising the following steps:
[0044]1) Prepare 1 kg of raw material with pure bismuth and indium metal at a mass ratio of 34:66 to prepare an alloy with a melting point of about 74 ° C. In addition, 100 g of cinnabar with a diameter of 400 nm and 25 g of titanium with a diameter of 600 nm are placed in a vacuum melting furnace and heated to Melting was carried out at 230°C, and the solution was stirred from time to time to mix thoroughly. Keep argon flowing throughout the stirring process to avoid oxidation of the melt. After the smelting is completed, the alloy is cast into a round rod with a diameter of 20mm, and the round rod is cooled in liquid nitrogen until the temperature is -30°C;
[0045] 2) The processed round bar is passed through a rolling mill to roll the alloy into a bar with a diameter of 8 mm, and the rolling deformation in each pass is 5%, and the bar should be put back into liq...
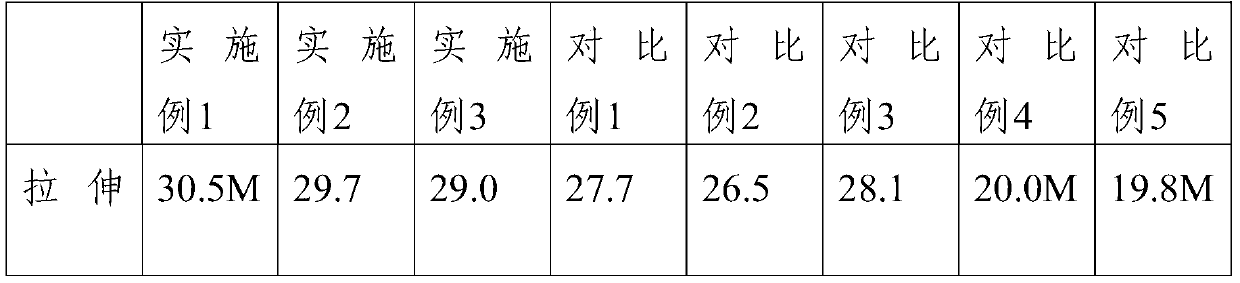
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com